File
... island. From the map (and the profile) we can see that this island has two "high" points. The highest point is above 30 ft elevation (inside the 30 ft contour line). The second high point is above 20 ft in elevation, but does not reach 30 ft. These high points are at the ends of a ridge that runs th ...
... island. From the map (and the profile) we can see that this island has two "high" points. The highest point is above 30 ft elevation (inside the 30 ft contour line). The second high point is above 20 ft in elevation, but does not reach 30 ft. These high points are at the ends of a ridge that runs th ...
Where in the Latitude Are You? A Longitude Here
... Tell the students they are now going to place the rest of the longitude and latitude lines on the globe. Students need to find the halfway point the Prime Meridian and the International Date Line. This will be the 90° lines. Be sure to keep the string in place and straight. Students can help one ano ...
... Tell the students they are now going to place the rest of the longitude and latitude lines on the globe. Students need to find the halfway point the Prime Meridian and the International Date Line. This will be the 90° lines. Be sure to keep the string in place and straight. Students can help one ano ...
Test Bank 1
... Persons traveling west across the International Date Line must ____. a. turn their calendar back one day b. turn their calendar ahead one day c. turn their watch 12 hours ahead d. turn their watch 12 hours back ...
... Persons traveling west across the International Date Line must ____. a. turn their calendar back one day b. turn their calendar ahead one day c. turn their watch 12 hours ahead d. turn their watch 12 hours back ...
Geography - Warren County Schools
... of geography we study in order to make connections to the world and how we interact with it: Location Place Movement Region Human-Environmental Interaction ...
... of geography we study in order to make connections to the world and how we interact with it: Location Place Movement Region Human-Environmental Interaction ...
Unit 1 – Geography, Its Nature and Perspectives Practice Questions
... C. Proportional symbol maps D. Isoline maps E. Cartograms Curves on a topographic map that are used to illustrate specific values of elevation above or below sea level are known as A. District lines B. Latitudinal lines C. Transmission lines D. Contour lines E. Longitudinal lines Which of the follow ...
... C. Proportional symbol maps D. Isoline maps E. Cartograms Curves on a topographic map that are used to illustrate specific values of elevation above or below sea level are known as A. District lines B. Latitudinal lines C. Transmission lines D. Contour lines E. Longitudinal lines Which of the follow ...
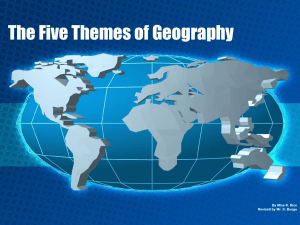
The Five Themes of Geography
... Region: • Regions are fundamental organizing units of geography. • Geographers use regions to give order to the earth’s surface. • We organize space into regions every day. Every time we refer to an area by saying: – “I’m going downtown” or “down South,” or “I’d like to live in that neighborhood,” ...
... Region: • Regions are fundamental organizing units of geography. • Geographers use regions to give order to the earth’s surface. • We organize space into regions every day. Every time we refer to an area by saying: – “I’m going downtown” or “down South,” or “I’d like to live in that neighborhood,” ...
The Attitude of Latitude - Arctic Climate Modeling Program
... to the south, much of the state’s climate is influenced by ocean currents. Coastal areas experience a moderating effect, with slightly warmer winter temperatures and slightly cooler summer temperatures when compared to inland areas of the same latitude. The ocean surface (the top 300 to 400 meters o ...
... to the south, much of the state’s climate is influenced by ocean currents. Coastal areas experience a moderating effect, with slightly warmer winter temperatures and slightly cooler summer temperatures when compared to inland areas of the same latitude. The ocean surface (the top 300 to 400 meters o ...
Jeopardy
... southern hemisphere and the eastern and western hemisphere. What are the Equator and Prime Meridian? ...
... southern hemisphere and the eastern and western hemisphere. What are the Equator and Prime Meridian? ...
Map projections
... ! central meridian and equator are straight lines ! scale is constant along any meridian ! central meridian mapped at true scale " slightly reduced scale (0.9996) in UTM system ...
... ! central meridian and equator are straight lines ! scale is constant along any meridian ! central meridian mapped at true scale " slightly reduced scale (0.9996) in UTM system ...
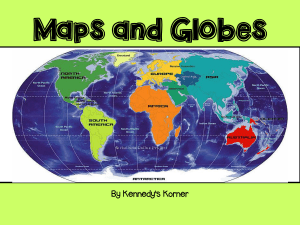
Maps and Globes - stmarys
... Continent- Any of the world's main continuous expanses of land (Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, South America). equator - An imaginary line drawn around the earth equally distant from both poles, dividing the earth into northern and southern hemispheres globe - a spherica ...
... Continent- Any of the world's main continuous expanses of land (Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, South America). equator - An imaginary line drawn around the earth equally distant from both poles, dividing the earth into northern and southern hemispheres globe - a spherica ...
SS 1st 9 weeks
... continents and oceans. *correlates with music 3.MU.9.1.1 re: singing music from around the world and identifying continent of origin. ...
... continents and oceans. *correlates with music 3.MU.9.1.1 re: singing music from around the world and identifying continent of origin. ...
AP Human Geography Notes
... Absolute Location • Absolute location describes a place using coordinates such as latitude and longitude • Notation – Latitude, Longitude – Degrees can be divided into minutes, and minutes can be divided into seconds • EX: Absolute Location of the United States Capitol Building – 38O 53 23 N, 77O 0 ...
... Absolute Location • Absolute location describes a place using coordinates such as latitude and longitude • Notation – Latitude, Longitude – Degrees can be divided into minutes, and minutes can be divided into seconds • EX: Absolute Location of the United States Capitol Building – 38O 53 23 N, 77O 0 ...
Equal Area World Maps: A Case Study
... The “dark side” of the earth is split in two with one piece shown on either side of the central circle. The mathematics involved in the construction below requires mainly high school algebra and trigonometry with only a bit of calculus (which can be plausibly avoided if one so desires). All of this ...
... The “dark side” of the earth is split in two with one piece shown on either side of the central circle. The mathematics involved in the construction below requires mainly high school algebra and trigonometry with only a bit of calculus (which can be plausibly avoided if one so desires). All of this ...
The Attitude of Latitude
... ocean – a continuous saltwater body; oceans cover about 72 percent of the surface of Earth; includes Atlantic, Pacific, Indian and Arctic Oceans region – a broad geographic area distinguished by similar features temperature – a measure of the average kinetic energy of atoms or molecules in a system; ...
... ocean – a continuous saltwater body; oceans cover about 72 percent of the surface of Earth; includes Atlantic, Pacific, Indian and Arctic Oceans region – a broad geographic area distinguished by similar features temperature – a measure of the average kinetic energy of atoms or molecules in a system; ...
Maps
... • Geographers study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. • Geographers look at many different things including cities, cultures, plants, climate, and resources. ...
... • Geographers study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. • Geographers look at many different things including cities, cultures, plants, climate, and resources. ...
Reading Maps
... • What is the purpose of a Physical map? • Physical maps show what the surface of the world ...
... • What is the purpose of a Physical map? • Physical maps show what the surface of the world ...
The 5 Themes of Geography - Effingham County Schools
... places by different names, but our world doesn’t know that! o Pennsylvania and New Jersey are not physically very different. We are part of the same “region” even though we are called by two different names. We have similar climates (weather) and similar types of land. We even share some important l ...
... places by different names, but our world doesn’t know that! o Pennsylvania and New Jersey are not physically very different. We are part of the same “region” even though we are called by two different names. We have similar climates (weather) and similar types of land. We even share some important l ...
BCS311 Module 1A
... scales, above, on, and beneath the Earth’s surface. In order to describe these phenomena, it is important to know where they occur in relation to the Earth’s surface: a coordinate grid system is needed. Earth scientists use a coordinate grid system consisting of parallels of latitude and meridians o ...
... scales, above, on, and beneath the Earth’s surface. In order to describe these phenomena, it is important to know where they occur in relation to the Earth’s surface: a coordinate grid system is needed. Earth scientists use a coordinate grid system consisting of parallels of latitude and meridians o ...
Chapter 1 (Let`s Talk Geography)
... to measure east and west. A common practice for cartographers—map makers—was to select their own nation’s capital city or a major port as 0° longitude. You can imagine how confusing this must have been. The problem was finally solved in 1884, at an international meeting in Washington, D.C. There an a ...
... to measure east and west. A common practice for cartographers—map makers—was to select their own nation’s capital city or a major port as 0° longitude. You can imagine how confusing this must have been. The problem was finally solved in 1884, at an international meeting in Washington, D.C. There an a ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... parts, or hemispheres. We divide our planet into North and South halves, OR into East and West halves. • Which 2 hemisphere’s do we live in? ...
... parts, or hemispheres. We divide our planet into North and South halves, OR into East and West halves. • Which 2 hemisphere’s do we live in? ...
Chapter 2
... Evaluate the advantages and limitations of different kinds of representations of Earth and its areas. Understand how the proper techniques, images, and maps can be used to best advantage in solving geographic problems. Recognize the benefits of spatial technologies such as geographic information sys ...
... Evaluate the advantages and limitations of different kinds of representations of Earth and its areas. Understand how the proper techniques, images, and maps can be used to best advantage in solving geographic problems. Recognize the benefits of spatial technologies such as geographic information sys ...
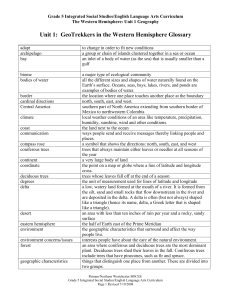
Unit 1: GeoTrekkers in the Western Hemisphere
... Earth’s surface. Oceans, seas, bays, lakes, rivers, and ponds are examples of bodies of water. the location where one place touches another place at the boundary north, south, east, and west. southern part of North America extending from southern border of Mexico to northwestern Colombia local weath ...
... Earth’s surface. Oceans, seas, bays, lakes, rivers, and ponds are examples of bodies of water. the location where one place touches another place at the boundary north, south, east, and west. southern part of North America extending from southern border of Mexico to northwestern Colombia local weath ...
Mapping Earth`s Surface
... 2. Write a proportion. Let d represent the distance between the two points. ...
... 2. Write a proportion. Let d represent the distance between the two points. ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude