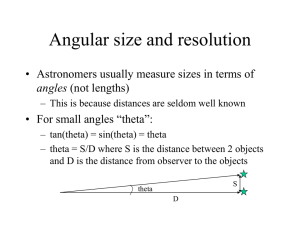
angles_telescopes
... magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – w/ small telescope can distinguish large craters (angular sizes of ...
... magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – w/ small telescope can distinguish large craters (angular sizes of ...
stars - science1d
... 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that seems to form the tail of the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located mi ...
... 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that seems to form the tail of the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located mi ...
Phys 1830: Lecture 33 - University of Manitoba Physics Department
... How many rocky planets reside in the Habitable Zone (HZ)? This zone is around each star and has a temperature such that water condenses on the planet’s surface but does not permanently freeze. That is, it is a spherical shell bound on the interior by regions with T > 100C and outside by T<0C. ...
... How many rocky planets reside in the Habitable Zone (HZ)? This zone is around each star and has a temperature such that water condenses on the planet’s surface but does not permanently freeze. That is, it is a spherical shell bound on the interior by regions with T > 100C and outside by T<0C. ...
- Stevenson High School
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our nighttime view. A chart of the night sky will map the locations of the stars; a star wheel will let us know which stars w ...
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our nighttime view. A chart of the night sky will map the locations of the stars; a star wheel will let us know which stars w ...
Chapter 3 - BITS Pilani
... pressure is too high (since temperatures are too high), and as the gravity falls with inverse square of the distance, particles would escape the Sun. ...
... pressure is too high (since temperatures are too high), and as the gravity falls with inverse square of the distance, particles would escape the Sun. ...
Science Olympiad 2008 Reach for the Stars Division B
... B) Less than one solar mass C) around 1 solar mass D) 1 to 3 solar masses E) More than 3 solar masses 95. Suppose that Betelgeuse were to become a supernova and be observed from Earth. What would it look like to the naked eye? A) Because the supernova event destroys the star, Betelgeuse would sudden ...
... B) Less than one solar mass C) around 1 solar mass D) 1 to 3 solar masses E) More than 3 solar masses 95. Suppose that Betelgeuse were to become a supernova and be observed from Earth. What would it look like to the naked eye? A) Because the supernova event destroys the star, Betelgeuse would sudden ...
Image Credit: NASA,ESA, HEIC, Hubble
... How Can We See Molecular Clouds? The Observation: Carbon Monoxide emission line in the Milky Way ...
... How Can We See Molecular Clouds? The Observation: Carbon Monoxide emission line in the Milky Way ...
Lecture 3: Emission and absorption
... Different transitions are labelled with Greek letters, so Lyα arises from the n = 2 to n = 1 transition; Balmer α (written Hα) arises from n = 3 to n = 2, Hβ is n = 4 to n = 2, etc. Lecture 3: Emission and absorption ...
... Different transitions are labelled with Greek letters, so Lyα arises from the n = 2 to n = 1 transition; Balmer α (written Hα) arises from n = 3 to n = 2, Hβ is n = 4 to n = 2, etc. Lecture 3: Emission and absorption ...
July, 2014 - Spy Hill .net
... traveling beyond the heliopause showed a tremendous rise in the flux of intermediate-to-high energy cosmic ray protons, proving that our Sun shields our solar system quite effectively. Finally, it showed that the outer edges of the heliosheath consist of two zones, where the solar wind slows and the ...
... traveling beyond the heliopause showed a tremendous rise in the flux of intermediate-to-high energy cosmic ray protons, proving that our Sun shields our solar system quite effectively. Finally, it showed that the outer edges of the heliosheath consist of two zones, where the solar wind slows and the ...
Taoist North Star Meditations (Fire Practice)
... I have been fortunate for a number of years now to live just a few miles from Mantak Chia's home. Over the years we have remained good friends and I was provided with the opportunity to learn and explore the very highest formulas of Taoist Internal Alchemy. Chia has never publicly taught some of the ...
... I have been fortunate for a number of years now to live just a few miles from Mantak Chia's home. Over the years we have remained good friends and I was provided with the opportunity to learn and explore the very highest formulas of Taoist Internal Alchemy. Chia has never publicly taught some of the ...
Click here to get the file
... Radio waves carry energy, and also represent the amount of energy in the source of radio waves. The goal of this module is to have the students understand how much energy some of the celestial radio objects emit. The students will measure the overall 21-cm brightness of a celestial object. Results w ...
... Radio waves carry energy, and also represent the amount of energy in the source of radio waves. The goal of this module is to have the students understand how much energy some of the celestial radio objects emit. The students will measure the overall 21-cm brightness of a celestial object. Results w ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... Our best-known star It wasn’t until after Galileo and Newton that stars were Sun-like objects, a long way away. A good way to learn more about distant stars, was to learn more about the star closest to us, the sun. Galileo observed sunspots on the surface of the sun, this lead to the discovery th ...
... Our best-known star It wasn’t until after Galileo and Newton that stars were Sun-like objects, a long way away. A good way to learn more about distant stars, was to learn more about the star closest to us, the sun. Galileo observed sunspots on the surface of the sun, this lead to the discovery th ...
in my own words Astronomy at the Frontier Matt Mountain, Ph.D.
