Solar Energy and a Spherical Earth
... At the north/south poles, the period of daylight changes from winter to summer and back again Winter in the north has darkness for almost 24 hrs Summer in the north has light for almost 24 hrs The opposite season/daylength exists at the south pole ...
... At the north/south poles, the period of daylight changes from winter to summer and back again Winter in the north has darkness for almost 24 hrs Summer in the north has light for almost 24 hrs The opposite season/daylength exists at the south pole ...
A Closer Look at Earth - James M. Hill High School
... Longitude is the angle measured east or west from the 0° line, which passes through Greenwich, England. For example, the eastern tip of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, is at 60° west longitude. Latitude is the angle measured north or south of the equator. For example, the border between the western ...
... Longitude is the angle measured east or west from the 0° line, which passes through Greenwich, England. For example, the eastern tip of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, is at 60° west longitude. Latitude is the angle measured north or south of the equator. For example, the border between the western ...
Physical Geography
... Zero Degrees longitude is the Prime Meridian. 180 degrees East or West is the International Date Line By international agreement - 0 degrees longitude runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England Numbers get higher the farther you move either East of West Longitude lines measure East or ...
... Zero Degrees longitude is the Prime Meridian. 180 degrees East or West is the International Date Line By international agreement - 0 degrees longitude runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England Numbers get higher the farther you move either East of West Longitude lines measure East or ...
5 Themes of Geography
... may tell you that one inch on the map equals one mile in the real world. OwlTeacher.com ...
... may tell you that one inch on the map equals one mile in the real world. OwlTeacher.com ...
Grade 9 Social Studies Exam
... 1. the exact coordinates of a place on the surface of the Earth 2 .the 0 degree line of longitude 3. a half of a shere ex the Northern hemisphere 4. the 0 degree line of latitude 5. the location of a place in terms of what is around it 6. the lines that measure directions east and west of the Prime ...
... 1. the exact coordinates of a place on the surface of the Earth 2 .the 0 degree line of longitude 3. a half of a shere ex the Northern hemisphere 4. the 0 degree line of latitude 5. the location of a place in terms of what is around it 6. the lines that measure directions east and west of the Prime ...
Name___________________ Period__________________ World
... These regions are made up of different places that are linked together and function as a unit. Examples include the transit system such as transporting people via train, bus, subway, etc. Malls or other central points are also examples of these regions known as __________functional regions _________ ...
... These regions are made up of different places that are linked together and function as a unit. Examples include the transit system such as transporting people via train, bus, subway, etc. Malls or other central points are also examples of these regions known as __________functional regions _________ ...
5 Themes of Geography - Canton Local Schools
... Fish cannot survive in the remaining waters, plants cannot be planted where the water used to be Industry is now destroyed ...
... Fish cannot survive in the remaining waters, plants cannot be planted where the water used to be Industry is now destroyed ...
Quiz 1 - Word Document
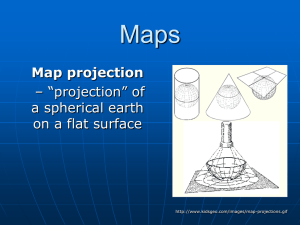
... polar projection - a cartographic projection of the sphere in which the point of sight is at the center and the plane of projection passes through one of the polar circles Possibilism - the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to ...
... polar projection - a cartographic projection of the sphere in which the point of sight is at the center and the plane of projection passes through one of the polar circles Possibilism - the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to ...
Maps
... Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. ...
... Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. ...
Physical Geography
... • Temperature is the degree of heat or cold in the atmosphere • Precipitation is the amount of moisture falling at any given moment. It can be in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or ice. ...
... • Temperature is the degree of heat or cold in the atmosphere • Precipitation is the amount of moisture falling at any given moment. It can be in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or ice. ...
Chapter 1 Key Issue 2
... Situation or relative location describes a place’s relationship relative to other places around it. Situation is a valuable way to indicate location, for two reasonsfinding an unfamiliar place and understanding its importance. ...
... Situation or relative location describes a place’s relationship relative to other places around it. Situation is a valuable way to indicate location, for two reasonsfinding an unfamiliar place and understanding its importance. ...
rubenstein - hhshurtgeo
... 15) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located 16) The hulk of a ship lies on the ocean floor at 41°46'N and 50°14'W. These coordinates tell us that the ship is located in the 17) Santa Fe, New Mexico ...
