Lat and Long Slides
... east-west and north-south directions. ► Latitude – lines drawn in an east-west direction and measure distance north & south of the equator. ► Longitude – lines of longitude are drawn in a north-south direction and measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian. ► Equator – imaginary line that ...
... east-west and north-south directions. ► Latitude – lines drawn in an east-west direction and measure distance north & south of the equator. ► Longitude – lines of longitude are drawn in a north-south direction and measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian. ► Equator – imaginary line that ...
Themes of Geography
... 2 Types of Locations a) Absolute location … is the exact latitude and longitude coordinates of a place. Ex: 30o N, 115o E b) Relative location ...
... 2 Types of Locations a) Absolute location … is the exact latitude and longitude coordinates of a place. Ex: 30o N, 115o E b) Relative location ...
Living Things - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... the equator because the sun’s rays hit Earth’s surface more directly at the equator than at the poles. •The tropical zone is the area near the equator, between about 23.5° north latitude and 23.5° south latitude. • Polar zones extend from about 66.5° to 90° north and 66.5° to 90° south latitudes. •B ...
... the equator because the sun’s rays hit Earth’s surface more directly at the equator than at the poles. •The tropical zone is the area near the equator, between about 23.5° north latitude and 23.5° south latitude. • Polar zones extend from about 66.5° to 90° north and 66.5° to 90° south latitudes. •B ...
First Nine Weeks Review Guide
... 2. What device is used to determine orientation on a map? 3. What lands were not known to Europeans during the time of Columbus? 4. How do lines of longitude differ from lines of latitude? 5. Giving directions to another person to your house using roads and landmarks is an example of using what type ...
... 2. What device is used to determine orientation on a map? 3. What lands were not known to Europeans during the time of Columbus? 4. How do lines of longitude differ from lines of latitude? 5. Giving directions to another person to your house using roads and landmarks is an example of using what type ...
Science / Chapter 2 - Serra Catholic Elementary School
... LOCATING POINTS ON EARTH’S SURFACE • Lines of LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE form a grid that can be used to find locations anywhere on Earth. Video: BrainPop http://www.brainpop.com/socialstudies/geography/latitudeandlongitude/ ...
... LOCATING POINTS ON EARTH’S SURFACE • Lines of LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE form a grid that can be used to find locations anywhere on Earth. Video: BrainPop http://www.brainpop.com/socialstudies/geography/latitudeandlongitude/ ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... How do Geographers use the five themes of Geography to analyze a specific area? How do you use longitude and latitude lines to find absolute location? ...
... How do Geographers use the five themes of Geography to analyze a specific area? How do you use longitude and latitude lines to find absolute location? ...
Geography
... 1 being not helpful at all (where is Penncrest!?) 5 being helpful but not helpful enough (I might recognize it if I passed it, but I’d have difficulty finding it). ...
... 1 being not helpful at all (where is Penncrest!?) 5 being helpful but not helpful enough (I might recognize it if I passed it, but I’d have difficulty finding it). ...
Graph
... • Combining Longitude and Latitude allow people to identify exact locations of places on the earth (absolute location) • (DON’T COPY below) Example: Denver is found at 39 degrees North Latitude and 104 degrees West Longitude ...
... • Combining Longitude and Latitude allow people to identify exact locations of places on the earth (absolute location) • (DON’T COPY below) Example: Denver is found at 39 degrees North Latitude and 104 degrees West Longitude ...
File
... rainfall. The three major climate zones on the Earth are the polar, temperate, and tropical zones. ...
... rainfall. The three major climate zones on the Earth are the polar, temperate, and tropical zones. ...
Document
... ____8. Building irrigation canals along the Nile River is an example of A. adapting to the environment. B. a push factor C. modifying the environment. ...
... ____8. Building irrigation canals along the Nile River is an example of A. adapting to the environment. B. a push factor C. modifying the environment. ...
Geography - Foxfire Schools
... Longitude Longitude Lines are imaginary lines that break the Earth into distance measurements from the Prime Meridian. i.e. – lines parallel to the Prime Meridian running North and South 180 degrees ...
... Longitude Longitude Lines are imaginary lines that break the Earth into distance measurements from the Prime Meridian. i.e. – lines parallel to the Prime Meridian running North and South 180 degrees ...
5 Themes of Geography Five Themes of
... Latitude and Longitude lines of latitude: run parallel to the equator and measure distance north and south of the EQUATOR lines of longitude: connect the north and south poles and measure distance east and west of the PRIME MERIDIAN ...
... Latitude and Longitude lines of latitude: run parallel to the equator and measure distance north and south of the EQUATOR lines of longitude: connect the north and south poles and measure distance east and west of the PRIME MERIDIAN ...
File
... actual feature on Earth’s surface The three main types of scales are ratio (fraction) scales, bar scales, and written scales Small Scale: Depicts a large area (such as the state of Arizona) but with less detail ...
... actual feature on Earth’s surface The three main types of scales are ratio (fraction) scales, bar scales, and written scales Small Scale: Depicts a large area (such as the state of Arizona) but with less detail ...
