* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Graph
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
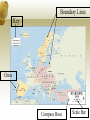
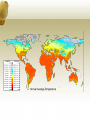
Introduction to Geography I am a Geographer Journal 1. How do you use geography every single day at home &/or school? Be specific and explain! 2. What tools do you use when you study geography? Be specific and explain! **Remember to put a DATE, TITLE, and PAGE NUMBER for all journal entries. ALWAYS update your table of contents. INTRO TO GEO NOTES • Geography is a description of the earth and the things on it…. • Physical • Human TOOLS OF GEO: • Direct Observation – visiting a region, aerial photos & satellite • Mapping / Cartography – study & making maps • Statistics - math • Technology • Graphic information systems (GIS) • Definition: computer systems that store and analyze geographic data • Global Positioning system (GPS) • Definition: a system that uses satellites and receivers to determine absolute location FIVE THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY • The earth is HUGE! So geographers divide this description into groups called the Five Themes of Geography 1. Location • Where is it? 1. Absolute Location: exactly where something is. • Ex: address, latitude and longitude 2. Relative Location: about where something is? Southwest, Converse 2. Place • What is it like there? • Physical Characteristics • Human Characteristics 3. Region • Areas united by similar features • How are areas similar and different? • Ex: climate, Latin America • Can be uniform or functional 3. Formal and Functional and Perceptual Regions Formal • There are three types of regions: • Formal: clear boundaries, defined by human or physical characteristic • Functional **ex: common government, Rocky Mountains • Functional- area defined by one function that can cross political boundaries; area organized around focal point ** ex: highway systems, river drainage basin • Perceptual: based on people’s attitudes and emotions about a place (may not be based on fact) ** ex: “Deep South” or “The Big Apple” (New York City) 4. Movement -IDEAS -PEOPLE -GOODS • How are people and places connected? • How do people shape the earth? • What are reasons for movement? 5. Human Environment Interaction • How does the environment affect Humans? • How do we humans impact the environment? FIVE THEMES PRACTICE • The White House is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue. • The I-35 Corridor is a major area of trade, travel, and commuting. • If you go to Antarctica, you’d better bring a coat! • San Antonio’s Riverwalk, the Alamo, and the Hemisphere tower are well known landmarks. • The Japanese tsunami caused a nuclear meltdown that made thousands evacuate the area. • When I think of the “West” I usually think of everything west of the Rockies. • In many of the countries colonized by Spain, they speak Spanish and practice Catholicism. • The Gulf states share the same coastline. • I live in Converse which is next to Randolph Air force Base. EXIT DISCUSSION: “L” • List AT LEAST THREE different things you learned today about Geography that you did not know before in the L of your KWL charts from DAY TWO. • IF YOU WERE NOT HERE: Just tell me three things you learned about geography. Why is Geography important? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lj3iNxZ8Dww Meridian (Longitude) • Lines that run north and south or vertical • 0 degrees called Prime Meridian • Goes through Greenwich, England • Opposite end called “International Date Line” and found at 180 degrees • Time is measured using meridians • Every 15 degrees (east or west) equals one hour of time Parallels (Latitude) • Imaginary lines that run west to east or horizontal • 0 degrees latitude called equator • Two other major parallels are the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn Grid • Combining Longitude and Latitude allow people to identify exact locations of places on the earth (absolute location) • (DON’T COPY below) Example: Denver is found at 39 degrees North Latitude and 104 degrees West Longitude Longitude and Time • 24 time zones were created by dividing 15 degrees (1 hour) into the total amount of Degrees in latitude (360) • The time at 0 degrees longitude is known as Greenwich Mean Time or Universal Time • When crossing the International Date Line you must either move your clock forward by 24 hours (heading west) or set your clock by 24 hours (heading east) What is a map? • A generalized view of an area, usually some portion of Earth’s surface, as seen from above at a greatly reduced size What is a Globe? • a 3-D representation of the earth Why make maps and not use globes? Represent a larger area Shows what we cannot see How do we read maps? • Size of the map relative to reality (scale) • What’s on the map (symbolization) • Shape of the map (projection) • Direction of a map (compass) • What the map is about (title) Map Scale Map Scale• Ratio of the distance on the map to the distance on the ground Large Scale Small Scale Reading a Map • Key: explains what the symbols stand for • Compass Rose: marker that indicates directions • Scale Bar: shows the relationship between map measurements and actual distances Boundary Lines Key Cities Compass Rose Scale Bar A map projection is the shape of a map and has distortions (mistakes). Conic Projection: Distances and directions are fairly accurately. This projection is best for showing limited eastwest areas that are not too far from the Equator. Pseudo cylindrical • Pseudocylindrical projections represent the central meridian (verical lines of longitude) and each parallel (horizontal lines of latitude) as a single straight line segment, but not the other meridians. • A sinusoidal projection shows relative sizes accurately, but grossly distorts shapes. Distortion can be reduced by "interrupting" the map. Mercator Projection Projection distorts size and distance as it moves away from the Equator. These projections do accurately show true directions & shapes of landmasses, making these maps useful for sea travel. Robinson Projection Projection has minor distortions; the size & shapes near the eastern and western edges of the map are accurate. Polar areas appear somewhat distorted. Main map used in your text book Types of Maps • Thematic maps: show a particular theme or topic. • Geographers can use these maps to illustrate various features of Earth’s surface. • Such features include: • Landforms: mountains, hills, plains and plateaus • Climate: long term weather patterns or rainfall • Natural Vegetation: plant life that grows in a certain area if people have not change the natural environment • Resources of an area Special Purpose Maps emphasize a single idea or particular kind of information about an area. The colors and symbols represent the location or distribution of activities / resources. Physical Maps show the location and the topography (shape) of earth’s physical features. Usage of different colors or patterns indicate relief. Political Maps show the boundaries between countries. These maps often show human-made features such as capitals, cities, roads and railroads. What are some visual ways to look at Data? • Graphs, Charts, and Tables • Graph: a visual presentation of information • Charts and Tables: facts displayed in a way that makes comparisons easy • Diagram: a drawing Graphs • Visual presentation of information • Generally consists of two axis in order to compare data • 4 basic types of Graphs • • • • Line Bar Circle Pictograph Line Graph • Change of two sets of variables over time • Allows for the study of trends and changes Bar Graph • Shows comparisons • Generally shows differences in quantities Circle Graph/Pie Graph • Shows relationship of parts to the whole • Percentages are indicated by size (Sometimes color) Pictograph • Similar to a bar graph • Uses pictures to represent a subject Charts and Tables • Data arranged in columns or rows • Facts displayed in an organized manner Diagram • Drawing • Shows what something is • How something is done 5 Themes Review: MR H/ELP • Converse, TX is next to Randolph Air Force Base. • My publishing company ships textbooks all over the world. • Southwest Airlines has interconnected travel routes all over the U.S. • India is a tropical place with beautiful architecture. • The river area needed electricity so we built a dam to generate power. • NAFTA is a trade alliance that links Canada, the U.S., and Mexico. Map Projections Journal 1. Using your notes, explain what a map projection is and why they sometimes are not accurate. 2. Also using your notes, explain which one of the map projections you would use for a road trip across the United States and why.