... 15) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located 16) The hulk of a ship lies on the ocean floor at 41°46'N and 50°14'W. These coordinates tell us that the ship is located in the 17) Santa Fe, New Mexico ...
Intro to Geography Study Guide
... 2. Relative Location: the location of something in relation to some other place 3. Map Scale: compares the distance on a map to the distance of the real world 4. Inset Map: a smaller map inside a larger map 5. Locator: a picture of a globe which shows where the main map is located within the state, ...
... 2. Relative Location: the location of something in relation to some other place 3. Map Scale: compares the distance on a map to the distance of the real world 4. Inset Map: a smaller map inside a larger map 5. Locator: a picture of a globe which shows where the main map is located within the state, ...
Basics of Geography
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
... Tell where the location of the scale is. Name and give symbols of 5 things located in the legend. What two states are included on this map? What river separates the two states listed in #3? What is this a map of? ...
What city is near 6 degrees north latitude and 10 degrees west
... 2. What is the longitude and latitude of Capetown, South Africa? 34 degrees South, 18 degrees East 3. In which two hemispheres would 40 degrees north latitude and 20 degrees east longitude be? Northern and Eastern Hemispheres 4. If you were to plot the point 20 degrees south latitude and 40 degrees ...
... 2. What is the longitude and latitude of Capetown, South Africa? 34 degrees South, 18 degrees East 3. In which two hemispheres would 40 degrees north latitude and 20 degrees east longitude be? Northern and Eastern Hemispheres 4. If you were to plot the point 20 degrees south latitude and 40 degrees ...
Document
... 16) Compass Rose-A symbol that displays the cardinal directions of North, South, East and West on a map. 17) Key- Shows the symbols and colors used on a map and tells what each stands for. 18) Scale Bar-Helps you find the actual distances between points shown on a map in both miles and kilometers. 1 ...
... 16) Compass Rose-A symbol that displays the cardinal directions of North, South, East and West on a map. 17) Key- Shows the symbols and colors used on a map and tells what each stands for. 18) Scale Bar-Helps you find the actual distances between points shown on a map in both miles and kilometers. 1 ...
Map scale: refers to a relationship
... earth. Can be a statement (1 inch equals 1 mile), a ration (1:100) or a graphic bar. 2. Location: where something is described as either absolute [blank] or relative [blank] 3. Cartography: the science of map making. 4. Distance: how far apart two features are 5. Distortion: this happens when trying ...
... earth. Can be a statement (1 inch equals 1 mile), a ration (1:100) or a graphic bar. 2. Location: where something is described as either absolute [blank] or relative [blank] 3. Cartography: the science of map making. 4. Distance: how far apart two features are 5. Distortion: this happens when trying ...
5 Themes of Geography Worksheet
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
... ______________________________, but the lines of ____________________ are ______________________. ...
Measuring the Earth
... surface you need two numbers or coordinates. Coordinate system- system for determining coordinates. What is the name of the coordinate system used to find a location on the Earth’s surface? Latitude-longitude Measured in degrees and minutes: 60minutes In 1 degree. ...
... surface you need two numbers or coordinates. Coordinate system- system for determining coordinates. What is the name of the coordinate system used to find a location on the Earth’s surface? Latitude-longitude Measured in degrees and minutes: 60minutes In 1 degree. ...
Earth`s Geography
... Latitude – The distance north or south of the equator, expressed in degrees. Longitude – The distance east or west of the prime meridian, expressed in degrees. Degree – A unit of measurement indicating the distance between lines of latitude and lines of longitude. Parallel – Any line of latitude. Li ...
... Latitude – The distance north or south of the equator, expressed in degrees. Longitude – The distance east or west of the prime meridian, expressed in degrees. Degree – A unit of measurement indicating the distance between lines of latitude and lines of longitude. Parallel – Any line of latitude. Li ...
What is Geography????
... do you sit and why? ► Do you sit where you do based on common interests, gender or another reason? ► Where are the teachers? ► Does everyone feel the same about the seating arrangements? ...
... do you sit and why? ► Do you sit where you do based on common interests, gender or another reason? ► Where are the teachers? ► Does everyone feel the same about the seating arrangements? ...
Intro to Geography
... equator a region is located. – Latitude is shown on a map with lines going east and west. – The hottest climates, also known as tropical climates, are found in low latitudes (closest to ...
... equator a region is located. – Latitude is shown on a map with lines going east and west. – The hottest climates, also known as tropical climates, are found in low latitudes (closest to ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude