* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Themes of Geography
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
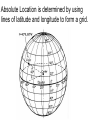
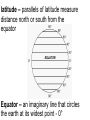
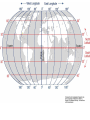
Chapter 1 – Section 1 Geography The study of the earth’s surface and the processes that shape it. Physical Geography: The study of the natural “physical” environment. Cultural “Human” Geography: The study of human characteristics and cultures around the world Five Themes of Geography 1. Location: Where is the place? 2. Place: What is the place like? 4. Region: How is a place similar/different to other places? 5. Human Interaction: How have people changed a place? 3. Movement: How do people, goods, & ideas move in a place? LOCATION 1. Absolute Location – Where a place is located on the earth 2. Relative Location – Where a place is located in relation to another place Grid System A system that uses lines of latitude and longitude to locate places. Absolute Location is determined by using lines of latitude and longitude to form a grid. latitude – parallels of latitude measure distance north or south from the equator Equator – an imaginary line that circles the earth at its widest point - 0° longitude – meridians measure distance east or west from the Prime Meridian. Prime Meridian – line of longitude that runs through Greenwich, England - 0° Hemisphere - ½ of the earth’s surface The relative location of Lyford is about 15 miles north of Harlingen Place What is a place like? This includes physical features and cultural characteristics culture – Every part of the way people live. Regions Formal Regions – Defined by a limited number of related characteristics. Example: Europe, Africa Functional Regions – Based on a set of interactions or connections between places. Example: A city and its suburbs Perceptual Regions – A region that people perceive. May not be the same to everyone. Example: The Midwest Culture Regions Areas connected by similar cultural characteristics and patterns. Human–Environment Interaction The relationship between people and their environment Movement How people, goods, and ideas move from one location to another.