Unit 1 Physical Geography
... world is usually described in spatial terms Spatial relations- refer to the links that places and people have to one another because of their location You could use the terms ...
... world is usually described in spatial terms Spatial relations- refer to the links that places and people have to one another because of their location You could use the terms ...
Geodesy and Map Projections
... • Hundreds of different datums have been used to frame position descriptions • Datums have evolved from those describing a spherical earth to ellipsoidal models derived from years of satellite measurements. ...
... • Hundreds of different datums have been used to frame position descriptions • Datums have evolved from those describing a spherical earth to ellipsoidal models derived from years of satellite measurements. ...
The Seasons (tropics version)
... Also on the summer solstice, the Sun can be seen on the horizon at midnight, at the latitude of the arctic or antarctic circles, as seen in Figure 3. On these days, the Sun never sets. You know that in the equatorial coordinate system, we project the Earth’s poles and equator onto the sky to give us ...
... Also on the summer solstice, the Sun can be seen on the horizon at midnight, at the latitude of the arctic or antarctic circles, as seen in Figure 3. On these days, the Sun never sets. You know that in the equatorial coordinate system, we project the Earth’s poles and equator onto the sky to give us ...
Five Frequently Encountered Map Projections
... parallel, but they do not fall at their normally projected positions; instead, they are mathematically spaced to produce the property of conformality or true shape. ...
... parallel, but they do not fall at their normally projected positions; instead, they are mathematically spaced to produce the property of conformality or true shape. ...
Transverse Mercator Projection
... parallel, but they do not fall at their normally projected positions; instead, they are mathematically spaced to produce the property of conformality or true shape. o ...
... parallel, but they do not fall at their normally projected positions; instead, they are mathematically spaced to produce the property of conformality or true shape. o ...
Geodesy and Map Projections
... • Hundreds of different datums have been used to frame position descriptions • Datums have evolved from those describing a spherical earth to ellipsoidal models derived from years of satellite measurements. ...
... • Hundreds of different datums have been used to frame position descriptions • Datums have evolved from those describing a spherical earth to ellipsoidal models derived from years of satellite measurements. ...
The Earth - Valhalla High School
... Locating Positions on Earth • Coordinate System – Scientists have established a surface grid (lines) that you can use to locate any position on Earth. – Each pair of coordinates (2 numbers) are called the latitude and longitude • Latitude are distances in degrees north or south of the equator – The ...
... Locating Positions on Earth • Coordinate System – Scientists have established a surface grid (lines) that you can use to locate any position on Earth. – Each pair of coordinates (2 numbers) are called the latitude and longitude • Latitude are distances in degrees north or south of the equator – The ...
The Earth
... Locating Positions on Earth • Coordinate System – Scientists have established a surface grid (lines) that you can use to locate any position on Earth. – Each pair of coordinates (2 numbers) are called the latitude and longitude • Latitude are distances in degrees north or south of the equator – The ...
... Locating Positions on Earth • Coordinate System – Scientists have established a surface grid (lines) that you can use to locate any position on Earth. – Each pair of coordinates (2 numbers) are called the latitude and longitude • Latitude are distances in degrees north or south of the equator – The ...
Unit 1
... 1. This assessment should be given at the end of the first unit. 2. This exam is worth 49 points for regular classes and 59 points for honors courses. Student scores will be entered as total points into the gradebook in the District Assessments category. 3. Tests must be done in class. The test is n ...
... 1. This assessment should be given at the end of the first unit. 2. This exam is worth 49 points for regular classes and 59 points for honors courses. Student scores will be entered as total points into the gradebook in the District Assessments category. 3. Tests must be done in class. The test is n ...
Review Guide Key
... Study Guide: Test 1 ***Suggestion: write answers on a separate sheet of paper Terms to Know (define each): Absolute Location — Exact ...
... Study Guide: Test 1 ***Suggestion: write answers on a separate sheet of paper Terms to Know (define each): Absolute Location — Exact ...
Place
... Study of places – both physical features (natural) and cultural (human) Geographers use the 5 Themes of Geography to understand any given place ...
... Study of places – both physical features (natural) and cultural (human) Geographers use the 5 Themes of Geography to understand any given place ...
Part III Practice Multiple Choice
... 24. Of these, the map using the smallest map scale would be the map of: a. The world b. Atlanta, Georgia c. Main Street, Small Town, Ohio d. Pennsylvania ...
... 24. Of these, the map using the smallest map scale would be the map of: a. The world b. Atlanta, Georgia c. Main Street, Small Town, Ohio d. Pennsylvania ...
Exploring Earth`s Surface
... a half circle from the North surface. Pole to the South Pole. It passes through Greenwich, England. Places to the east of the Prime Meridian are in the Eastern Hemisphere and places to the west are in the Western Hemisphere. ...
... a half circle from the North surface. Pole to the South Pole. It passes through Greenwich, England. Places to the east of the Prime Meridian are in the Eastern Hemisphere and places to the west are in the Western Hemisphere. ...
GEOG370_Ch3p2
... Planar projections, also called azimuthal projections, project map data onto a flat surface. When the plane touches the earth at either the north or south poles latitude lines appear as concentric circles and longitude lines radiate from the pole at their true angle like the spokes on a wheel. This ...
... Planar projections, also called azimuthal projections, project map data onto a flat surface. When the plane touches the earth at either the north or south poles latitude lines appear as concentric circles and longitude lines radiate from the pole at their true angle like the spokes on a wheel. This ...
Landslide Video Questions
... A conic projection that distorts scale and distance except along standard parallels. Areas are proportional and directions are true in limited areas. Used in the United States and other large countries with a larger east-west than north-south extent. ...
... A conic projection that distorts scale and distance except along standard parallels. Areas are proportional and directions are true in limited areas. Used in the United States and other large countries with a larger east-west than north-south extent. ...
IntroBasics
... The Global Grid of Latitude and Longitude lines essentially forms a giant coordinate plane on Earth. We use this plane to determine specific locations on our planet. Each location has a set of Coordinates. These coordinates are found by finding a locations numerical latitude and cardinal direction f ...
... The Global Grid of Latitude and Longitude lines essentially forms a giant coordinate plane on Earth. We use this plane to determine specific locations on our planet. Each location has a set of Coordinates. These coordinates are found by finding a locations numerical latitude and cardinal direction f ...
Unit 1 Test - Owl Teacher
... 3. The study of the Earth is called ________________________. 4. The unit of measure used to determine an absolute location on a map or a globe is a(n) ________. 5. A geographer who created a flat map in 1569 to help sailors navigate long journeys around the globe: ________________________. 6. A rep ...
... 3. The study of the Earth is called ________________________. 4. The unit of measure used to determine an absolute location on a map or a globe is a(n) ________. 5. A geographer who created a flat map in 1569 to help sailors navigate long journeys around the globe: ________________________. 6. A rep ...
Map Projections notes from PPT
... – Developed a grid system that became a forerunner for latitude and longitude ...
... – Developed a grid system that became a forerunner for latitude and longitude ...
Introduction to Geography
... maps will have some distortion. The scientific method of transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a flat map is called projection. ...
... maps will have some distortion. The scientific method of transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a flat map is called projection. ...
Flash Earth - GWA 6th Grade
... • As the earth rotates, the sun shines in different areas, moving from east to west (generally speaking) during the course of a ...
... • As the earth rotates, the sun shines in different areas, moving from east to west (generally speaking) during the course of a ...
Geography Quest Word Doc
... regions; describe physical and cultural characteristics; and locate states, capitals and major physical features of the United States. They will also explain the changing interaction of people with their environment in regions of the United States and show how the United States is related geographic ...
... regions; describe physical and cultural characteristics; and locate states, capitals and major physical features of the United States. They will also explain the changing interaction of people with their environment in regions of the United States and show how the United States is related geographic ...
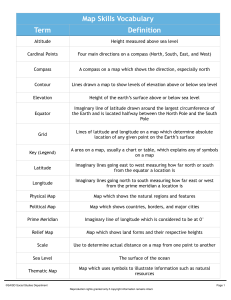
Map Skills Vocabulary Term Definition
... Lines drawn a map to show levels of elevation above or below sea level ...
... Lines drawn a map to show levels of elevation above or below sea level ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude