MATH 8 - Humble ISD
... continent, absolute location (latitude/longitude), relative location, plateau, valley, compass rose (cardinal and intermediate directions), scale, geography, greenhouse effect, physical geography, tropics, globe, Equator hemispheres, Prime Meridian, deserts, poles I know the cardinal and intermedi ...
... continent, absolute location (latitude/longitude), relative location, plateau, valley, compass rose (cardinal and intermediate directions), scale, geography, greenhouse effect, physical geography, tropics, globe, Equator hemispheres, Prime Meridian, deserts, poles I know the cardinal and intermedi ...
Unit #2: U
... 6. A ________ shows how much the distances have been reduced on a map. 7. A ___________ is a chart made up of parallel bars used to compare two or more items. 8. The _______ axis runs from bottom to top. ...
... 6. A ________ shows how much the distances have been reduced on a map. 7. A ___________ is a chart made up of parallel bars used to compare two or more items. 8. The _______ axis runs from bottom to top. ...
Map Reading Skills
... vertical lines on a map, he or she is creating a grid system to help with finding location In your book the horizontal lines are lettered and the vertical lines are numbered These are also called Latitude and Longitude which are labeled with numbers going east/west and north/south. ...
... vertical lines on a map, he or she is creating a grid system to help with finding location In your book the horizontal lines are lettered and the vertical lines are numbered These are also called Latitude and Longitude which are labeled with numbers going east/west and north/south. ...
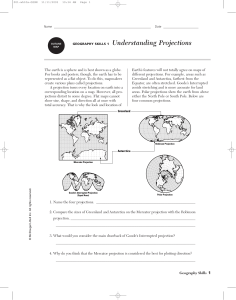
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections
... create various plans called projections. A projection turns every location on earth into a corresponding location on a map. However, all projections distort to some degree. Flat maps cannot show size, shape, and direction all at once with total accuracy. That is why the look and location of ...
... create various plans called projections. A projection turns every location on earth into a corresponding location on a map. However, all projections distort to some degree. Flat maps cannot show size, shape, and direction all at once with total accuracy. That is why the look and location of ...
GRAVITY II Surface Gravity Anomalies Due to Buried Bodies Simple
... structure of the lower crust (at say 20-40 km), gravity measurements must be made over an extensive area, as the width of the these anomalies is much larger than the width of upper crust anomalies. ...
... structure of the lower crust (at say 20-40 km), gravity measurements must be made over an extensive area, as the width of the these anomalies is much larger than the width of upper crust anomalies. ...
Geography
... 27. region – a group of places that share common features such as climate, land, population, history, language, or government ...
... 27. region – a group of places that share common features such as climate, land, population, history, language, or government ...
2A-Map_Projections_and_Scales.pps
... magnetic variation is a synonym, and is more often used in navigation. Isogonic lines are where the declination has the same value, and the lines where the declination is zero are called agonic lines. On most maps intended for wilderness or navigational use, including the topographic maps of the USG ...
... magnetic variation is a synonym, and is more often used in navigation. Isogonic lines are where the declination has the same value, and the lines where the declination is zero are called agonic lines. On most maps intended for wilderness or navigational use, including the topographic maps of the USG ...
GEOG - Unit 1
... • Geographers use latitude lines to locate places north and south • Latitude — imaginary lines that run parallel to the equator • Tropic of Cancer – 23.5* N, represents the furthest point the northern hemisphere tilts towards the sun • Tropic of Capricorn – 23.5* S, southern version ...
... • Geographers use latitude lines to locate places north and south • Latitude — imaginary lines that run parallel to the equator • Tropic of Cancer – 23.5* N, represents the furthest point the northern hemisphere tilts towards the sun • Tropic of Capricorn – 23.5* S, southern version ...
Sep12 - 5ThemesOfGeog - John Bowne High School
... • Ways that different things relate to each other at specific places. • Ways that places connect/interact with each other. ...
... • Ways that different things relate to each other at specific places. • Ways that places connect/interact with each other. ...
5 Themes of Geography Reference sheet
... to its latitude and longitude. Latitude lines measure distances north and south of the Equator. Longitude lines measure distances east and west of the Prime Meridian. A place's absolute location is defined with latitude and longitude lines. This is its exact location. The geography theme of location ...
... to its latitude and longitude. Latitude lines measure distances north and south of the Equator. Longitude lines measure distances east and west of the Prime Meridian. A place's absolute location is defined with latitude and longitude lines. This is its exact location. The geography theme of location ...
Unit One - smallworldbigthoughts-eub-geo
... • The prime meridian is located at the observatory in Greenwich, England at 0 degrees. The meridian at the opposite side of the globe is 180 degrees, and all meridians placed in between are designated as either “east” or “west” of the prime meridian. A parallel is a circle drawn around the globe pa ...
... • The prime meridian is located at the observatory in Greenwich, England at 0 degrees. The meridian at the opposite side of the globe is 180 degrees, and all meridians placed in between are designated as either “east” or “west” of the prime meridian. A parallel is a circle drawn around the globe pa ...
File
... study the use of space on earth. The most common one is a map. Maps are visual representations of a portion of the earth. Maps do not have to be written down to be useful. Since people began roaming the earth, they have created mental maps—maps that they carry in their minds. You use a mental map ev ...
... study the use of space on earth. The most common one is a map. Maps are visual representations of a portion of the earth. Maps do not have to be written down to be useful. Since people began roaming the earth, they have created mental maps—maps that they carry in their minds. You use a mental map ev ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... to be written down to be useful. Since people began roaming the earth, they have created mental maps—maps that they carry in their minds. You use a mental map every day as you go to and from school. The maps that you are probably most familiar with appear in printed form, such as in road atlases and ...
... to be written down to be useful. Since people began roaming the earth, they have created mental maps—maps that they carry in their minds. You use a mental map every day as you go to and from school. The maps that you are probably most familiar with appear in printed form, such as in road atlases and ...
1- The Five Themes of Geography
... equator. These lines are called latitude lines. The equator is designated as the zero-degree line for latitude. Lines north of the equator are called north latitude lines, and lines south of the equator are called south latitude lines. LONGITUDE LINES To complete the grid system, geographers use a s ...
... equator. These lines are called latitude lines. The equator is designated as the zero-degree line for latitude. Lines north of the equator are called north latitude lines, and lines south of the equator are called south latitude lines. LONGITUDE LINES To complete the grid system, geographers use a s ...
5 Themes of Geography
... The theme of LOCATION is the basis of our study of geography. LOCATION answers the question, "Where is it?" There are two different types of location that we will study: ABSOLUTE LOCATION RELATIVE LOCATION RELATIVE LOCATION: If you ask someone, "Where is Marshall Elementary School?" Chances are they ...
... The theme of LOCATION is the basis of our study of geography. LOCATION answers the question, "Where is it?" There are two different types of location that we will study: ABSOLUTE LOCATION RELATIVE LOCATION RELATIVE LOCATION: If you ask someone, "Where is Marshall Elementary School?" Chances are they ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... • This is called globalization! • When we are interdependent on each other for our economy, culture, politics, socialization, and technology. ...
... • This is called globalization! • When we are interdependent on each other for our economy, culture, politics, socialization, and technology. ...
Reading Maps - CoconinoHighSchool
... One-dimensional Mostly taken for granted (borders, roads) Contour connect same values Flow-line maps indicate value by width of line ...
... One-dimensional Mostly taken for granted (borders, roads) Contour connect same values Flow-line maps indicate value by width of line ...
unit 1: american geography
... LATITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance north and south from the Equator. LONGITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance east and west from the Prime Meridian. Latitude: Lines that run north (above) and south (below) of the equator. They go left to right on the map. ...
... LATITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance north and south from the Equator. LONGITUDE: Lines on a map that measure distance east and west from the Prime Meridian. Latitude: Lines that run north (above) and south (below) of the equator. They go left to right on the map. ...
document
... It is distorted greatly at the poles and is least distorted near the equator. (ex: Greenland is huge compared to South America) This projection is useful for ship navigation because the directions are accurate. ...
... It is distorted greatly at the poles and is least distorted near the equator. (ex: Greenland is huge compared to South America) This projection is useful for ship navigation because the directions are accurate. ...
Rubenstein Chapter 1.2 - Mounds View Public Schools
... -longitude is important in calculating time -every 15° is equivalent of traveling to a place 1 hour earlier or later (360° / 24 hours = 15°) Equator: 0° latitude -North Pole is 90° North latitude -South Pole is 90° South latitude -New York City is 41° North -Wellington, New Zealand is 41° South -San ...
... -longitude is important in calculating time -every 15° is equivalent of traveling to a place 1 hour earlier or later (360° / 24 hours = 15°) Equator: 0° latitude -North Pole is 90° North latitude -South Pole is 90° South latitude -New York City is 41° North -Wellington, New Zealand is 41° South -San ...
Geography Skills Handbook
... can be answered in many ways the basic tool for finding the answer is location. Lines on globes and maps provide information that can help you locate places. These lines cross one another, forming a pattern called a grid system. This system helps you find exact places on the Earth’s surface. ...
... can be answered in many ways the basic tool for finding the answer is location. Lines on globes and maps provide information that can help you locate places. These lines cross one another, forming a pattern called a grid system. This system helps you find exact places on the Earth’s surface. ...
EUROPEAN GEOGRAPHY - Glassboro Public Schools
... GLASSBORO, NJ Latitude= 39 º 42.2’ North Long = 75 º 6.7’ West ...
... GLASSBORO, NJ Latitude= 39 º 42.2’ North Long = 75 º 6.7’ West ...
sample
... 29. Lines of latitude are also known as meridians. Answer: FALSE [Pg. 4] 30. Lines of latitude are also known as parallels. Answer: TRUE [Pg. 4] 31. In a Robinson projection, the shapes of landmasses are slightly distorted. Answer: TRUE [Pg. 5] 32. A map is by definition an unbiased view of the worl ...
... 29. Lines of latitude are also known as meridians. Answer: FALSE [Pg. 4] 30. Lines of latitude are also known as parallels. Answer: TRUE [Pg. 4] 31. In a Robinson projection, the shapes of landmasses are slightly distorted. Answer: TRUE [Pg. 5] 32. A map is by definition an unbiased view of the worl ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude