
Mon Oct 28, 2013 MOON AND MARS IN PREDAWN SKY Tonight
... Tonight the moon rises shortly before three in the morning, while Mars comes up a little after 3. By 4 am you can find the red planet off to the left of the moon and slightly below it. Although they appear right next to each other, these two celestial objects are in different constellations: Mars is ...
... Tonight the moon rises shortly before three in the morning, while Mars comes up a little after 3. By 4 am you can find the red planet off to the left of the moon and slightly below it. Although they appear right next to each other, these two celestial objects are in different constellations: Mars is ...
28. What causes waves - Summer Science Safari
... apparent magnitude how bright a star appears from earth galaxy largest grouping of stars in space absolute magnitude the actual brightness of a star parallax one of the ways we measure distances in space; apparent shift in a star’s location nebulae cloud of hyrdogen gas and dust; birthplace of stars ...
... apparent magnitude how bright a star appears from earth galaxy largest grouping of stars in space absolute magnitude the actual brightness of a star parallax one of the ways we measure distances in space; apparent shift in a star’s location nebulae cloud of hyrdogen gas and dust; birthplace of stars ...
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... Reflection and Transmission Most materials reflect light (partially or totally). For example, metals reflect light (almost totally) because an incident oscillating light beam causes the metal’s nearly free electrons to oscillate, setting up another (reflected) electromagnetic wave. Opaque materials ...
... Reflection and Transmission Most materials reflect light (partially or totally). For example, metals reflect light (almost totally) because an incident oscillating light beam causes the metal’s nearly free electrons to oscillate, setting up another (reflected) electromagnetic wave. Opaque materials ...
lecture
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
PS 20: Final Exam Review
... 6) Calculate the heat required to heat 200.0 g of water for soup from 10.0°C to boiling point. 7) What amount of heat is needed to heat 50.0 kg of water in a dishwasher from 10.0°C to 70.0°C? 8) You have 2.50 kg of mercury at 22.0°C. You find that it requires 3.20 x 103 J of energy to raise its temp ...
... 6) Calculate the heat required to heat 200.0 g of water for soup from 10.0°C to boiling point. 7) What amount of heat is needed to heat 50.0 kg of water in a dishwasher from 10.0°C to 70.0°C? 8) You have 2.50 kg of mercury at 22.0°C. You find that it requires 3.20 x 103 J of energy to raise its temp ...
Small images
... short hard bursts were localized by the HETE-2 and SWIFT satellites. These bursts did not come from star forming regions, and in fact showed all the characteristics expected of merging neutron stars. It is widely believed that merging neutron stars (and neutron stars merging with black holes) have n ...
... short hard bursts were localized by the HETE-2 and SWIFT satellites. These bursts did not come from star forming regions, and in fact showed all the characteristics expected of merging neutron stars. It is widely believed that merging neutron stars (and neutron stars merging with black holes) have n ...
Stars Part Two
... How do we know all this? By observing Globular clusters… 1. Globular clusters are thousands of stars that all formed at more or less the same time. 2. Globular clusters are much smaller than galaxies. 3. Galaxies create stars in an on-going process. 4. The stars in a globular cluster accrete sudde ...
... How do we know all this? By observing Globular clusters… 1. Globular clusters are thousands of stars that all formed at more or less the same time. 2. Globular clusters are much smaller than galaxies. 3. Galaxies create stars in an on-going process. 4. The stars in a globular cluster accrete sudde ...
1 Sep: 6.13am BST 15 Sep: 6.43am BST 30 Sep: 7.14am BST
... hat, just above IC1396, is µ Cephei or Herschel’s Garnet Star, a red super giant. Comet 2009 P1 (Garradd) Comet 2009 P1 (Garradd) was discovered on 13th August 2009 by G J Garradd of Siding Spring Observatory Australia. While it is presently at Mag 8.0, it’s been reported as a hazy patch in binocula ...
... hat, just above IC1396, is µ Cephei or Herschel’s Garnet Star, a red super giant. Comet 2009 P1 (Garradd) Comet 2009 P1 (Garradd) was discovered on 13th August 2009 by G J Garradd of Siding Spring Observatory Australia. While it is presently at Mag 8.0, it’s been reported as a hazy patch in binocula ...
EVOLUTION OF A SOLAR
... These notes describe the evolutionary path taken by a Sun-like star, one with an initial mass comparable to the Sun’s mass. Stars can be thought of as a series of nested shells, surrounding a core. The core is more dense, hotter, and at higher pressure than the surrounding shells of plasma. ...
... These notes describe the evolutionary path taken by a Sun-like star, one with an initial mass comparable to the Sun’s mass. Stars can be thought of as a series of nested shells, surrounding a core. The core is more dense, hotter, and at higher pressure than the surrounding shells of plasma. ...
