Mass and the Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... neutrons, and releasing neutrinos and energy at the same time Supernova explosion. Eventually the neutron degeneracy pressure will balance the gravitational pressure (if the star is not too massive) to form a neutron star. The estimated of the neutron stars are about 10 km in diameter, with a mass ...
... neutrons, and releasing neutrinos and energy at the same time Supernova explosion. Eventually the neutron degeneracy pressure will balance the gravitational pressure (if the star is not too massive) to form a neutron star. The estimated of the neutron stars are about 10 km in diameter, with a mass ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Neutron stars, pulsars and black
... • The discovery of pulsars that were spinning more than 100 times per second (the first was spinning 640 times per second) threw the field for a loop. When some millisecond pulsars were discovered in old star clusters it was even more confusing. • Eventually it was determined that all millisecond pu ...
... • The discovery of pulsars that were spinning more than 100 times per second (the first was spinning 640 times per second) threw the field for a loop. When some millisecond pulsars were discovered in old star clusters it was even more confusing. • Eventually it was determined that all millisecond pu ...
Atomic Structure and Atomic Spectra
... K. Krane, Modern Physics, Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1996). ...
... K. Krane, Modern Physics, Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York (1996). ...
... NGC 253 is the jewel of Sculptor. It is a magnitude 7, nearly edgeon spiral galaxy. It is nearly half a degree long and while it can be picked up in binocular, an aperture of at least 100mm is required to just make out the smudge of the spiral arms. A medium aperture telescope will start to resolve ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... • Display devices, such as CRT or LCD computer screens. • Light sensors, including infrared security systems. • Digital data transmission over fiber-optic cables. ...
... • Display devices, such as CRT or LCD computer screens. • Light sensors, including infrared security systems. • Digital data transmission over fiber-optic cables. ...
The Life Cycles of Stars, Part I
... our Sun. After the outer layers of the star have swollen into a red supergiant (i.e., a very big red giant), the core begins to yield to gravity and starts to shrink. As it shrinks, it grows hotter and denser, and a new series of nuclear reactions begin to occur, temporarily halting the collapse of ...
... our Sun. After the outer layers of the star have swollen into a red supergiant (i.e., a very big red giant), the core begins to yield to gravity and starts to shrink. As it shrinks, it grows hotter and denser, and a new series of nuclear reactions begin to occur, temporarily halting the collapse of ...
Question paper
... A All giant stars are larger and cooler than our Sun. B All giant stars are larger and hotter than our Sun. C All white dwarf stars are smaller and hotter than our Sun. D All white dwarf stars are hotter and brighter than our Sun. (Total for Question 5 = 1 mark) 6 In which of the following situation ...
... A All giant stars are larger and cooler than our Sun. B All giant stars are larger and hotter than our Sun. C All white dwarf stars are smaller and hotter than our Sun. D All white dwarf stars are hotter and brighter than our Sun. (Total for Question 5 = 1 mark) 6 In which of the following situation ...
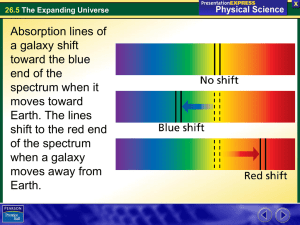
26.5 The Expanding Universe
... This relationship, called Hubble’s Law, says that the speed at which a galaxy is moving away is proportional to its distance from us. The most distant observed galaxies are moving away at more than 90 percent of the speed of light! ...
... This relationship, called Hubble’s Law, says that the speed at which a galaxy is moving away is proportional to its distance from us. The most distant observed galaxies are moving away at more than 90 percent of the speed of light! ...
May - Fort Worth Astronomical Society
... the alignment of the five visible planets. However, Yolanda Navarette did manage to "sneak a peak" between clouds of Venus and Saturn and the moon by Jupiter and do an observation report. Yolanda has been diligent all year in her observing projects. Hopefully, the skies will clear over the next two ...
... the alignment of the five visible planets. However, Yolanda Navarette did manage to "sneak a peak" between clouds of Venus and Saturn and the moon by Jupiter and do an observation report. Yolanda has been diligent all year in her observing projects. Hopefully, the skies will clear over the next two ...
Big Bang and Steady State Theories
... red-shift and CMBR give supporting evidence for the Big Bang theory, e.g. light was seen to be shifted towards a longer wavelength. This means that the galaxies are moving away from each other so the Universe must be expanding. This is evidence for the Big Bang theory. Cosmic Background Radiation co ...
... red-shift and CMBR give supporting evidence for the Big Bang theory, e.g. light was seen to be shifted towards a longer wavelength. This means that the galaxies are moving away from each other so the Universe must be expanding. This is evidence for the Big Bang theory. Cosmic Background Radiation co ...
Astronomy Activity: The Life-Line of the Stars
... A. Background: Brightness of Stars The brightness that a star has as seen from the Earth is called the apparent brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible ...
... A. Background: Brightness of Stars The brightness that a star has as seen from the Earth is called the apparent brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible ...
