* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography Notes
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
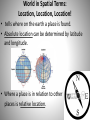
The Six Elements of Geography ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS • How do physical and human geography affect people, places and regions? • How do the movements of people and ideas (cultural diffusion) affect world history? What is Geography? • The study of people, their environment, and the resources available to them. • The scientific study of Earth and its place in the universe (i.e., the distribution of people, animals, plants, resources, and industry around the world). • The bridge between the human and the natural sciences. • Anything that can be mapped. Why Study Geography? • It enables humans to understand where they are, literally and figuratively. • Provides a basis for humans to cooperate in the best interest of our planet. • People are better able to solve issues at both local and global levels. Geography is documented on maps and globes. • The various map projections show the earth in various ways. • Special purpose maps show a variety of information, such as climate, borders, population or topography. • Culture has historically influenced how maps are made. 6 Elements of Geography World in Spatial Terms: Location, Location, Location! • tells where on the earth a place is found. • Absolute location can be determined by latitude and longitude. • Where a place is in relation to other places is relative location. Places and Regions • Refers to the characteristics of any location that gives meaning to the place and distinguishes it from other places. Its PERSONALITY! • Language • Government • Land Marks • Food • Music etc. Physical Systems • They shape the world as we see it. • Physical characteristics include the natural elements of any location (i.e., soil type, animal life, landforms). – Ecosystems and how they work – Earth-Sun Relationships – Consequences of physical processes on the Earth. Human Systems • Describe patterns of migration and explain effects it may have on places • Why do people live where they live? • Language, architecture, communication, transportation, populations • Economic Activities • Geographic causes for world trade • Identifies conflict within and between countries Environment and Society • Looks at all the effects, positive and negative, that occur when people interact with their surroundings. • How do human actions modify the physical environment? • How are human activities influenced by the environment? Uses of Geography • How to apply Geography to interpret the past and present, as well as plan for the future! • The events of history take place within geographic contexts. • Those events are motivated by people’s perceptions, correct or otherwise, of geographic contexts. • By exploring what the world was like and how it is perceived at a given time, the geographically informed person is able to interpret major historical issues. Additional Vocabulary • Movement – refers to how people interact with other people, places and things. How people and places are linked to each other. • Regions – an area on the earth’s surface that is defined by certain unifying characteristics. • Used to identify and organize areas of the Earth’s surface for various purposes. • Characteristics may be physical, human or cultural. • Latitude- Lines that run parallel to the equator and measure the distance North and South from the equator • These lines are also called parallels because they run parallel with the Equator Think of latitude like the rungs of a ladder (ladder sounds a lot like latitude). Latitude lines run east and west, but they tell how far up (north) you can go or how far down (south) you can go. • Longitude- Lines that run North and South and measure the distance East and West of the Prime Meridian • These lines are also called meridians because they run parallel with the Equator When you think of longitude, think of long, tall telephone poles (because longitude lines run from pole to pole). Longitude lines run north and south, but they tell how far east you can go or how far west you can go • Hemisphere-The Northern or Southern half of the Earth divided by the Equator, or the Eastern or Western half as divided by a meridian Maps • Physical or Relief Map-these maps illustrate the natural landscape of landforms that mark the Earth’s surface. (Mountains, Hills, Valleys, elevation or height above sea level) • Political Maps- Illustrate political units such as states, nations and use of color variations and lines to mark boundaries, dots for major cities and stars within circles for a Capital. These maps show territorial changes or military alliances. • Climate Feature Maps- Illustrate how climates govern human progress and help to explain why things have happened in the region throughout history due to climate. • Population Distribution Map- Illustrate distributions of populations. • Thematic Maps- These maps show hemispheres, climates, landforms, settlement patterns, empires, war strategies, and invasion and migration routes. These are the maps found in your Global History Book!