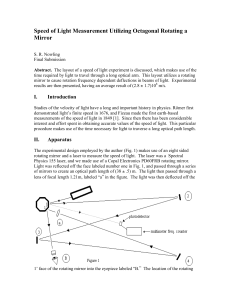
Speed of Light Measurement Utilizing Octagonal
... the optical path length, the focal length of the lens, and increasing the rotational frequency. The main obstacle in these measurements will be to have a beam intense enough to view. Because our optical path length, lensÕ focal length, and rotational frequencies were low intensity was not a problem. ...
... the optical path length, the focal length of the lens, and increasing the rotational frequency. The main obstacle in these measurements will be to have a beam intense enough to view. Because our optical path length, lensÕ focal length, and rotational frequencies were low intensity was not a problem. ...
Ch 6 notes 6.1 to 6.4
... The Bohr model explains the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom, but not (accurately) the spectra of other atoms. Also, the Bohr model assumes the electron behaves as a particle. Electrons also have wave-like properties. ...
... The Bohr model explains the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom, but not (accurately) the spectra of other atoms. Also, the Bohr model assumes the electron behaves as a particle. Electrons also have wave-like properties. ...
EARTH IN THE UNIVERSE TOPIC 3 2011-2012
... Our galaxy is spiral shaped. The name for our galaxy is the Milky Way. ...
... Our galaxy is spiral shaped. The name for our galaxy is the Milky Way. ...
Lecture5
... component stars, etc., by measuring periodic shifting of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect as the stars move around the COM. In most cases the component two stars cannot be visually resolved separately, however (too far from us, too close to each other, or both). In some cases, the shifting o ...
... component stars, etc., by measuring periodic shifting of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect as the stars move around the COM. In most cases the component two stars cannot be visually resolved separately, however (too far from us, too close to each other, or both). In some cases, the shifting o ...
The nuclear and extended mid-infrared emission of Seyfert
... Only few galaxies have similar structures For the majority of the galaxies, the IRAC PSF is larger than the HR extended emission ...
... Only few galaxies have similar structures For the majority of the galaxies, the IRAC PSF is larger than the HR extended emission ...
Lab 15 How Many Galaxies Are There in the
... spend 10 entire days training this telescope on one small region of the sky to observe the faintest galaxies and learn about them. The image that was obtained is shown in Figure 15.2. First, let’s figure out how long it would take for the Space Telescope to take pictures like this over the entire sk ...
... spend 10 entire days training this telescope on one small region of the sky to observe the faintest galaxies and learn about them. The image that was obtained is shown in Figure 15.2. First, let’s figure out how long it would take for the Space Telescope to take pictures like this over the entire sk ...
Protoplanetary disks, jets, and the birth of the stars
... The birth of a star is accompanied by the formation of a surrounding disk of gas and dust containing the high-angular-momentum material of the collapsing envelope that could not fall directly onto the central (proto)star. This disk constitutes a reservoir of mass that slowly accretes onto the centra ...
... The birth of a star is accompanied by the formation of a surrounding disk of gas and dust containing the high-angular-momentum material of the collapsing envelope that could not fall directly onto the central (proto)star. This disk constitutes a reservoir of mass that slowly accretes onto the centra ...
Evolutionary properties of galaxies and mass assembly up
... While the higher fraction of bright galaxies in over-dense regions seen locally is already present at z ~ 1.2, the environmental dependency of the LF shape at high redshift appears to be different from what is seen at low redshift. Is this difference due to an increase with cosmic time of the number ...
... While the higher fraction of bright galaxies in over-dense regions seen locally is already present at z ~ 1.2, the environmental dependency of the LF shape at high redshift appears to be different from what is seen at low redshift. Is this difference due to an increase with cosmic time of the number ...
Where to begin the adventure with variable stars?
... In this way we have found the stars and we can begin photometric observations. Their result will probably impress not only us, but also other students and our friends. Also the acquired skills of navigating in the sky will be a source of satisfaction! ...
... In this way we have found the stars and we can begin photometric observations. Their result will probably impress not only us, but also other students and our friends. Also the acquired skills of navigating in the sky will be a source of satisfaction! ...
The lives of stars
... from Hydrogen fusion to Helium fusion with Hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core. The cores are more massive and produce more energy than the cores of Red Giant stars. ...
... from Hydrogen fusion to Helium fusion with Hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core. The cores are more massive and produce more energy than the cores of Red Giant stars. ...
God*s Faithfulness as Seen in Our Universe
... If it were thinner, there would be too many earthquakes and too much volcanism for life to function well. If it were thicker, the crust would eat up too much of the atmospheric oxygen. ...
... If it were thinner, there would be too many earthquakes and too much volcanism for life to function well. If it were thicker, the crust would eat up too much of the atmospheric oxygen. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.





















![Lecture 15.Dark.Matter.Dark.Energy [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001653481_1-24d181abb7aa2350426c5e71bf17efb8-300x300.png)
