More about the game plan:
... • Orbital velocity of stars different than pattern speed • Stars, gas bunch up at position of spiral arms • Causes higher grav. potential • Unclear if self-sustaining or forced. ...
... • Orbital velocity of stars different than pattern speed • Stars, gas bunch up at position of spiral arms • Causes higher grav. potential • Unclear if self-sustaining or forced. ...
Detection of [Ne ii] Emission from Young Circumstellar Disks
... et al. (1995), and adopting the distances in Table 1. These X-ray luminosities are representative for the energy band 0.1–2.4 keV (or 120–5 Å). The errors in LX include the uncertainties in the count–rates, HR1, and distances. Note however that the intrinsic variability of log(Lx ) due to stellar a ...
... et al. (1995), and adopting the distances in Table 1. These X-ray luminosities are representative for the energy band 0.1–2.4 keV (or 120–5 Å). The errors in LX include the uncertainties in the count–rates, HR1, and distances. Note however that the intrinsic variability of log(Lx ) due to stellar a ...
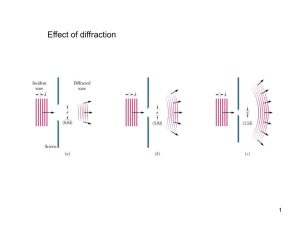
Example
... Taking = 550 nm, n = 1.33, and d = 2 mm as typical values, R is about 0.025 rad. So, two objects 1 m away from you cannot be resolved by the eye if they are less than 0.25 mm apart. This is not the result of defective eyesight. It is the result of diffraction. ...
... Taking = 550 nm, n = 1.33, and d = 2 mm as typical values, R is about 0.025 rad. So, two objects 1 m away from you cannot be resolved by the eye if they are less than 0.25 mm apart. This is not the result of defective eyesight. It is the result of diffraction. ...
PPT - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... •Looking at the very distant parts of the universe allows astronomers to take a snapshot very early universe to understand how matter and energy interact at these high energies. •Some specific theories also predict particles that can provide the dark matter and dark energy seen in the universe. •The ...
... •Looking at the very distant parts of the universe allows astronomers to take a snapshot very early universe to understand how matter and energy interact at these high energies. •Some specific theories also predict particles that can provide the dark matter and dark energy seen in the universe. •The ...
Photons
... telescope provides imaging of excellent quality over a 34′ × 33′ field of view. It contains a peculiar set of broad-band filters, VEGAmag system assuming all Vega apparent magnitudes to very different from the “standard” Johnson-Cousins ones. This be 0.03, and in the ABmag system, which is adopted by ...
... telescope provides imaging of excellent quality over a 34′ × 33′ field of view. It contains a peculiar set of broad-band filters, VEGAmag system assuming all Vega apparent magnitudes to very different from the “standard” Johnson-Cousins ones. This be 0.03, and in the ABmag system, which is adopted by ...
Stellar Evolution
... the luminosity now starts to increase. The large cool envelope will be very opaque (it has a high opacity). This will help to trap in heat and lead to a great deal of convection in the outer layers of the star. Some of this convective motion can reach from the surface all of the way into the core. S ...
... the luminosity now starts to increase. The large cool envelope will be very opaque (it has a high opacity). This will help to trap in heat and lead to a great deal of convection in the outer layers of the star. Some of this convective motion can reach from the surface all of the way into the core. S ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... Astronomy is a Time Machine When we observe a star that is 100 light-years distant, then the light took 100 years to reach us. We are seeing it as it was 100 years ago. The nearest galaxy is about a million light-years from Earth. We see it as it was 1 million years ago. The most distant objects ob ...
... Astronomy is a Time Machine When we observe a star that is 100 light-years distant, then the light took 100 years to reach us. We are seeing it as it was 100 years ago. The nearest galaxy is about a million light-years from Earth. We see it as it was 1 million years ago. The most distant objects ob ...
Experiment 3 1 The Michelson Interferometer and the He
... The basic idea of a laser is illustrated in Fig. 3 where the energy levels of an atom are pictured. In the normal state, almost all of the atoms would be in their ground state, E1. If, on ...
... The basic idea of a laser is illustrated in Fig. 3 where the energy levels of an atom are pictured. In the normal state, almost all of the atoms would be in their ground state, E1. If, on ...
1 Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves 2 Speed of an
... linearly polarized : a wave with displacement in only one plane polarizing filter or polarizer : a filter that polarizes a wave in a certain direction dichroism: the selective absorption of one of the polarized components much more strongly than the other polarizing axis: the axis in which the light ...
... linearly polarized : a wave with displacement in only one plane polarizing filter or polarizer : a filter that polarizes a wave in a certain direction dichroism: the selective absorption of one of the polarized components much more strongly than the other polarizing axis: the axis in which the light ...
STANDARD SET 4. Earth Sciences
... The Sun is a star located on the rim of a typical spiral galaxy called the Milky Way and orbits the galactic center. In similar spiral galaxies this galactic center appears as a bulge of stars in the heart of the disk. The bright band of stars cutting across the night sky is the edge of the Milky Wa ...
... The Sun is a star located on the rim of a typical spiral galaxy called the Milky Way and orbits the galactic center. In similar spiral galaxies this galactic center appears as a bulge of stars in the heart of the disk. The bright band of stars cutting across the night sky is the edge of the Milky Wa ...
Chapter 23 notes
... linearly polarized : a wave with displacement in only one plane polarizing filter or polarizer : a filter that polarizes a wave in a certain direction dichroism: the selective absorption of one of the polarized components much more strongly than the other polarizing axis: the axis in which the light ...
... linearly polarized : a wave with displacement in only one plane polarizing filter or polarizer : a filter that polarizes a wave in a certain direction dichroism: the selective absorption of one of the polarized components much more strongly than the other polarizing axis: the axis in which the light ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... the estimated CCSN rate. We therefore conclude that SN 2004ip was very likely a core-collapse event. After correcting for a Galactic extinction of AV p 0.47 (Schlegel et al. 1998), the absolute magnitude of the SN at the time of the discovery becomes MK s p ⫺15.85 (before correcting for the host gal ...
... the estimated CCSN rate. We therefore conclude that SN 2004ip was very likely a core-collapse event. After correcting for a Galactic extinction of AV p 0.47 (Schlegel et al. 1998), the absolute magnitude of the SN at the time of the discovery becomes MK s p ⫺15.85 (before correcting for the host gal ...
Part 1
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
... The sign between kx and t determines the direction the wave travels along the x-axis. + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match ...
Olbers` Paradox
... years old (the latest figure) are too far away for their light ever to reach us. • Redshift effect certainly contributes. But the finite age of the Universe is the most important effect. ...
... years old (the latest figure) are too far away for their light ever to reach us. • Redshift effect certainly contributes. But the finite age of the Universe is the most important effect. ...
Physical Science
... begins the descent to the lunar surface only to stop short and conduct a planned “abort”, never reaching the lunar surface. 5. Apollo 11: July 20, 1969 - First humans to walk on the moon: a. Neil Armstrong: 1st to walk on the moon. b. Buzz Aldrin: 2nd to walk on the moon, took communion on the lunar ...
... begins the descent to the lunar surface only to stop short and conduct a planned “abort”, never reaching the lunar surface. 5. Apollo 11: July 20, 1969 - First humans to walk on the moon: a. Neil Armstrong: 1st to walk on the moon. b. Buzz Aldrin: 2nd to walk on the moon, took communion on the lunar ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.
![Detection of [Ne ii] Emission from Young Circumstellar Disks](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014394769_1-fdf9c6283148d488005c87b005dab353-300x300.png)