Unit I Studyguide
... Answer the following Questions 1. Green Bay, Wisconsin, is located at an imaginary line running north south on the globe. What does this line represent? 2. What would be a project for a cartographer? 3. Roanoke, Virginia, is located about 40 miles from Lynchburg. What does this describe? 4. How can ...
... Answer the following Questions 1. Green Bay, Wisconsin, is located at an imaginary line running north south on the globe. What does this line represent? 2. What would be a project for a cartographer? 3. Roanoke, Virginia, is located about 40 miles from Lynchburg. What does this describe? 4. How can ...
Lecture 05: Mountain Climates
... In equatorial regions, day length & solar angle change little with season. Little seasonal variability, mostly diurnal changes. ...
... In equatorial regions, day length & solar angle change little with season. Little seasonal variability, mostly diurnal changes. ...
Geography Unit One
... These gases are released from industry, automobiles, and homes. Too much Carbon Dioxide traps radiation from the sun inside the earth’s atmosphere causing the earth to become warmer. ...
... These gases are released from industry, automobiles, and homes. Too much Carbon Dioxide traps radiation from the sun inside the earth’s atmosphere causing the earth to become warmer. ...
“Take Five”
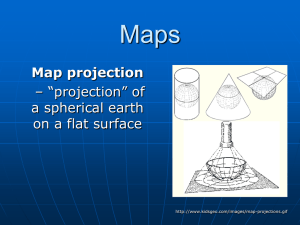
... Planar projections or azimuthal—gives the shortest distance between 2 points Conical projections—projections onto a cone shape—used to show landmasses that extend over large areas going east and west Cylindrical projections or Mercator—projections onto a cylinder that shows the whole earth ...
... Planar projections or azimuthal—gives the shortest distance between 2 points Conical projections—projections onto a cone shape—used to show landmasses that extend over large areas going east and west Cylindrical projections or Mercator—projections onto a cylinder that shows the whole earth ...
Maps - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... Equator—The line which encircles the Earth at an equal distance from the North and South Poles. Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circ ...
... Equator—The line which encircles the Earth at an equal distance from the North and South Poles. Meridian—any line of longitude; A great circle on the surface of the Earth, passing through the geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circ ...
Key Terms/People Overview - DC Everest Website has moved!
... Isoline- a map line that connects points of equal/similar values. Time space convergence – As communication increases efficiency the distance between two places is effectively diminished. Gravity Model – Formula based on population and distance and how it effects interaction between two places. Geoi ...
... Isoline- a map line that connects points of equal/similar values. Time space convergence – As communication increases efficiency the distance between two places is effectively diminished. Gravity Model – Formula based on population and distance and how it effects interaction between two places. Geoi ...
North Carolina - River Mill Academy
... • Where a place is in relation to another place • Uses directional words to describe – Cardinal and ...
... • Where a place is in relation to another place • Uses directional words to describe – Cardinal and ...
Name - JacksonLeith
... Location & Types of Maps Quiz I. Matching. Match each term with the correct definition. Write your answer in the answer column in capital letters (1 pt. each). Answer ...
... Location & Types of Maps Quiz I. Matching. Match each term with the correct definition. Write your answer in the answer column in capital letters (1 pt. each). Answer ...
Latitude
In geography, latitude (φ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle (defined below) which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° (North or South) at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definition of these coordinates. In the first step the physical surface is modelled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oceans and its continuation under the land masses. The second step is to approximate the geoid by a mathematically simpler reference surface. The simplest choice for the reference surface is a sphere, but the geoid is more accurately modelled by an ellipsoid. The definitions of latitude and longitude on such reference surfaces are detailed in the following sections. Lines of constant latitude and longitude together constitute a graticule on the reference surface. The latitude of a point on the actual surface is that of the corresponding point on the reference surface, the correspondence being along the normal to the reference surface which passes through the point on the physical surface. Latitude and longitude together with some specification of height constitute a geographic coordinate system as defined in the specification of the ISO 19111 standard.Since there are many different reference ellipsoids the latitude of a feature on the surface is not unique: this is stressed in the ISO standard which states that ""without the full specification of the coordinate reference system, coordinates (that is latitude and longitude) are ambiguous at best and meaningless at worst"". This is of great importance in accurate applications, such as GPS, but in common usage, where high accuracy is not required, the reference ellipsoid is not usually stated.In English texts the latitude angle, defined below, is usually denoted by the Greek lower-case letter phi (φ or ɸ). It is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds or decimal degrees, north or south of the equator. Measurement of latitude requires an understanding of the gravitational field of the Earth, either for setting up theodolites or for determination of GPS satellite orbits. The study of the figure of the Earth together with its gravitational field is the science of geodesy. These topics are not discussed in this article. (See for example the textbooks by Torge and Hofmann-Wellenhof and Moritz.)This article relates to coordinate systems for the Earth: it may be extended to cover the Moon, planets and other celestial objects by a simple change of nomenclature.The following lists are available: List of cities by latitude List of countries by latitude