Map Master Skills Handbook
... A Compass Rose shows you directions (North, South, East, and West) on a map or globe. ...
... A Compass Rose shows you directions (North, South, East, and West) on a map or globe. ...
EARLY EXPLORATION – Grade 4
... • 5. 1 The earliest explorations of the New World by the Vikings, the period and locations of their explorations, and the evidence for them. • 5.2, 5.4 The three major pre-Columbian civilizations that existed in Central and South America (Maya, Aztec and Inca) their locations and prominent features ...
... • 5. 1 The earliest explorations of the New World by the Vikings, the period and locations of their explorations, and the evidence for them. • 5.2, 5.4 The three major pre-Columbian civilizations that existed in Central and South America (Maya, Aztec and Inca) their locations and prominent features ...
Review Questions
... 2. The study of the earth, its features and people is called geography. 3. Location is the theme that answers the question of where we are. 4. There are two types of location—absolute location and relative location. 5. Absolute location is an exact street address or the exact coordinates in degrees ...
... 2. The study of the earth, its features and people is called geography. 3. Location is the theme that answers the question of where we are. 4. There are two types of location—absolute location and relative location. 5. Absolute location is an exact street address or the exact coordinates in degrees ...
Unit 1: Chapter 1 Section 1
... horizontally around the entire globe. The equator is the exact center of the earth’s latitude and divides the World into Northern and Southern Hemisphere. Theme of North/South Divide most Southern Hemisphere countries are poorer than the North. Longitude measures distance East and West. The Prime Me ...
... horizontally around the entire globe. The equator is the exact center of the earth’s latitude and divides the World into Northern and Southern Hemisphere. Theme of North/South Divide most Southern Hemisphere countries are poorer than the North. Longitude measures distance East and West. The Prime Me ...
ESSR_PNE_CoordntesSeasns_V01
... – All objects seem to be on the surface of this imaginary sphere – Earth’s poles extends and intersect with the celestial sphere as the North Celestial Pole and the South Celestial Pole – Earth’s equator extends and intersects with the celestial sphere as Celestial Equator – To locate an object, two ...
... – All objects seem to be on the surface of this imaginary sphere – Earth’s poles extends and intersect with the celestial sphere as the North Celestial Pole and the South Celestial Pole – Earth’s equator extends and intersects with the celestial sphere as Celestial Equator – To locate an object, two ...
physical geography lab exam 1 study guide
... Analyzing Geographic Data – interpret graphs, calculate rates of change, use a compass, draw isolines GIS and RS – use a computer desktop GIS/imagery to answer questions about an environment Mapping and Geographic Coordinates – make a map based on pace and bearing measurements, find the latitude and ...
... Analyzing Geographic Data – interpret graphs, calculate rates of change, use a compass, draw isolines GIS and RS – use a computer desktop GIS/imagery to answer questions about an environment Mapping and Geographic Coordinates – make a map based on pace and bearing measurements, find the latitude and ...
Projections & Coordinate Systems
... Increasingly distorted toward the polar regions. For example, in the Mercator projection, although Greenland is only one-eighth the size of South America, Greenland appears to be larger. Any straight line drawn on this projection represents an actual compass bearing. These true direction lines are r ...
... Increasingly distorted toward the polar regions. For example, in the Mercator projection, although Greenland is only one-eighth the size of South America, Greenland appears to be larger. Any straight line drawn on this projection represents an actual compass bearing. These true direction lines are r ...
Capital Connections - Indiana University Bloomington
... prime meridian (Greenwich meridian): 0°; standard meridian from which longitude is measured principle meridians: prime meridian and the International Date Line principle parallels: equator, the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N), the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S), the Artic Circle (66.5°N), and Antarctic Circ ...
... prime meridian (Greenwich meridian): 0°; standard meridian from which longitude is measured principle meridians: prime meridian and the International Date Line principle parallels: equator, the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N), the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S), the Artic Circle (66.5°N), and Antarctic Circ ...
100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300
... The kind of map that shows the way people have divided the earth into different governmental boundaries like countries, states, cities, etc. C 200 ...
... The kind of map that shows the way people have divided the earth into different governmental boundaries like countries, states, cities, etc. C 200 ...
region - slloyd
... b. the attributes of the setting c. the cultural landscape d. the natural landscape e. human geography 14. The acquisition of data about Earth’s surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or from another longdistance method is: a. GIS b. GPS c. Remote sensing d. USGS e. Topographic analysis 25. Ne ...
... b. the attributes of the setting c. the cultural landscape d. the natural landscape e. human geography 14. The acquisition of data about Earth’s surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or from another longdistance method is: a. GIS b. GPS c. Remote sensing d. USGS e. Topographic analysis 25. Ne ...
Geography Notes
... • Latitude- Lines that run parallel to the equator and measure the distance North and South from the equator • These lines are also called parallels because they run parallel with the Equator Think of latitude like the rungs of a ladder (ladder sounds a lot like latitude). Latitude lines run east a ...
... • Latitude- Lines that run parallel to the equator and measure the distance North and South from the equator • These lines are also called parallels because they run parallel with the Equator Think of latitude like the rungs of a ladder (ladder sounds a lot like latitude). Latitude lines run east a ...
Notes Unit 1 - novacentral.ca
... There are 3 main types of interactions, both positive and negative, that geographers study. They are: 1. Natures impact on people. 2. Peoples impact on nature. 3. Peoples impact on other people. 1 - Natures Impact on People Nature affects where people decide to settle. Climate, soil, food, water and ...
... There are 3 main types of interactions, both positive and negative, that geographers study. They are: 1. Natures impact on people. 2. Peoples impact on nature. 3. Peoples impact on other people. 1 - Natures Impact on People Nature affects where people decide to settle. Climate, soil, food, water and ...
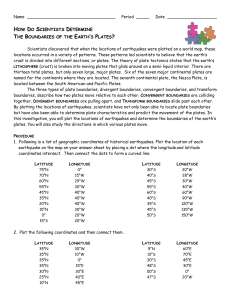
How do Scientists determine the boundaries of the plates?
... Scientists discovered that when the locations of earthquakes were plotted on a world map, these locations occurred in a variety of patterns. These patterns led scientists to believe that the earth’s crust is divided into different sections, or plates. The theory of plate tectonics states that the ea ...
... Scientists discovered that when the locations of earthquakes were plotted on a world map, these locations occurred in a variety of patterns. These patterns led scientists to believe that the earth’s crust is divided into different sections, or plates. The theory of plate tectonics states that the ea ...
Geography Handbook Notes
... The prime meridian is a longitude line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. It passes through Greenwich, England, and measures 0* longitude. Latitude Lines Imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe and are known as parallels. Show distance in degrees north or south of the eq ...
... The prime meridian is a longitude line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. It passes through Greenwich, England, and measures 0* longitude. Latitude Lines Imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe and are known as parallels. Show distance in degrees north or south of the eq ...
The 5 Themes of Geography
... 4. Movement How people, goods, information and ideas move from place to place. ...
... 4. Movement How people, goods, information and ideas move from place to place. ...
Chapter 1 Guided Notes Ans
... Where is it? - Absolute location—exact place where a geographic feature is found - Relative location—location of a place compared to places around it Absolute Location - Earth is divided into two equal halves, vertically and horizontally - Each vertical and horizontal half is called a hemisphere - A ...
... Where is it? - Absolute location—exact place where a geographic feature is found - Relative location—location of a place compared to places around it Absolute Location - Earth is divided into two equal halves, vertically and horizontally - Each vertical and horizontal half is called a hemisphere - A ...
What in the world is Geography anyway?
... In order to hold discussion, please do not talk over one another. Raise your hand, stand up, state your name and your contribution. What makes up geography? What importance does the land have on humans? Why do we need to study these elements of geography? ...
... In order to hold discussion, please do not talk over one another. Raise your hand, stand up, state your name and your contribution. What makes up geography? What importance does the land have on humans? Why do we need to study these elements of geography? ...
What is a Map?
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
... latitude and its longitude. • Who uses latitude and longitude “coordinates”? – Pilot – Captain of a Ship – GPS (Global Positioning System) ...
Geographer`s World
... where a place is found • Also known as site • Latitude – Lines that run parallel to the equator • Show distant north and south of the equator ...
... where a place is found • Also known as site • Latitude – Lines that run parallel to the equator • Show distant north and south of the equator ...
August XX, 2010 - Dublin City Schools
... • Antarctic Circle – 66.5* South of the Equator • begins South polar regions ...
... • Antarctic Circle – 66.5* South of the Equator • begins South polar regions ...
1.4 Understanding Geographic Terms for Water and
... • latitude and longitude – types of measurement that can pinpoint any spot on Earth • Latitude lines – run west to east (p.14) – Always have the same distance in between them. – Are measured starting at the equator. – Equator – 0 ° latitude – North Pole - 90° latitude – South Pole - 90° latitude ...
... • latitude and longitude – types of measurement that can pinpoint any spot on Earth • Latitude lines – run west to east (p.14) – Always have the same distance in between them. – Are measured starting at the equator. – Equator – 0 ° latitude – North Pole - 90° latitude – South Pole - 90° latitude ...
chapter 2 notes/study guide
... who live in a region. An _______________________ map shows how high the land is above sea level. The height of the ocean, or sea level is zero elevation. The highest point in North America is Mt. McKinley in Alaska. It ...
... who live in a region. An _______________________ map shows how high the land is above sea level. The height of the ocean, or sea level is zero elevation. The highest point in North America is Mt. McKinley in Alaska. It ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude