Universe and Stars Project Final Due Date
... 1. Describe how the Universe was formed and provide at least 3 pieces of evidence of the Big Bang. ( LT A) Make sure you include what red shift and steady state means. 2. Describe scientific explanations and conditions that explain and contributed to the origin of life on Earth (give at least 3 exam ...
... 1. Describe how the Universe was formed and provide at least 3 pieces of evidence of the Big Bang. ( LT A) Make sure you include what red shift and steady state means. 2. Describe scientific explanations and conditions that explain and contributed to the origin of life on Earth (give at least 3 exam ...
Search for Life - Scholars Archive
... Does life elsewhere follow similar evolutionary trends and evolutionary rates? Is intelligence inevitable during evolution? What was the Earth like when life formed? ...
... Does life elsewhere follow similar evolutionary trends and evolutionary rates? Is intelligence inevitable during evolution? What was the Earth like when life formed? ...
The professional project VEGA/CHARA and participation of ASPA
... Scargle-diagram has been performed with an additional weighting method. Nevertheless the results are nearly the same within of a 2sigma uncertainty. The smaller peak at 230 days is a so-called alias frequency, a well-known phenomenon, resulting from the discrete sampling and the fact, that the data ...
... Scargle-diagram has been performed with an additional weighting method. Nevertheless the results are nearly the same within of a 2sigma uncertainty. The smaller peak at 230 days is a so-called alias frequency, a well-known phenomenon, resulting from the discrete sampling and the fact, that the data ...
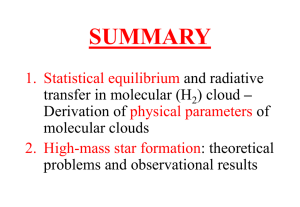
The physics of high-mass star formation
... large distance: >400 pc, typically a few kpc formation in clusters confusion ...
... large distance: >400 pc, typically a few kpc formation in clusters confusion ...
The Interstellar Medium in High Redshift Galaxies Comes of Age
... Studying the astrochemistry of the early Universe is crucial for understanding the properties of molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, ...
... Studying the astrochemistry of the early Universe is crucial for understanding the properties of molecular gas in galaxy formation and for providing fundamental constraints on galaxy evolution. To date, a fairly small number of species, other than CO, have been detected at z > 2 (e.g. HCN, HNC, CN, ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... Astronomy Assignment #2: The Celestial Sphere and The Apparent Motion of the Stars and Sun Your Name______________________________________ ...
... Astronomy Assignment #2: The Celestial Sphere and The Apparent Motion of the Stars and Sun Your Name______________________________________ ...
Scavenger Hunt: Who am I
... _____________________ 1. I invented the first telescope and discovered the 4 moons of Jupiter. _____________________ 2. We discovered the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness. _____________________ _____________________ 3. I discovered Pluto. _____________________ 4. My theor ...
... _____________________ 1. I invented the first telescope and discovered the 4 moons of Jupiter. _____________________ 2. We discovered the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness. _____________________ _____________________ 3. I discovered Pluto. _____________________ 4. My theor ...
Physics Midterm
... A clean copy of this booklet should be issued to candidates for their use during each GCE Physics examination in the new specification. It is not to be used in legacy specification examinations. Centres are asked to issue this booklet to candidates at the start of the GCE Physics course to enable th ...
... A clean copy of this booklet should be issued to candidates for their use during each GCE Physics examination in the new specification. It is not to be used in legacy specification examinations. Centres are asked to issue this booklet to candidates at the start of the GCE Physics course to enable th ...
Optics - Tensors for Tots
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
... Dispersion and Refraction Prisms display the phenomena called dispersion by separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted t ...
Simultaneous Measurements of Hard X Rays and Second
... light. On the other hand, since the energy lost by the wave is efficiently converted into electron kinetic energy, bremsstrahlung x-ray emission, originating from these hot electrons, is expected to reach its maximum in this condition. This result is also in agreement with the plot of Fig. 2 which s ...
... light. On the other hand, since the energy lost by the wave is efficiently converted into electron kinetic energy, bremsstrahlung x-ray emission, originating from these hot electrons, is expected to reach its maximum in this condition. This result is also in agreement with the plot of Fig. 2 which s ...
Math Notes - UNC Physics and Astronomy
... vesc = (2GM / R)1/2 Solving for R yields: R = 2GM / vesc2 Setting vesc = c yields the Schwazschild radius of the object: Rs = 2GM / c2 If an object of mass M is compressed to the point that its radius R is less than its Schwarzschild radius Rs, then it would require a speed greater than ...
... vesc = (2GM / R)1/2 Solving for R yields: R = 2GM / vesc2 Setting vesc = c yields the Schwazschild radius of the object: Rs = 2GM / c2 If an object of mass M is compressed to the point that its radius R is less than its Schwarzschild radius Rs, then it would require a speed greater than ...
How far away are the Stars?
... • If distance to an object is known, we can measure its size. Diameter 2 Dis tan ce ...
... • If distance to an object is known, we can measure its size. Diameter 2 Dis tan ce ...
CHAPTER 15: General Relativity
... Taylor and Hulse discovered a binary system of two neutron stars that lose energy due to gravitational waves that agrees with the predictions of general relativity. LIGO is a large Michelson interferometer device that uses four test masses on two arms of the interferometer. The device will detect ch ...
... Taylor and Hulse discovered a binary system of two neutron stars that lose energy due to gravitational waves that agrees with the predictions of general relativity. LIGO is a large Michelson interferometer device that uses four test masses on two arms of the interferometer. The device will detect ch ...
Slide 1
... The motion of the planets is related to basic principles. The planets are not independent of each other as the Greeks thought. Reality is now subject to experience ...
... The motion of the planets is related to basic principles. The planets are not independent of each other as the Greeks thought. Reality is now subject to experience ...
ISP205L Visions of the Universe Laboratory
... Properties of light. Spectroscopy of arc lamps (hands-on lab exercise in PL lobby). ...
... Properties of light. Spectroscopy of arc lamps (hands-on lab exercise in PL lobby). ...
Astronomy Exam #2 for the 10
... around Jupiter for the purpose of measuring stellar parallaxes. In a couple of sentences, explain why a mission like this would be superior to the original Hipparchus spacecraft in orbit around the Earth during the early Proposed orbit of new 1990’s. spacecraft orbiting Jupiter ...
... around Jupiter for the purpose of measuring stellar parallaxes. In a couple of sentences, explain why a mission like this would be superior to the original Hipparchus spacecraft in orbit around the Earth during the early Proposed orbit of new 1990’s. spacecraft orbiting Jupiter ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.