Tohoku-Hiroshima-Nagoya planetary spectra library: a method for
... absorption and the spectral response of TRISPEC, we observed standard stars with airmasses similar to the target. Because the exposure time used for each of TRISPEC’s three channels has an effect on the true exposure time of the other two channels, we were careful to use exactly the same exposure tim ...
... absorption and the spectral response of TRISPEC, we observed standard stars with airmasses similar to the target. Because the exposure time used for each of TRISPEC’s three channels has an effect on the true exposure time of the other two channels, we were careful to use exactly the same exposure tim ...
Final exam solutions - University of Rochester
... Problem 10 (3 pts, no need to show work): Our sun is expected to end its life as a a) red giant star. b) black hole. c) brown dwarf star. d) white dwarf star. e) smouldering mass of dark matter. Problem 11 (3 pts, no need to show work): Galaxies are thought to be made mostly of dark matter. Evidence ...
... Problem 10 (3 pts, no need to show work): Our sun is expected to end its life as a a) red giant star. b) black hole. c) brown dwarf star. d) white dwarf star. e) smouldering mass of dark matter. Problem 11 (3 pts, no need to show work): Galaxies are thought to be made mostly of dark matter. Evidence ...
Misc-ReviewForAstroTest
... 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
... 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
Double Stars Discovered by IOTA Predicted Occultations July, 2010
... A double asteroid was initially considered, but because the measured magnitude drops did not agree with the predicted magnitude drop and because the single event measured magnitude drops agreed with the single occultation of a double star, the combination of all the chords precluded a double asteroi ...
... A double asteroid was initially considered, but because the measured magnitude drops did not agree with the predicted magnitude drop and because the single event measured magnitude drops agreed with the single occultation of a double star, the combination of all the chords precluded a double asteroi ...
Massive quiescent galaxies at cosmic noon Robert Feldmann UC Berkeley
... • galaxy & halo growth are strongly correlated (similar timescales) • Low specific growth rates necessary to become quiescent ...
... • galaxy & halo growth are strongly correlated (similar timescales) • Low specific growth rates necessary to become quiescent ...
Zach Stephen Richard Worhatch Royce Grewer
... •A laser beam is focused by a lens on an object (like micron-sized polystyrene spheres). •The light reflecting and refracting on the object causes changes in the momentum of the light. By Conservation of Momentum, equal and opposite forces must also act on the sphere. •These forces trap the object a ...
... •A laser beam is focused by a lens on an object (like micron-sized polystyrene spheres). •The light reflecting and refracting on the object causes changes in the momentum of the light. By Conservation of Momentum, equal and opposite forces must also act on the sphere. •These forces trap the object a ...
Interacting Binary Star System Activity
... Describe what happens to the brightness just before, just after, and when the red dwarf moves between the solar cell and the white dwarf. Explain why the shape of the light curve looks like it does and compare what is happening in the light curve to the physical 3-D model. ...
... Describe what happens to the brightness just before, just after, and when the red dwarf moves between the solar cell and the white dwarf. Explain why the shape of the light curve looks like it does and compare what is happening in the light curve to the physical 3-D model. ...
Dark Matter Capture in the first stars
... • Dark stars are giant objects with core radii > 1 a.u. – Find them with JWST: NASA’s 4 billion dollar sequel to HST plans to see the first stars and should be able to differentiate standard fusion driven ones from dark stars, which will be cooler ...
... • Dark stars are giant objects with core radii > 1 a.u. – Find them with JWST: NASA’s 4 billion dollar sequel to HST plans to see the first stars and should be able to differentiate standard fusion driven ones from dark stars, which will be cooler ...
doc - StealthSkater
... usual dark matter models. The following text is a strongly-updated version of the original one which contained several errors and was badly organized. Observations First, consider in some detail what has been observed. Since the lifespan of the astronomers is not astronomical, they are not able to m ...
... usual dark matter models. The following text is a strongly-updated version of the original one which contained several errors and was badly organized. Observations First, consider in some detail what has been observed. Since the lifespan of the astronomers is not astronomical, they are not able to m ...
Supervisors
... which is defined as the temperature of a black body that emits the same amount of energy in the same amount of time and from the same surface area as the star in question. Pressure in a stellar atmosphere is determined primarily by its surface gravity as the two are related by Equation 1.11 in the ...
... which is defined as the temperature of a black body that emits the same amount of energy in the same amount of time and from the same surface area as the star in question. Pressure in a stellar atmosphere is determined primarily by its surface gravity as the two are related by Equation 1.11 in the ...
Scientific American`s Ask the Experts
... effort to find an object that was located even roughly along Galileo’s path. Special targeting was required to reach this object, but the result was the first close-up view of an asteroid, the one called Gaspra. The number of objects in the asteroid belt increases steeply with decreasing size, but eve ...
... effort to find an object that was located even roughly along Galileo’s path. Special targeting was required to reach this object, but the result was the first close-up view of an asteroid, the one called Gaspra. The number of objects in the asteroid belt increases steeply with decreasing size, but eve ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.