... Twenty years ago, astronomers agreed amongst themselves, internationally, on a standard format for all their data irrespective of which telescope it came from or what waveband they use. This has allowed us to build amazing archives of data. Today, half the refereed papers from Hubble—which is a meas ...
... Twenty years ago, astronomers agreed amongst themselves, internationally, on a standard format for all their data irrespective of which telescope it came from or what waveband they use. This has allowed us to build amazing archives of data. Today, half the refereed papers from Hubble—which is a meas ...
2014-2015 SCIENCE Instructional Curriculum Plan Grade: K
... SC.4.E.5.In.4: Recognize that the Sun appears to rise and set because of Earth’s rotation in a 24hour day. SC.4.E.5.Su.4: Recognize that the side of Earth facing the Sun has daylight. SC.4.E.5.Pa.3: Identify morning, noon, and night. SC.4.E.5.In.5: Identify objects and people related to the space pr ...
... SC.4.E.5.In.4: Recognize that the Sun appears to rise and set because of Earth’s rotation in a 24hour day. SC.4.E.5.Su.4: Recognize that the side of Earth facing the Sun has daylight. SC.4.E.5.Pa.3: Identify morning, noon, and night. SC.4.E.5.In.5: Identify objects and people related to the space pr ...
The magnitudes of stars
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
Using Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope arrays as Intensity Interferometers S. LeBohec and J. Holder
... baseline from 10m to 188m to track any star while keeping the line joining the two telescopes perpendicular to the direction of the star in such a way that no delay was required to bring the signals in time. At the focus of each telescope, the converging light was collimated and passed through an in ...
... baseline from 10m to 188m to track any star while keeping the line joining the two telescopes perpendicular to the direction of the star in such a way that no delay was required to bring the signals in time. At the focus of each telescope, the converging light was collimated and passed through an in ...
Stellar aberration
... Reversal of direction of earth’s motion is not an essential requirement to recognize stellar aberration. Magnitude and direction of stellar aberration, from any planetary body, depends only on its relative position with respect to central body. As the aberration is caused (mainly) due to matter-cont ...
... Reversal of direction of earth’s motion is not an essential requirement to recognize stellar aberration. Magnitude and direction of stellar aberration, from any planetary body, depends only on its relative position with respect to central body. As the aberration is caused (mainly) due to matter-cont ...
Physics 416 Quiz Quiz 2 Capitalization Name: ___________________________________
... 1. The milky way galaxy is the most impressive galaxy in the entire universe. 2. I xeroxed my applications to the university of michigan and the ohio state university. 3. On wednesday february 2nd at 2:00 p.m. I have an appointment with dr. i. m. smart, phd. 4. It makes sense that bosons should obey ...
... 1. The milky way galaxy is the most impressive galaxy in the entire universe. 2. I xeroxed my applications to the university of michigan and the ohio state university. 3. On wednesday february 2nd at 2:00 p.m. I have an appointment with dr. i. m. smart, phd. 4. It makes sense that bosons should obey ...
16. Hubble`s Law and Dark Matter
... need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. • The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with each galaxy. ...
... need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. • The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with each galaxy. ...
RESEARCH STATEMENT Chromospheres and winds
... Mass loss from late–type evolved stars contributes material to the next generation of stars and planets and plays an important role in both stellar and galactic evolution. The mechanisms that drive winds from cool (.8000K) evolved stars such as K and early-M stars are not well known. Unlike hot star ...
... Mass loss from late–type evolved stars contributes material to the next generation of stars and planets and plays an important role in both stellar and galactic evolution. The mechanisms that drive winds from cool (.8000K) evolved stars such as K and early-M stars are not well known. Unlike hot star ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematical computations, telescopic observation, and just plain imagination. Scientists have made startling new ...
... motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematical computations, telescopic observation, and just plain imagination. Scientists have made startling new ...
Autumn Night sky Guide
... M15 – globular cluster in Pegasus Find Enif and move the binoculars until Enif is at about the 8 o’clock position on the edge of your view. Keep moving until what is a 2 o’clock is in the centre of your view. M15 should be visible as a fuzzy star. M15 is a little larger than M13 but at 30,600 light- ...
... M15 – globular cluster in Pegasus Find Enif and move the binoculars until Enif is at about the 8 o’clock position on the edge of your view. Keep moving until what is a 2 o’clock is in the centre of your view. M15 should be visible as a fuzzy star. M15 is a little larger than M13 but at 30,600 light- ...
Invisibility Cup - Purdue Engineering
... similar role. They show that if the metal wires are small enough (subwavelength) and of the correct geometry, they form an optical metamaterial that potentially acts as an invisibility cup for visible light. In effect, the tiny wires act like artificial atoms and have a resonance with light that dep ...
... similar role. They show that if the metal wires are small enough (subwavelength) and of the correct geometry, they form an optical metamaterial that potentially acts as an invisibility cup for visible light. In effect, the tiny wires act like artificial atoms and have a resonance with light that dep ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.























