* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Themes of Geography
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
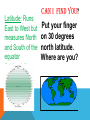
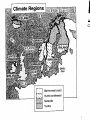
DEFINITION OF GEOGRAPHY ge·og·ra·phy 1 : a science that deals with the description, distribution, and interaction of the diverse physical, biological, and cultural features of the earth's surface In Plain English: Geography is the study of the earth and everything on it. WHERE DID THE 5 THEMES COME FROM? The 5 Themes of Geography originated by the National Geographic Society to fulfill a need for geographers (people who study the earth and everything on it) categorize Humaneverything they learn. Location Place Region Movement Environment Interaction LOCATION – ABSOLUTE WHERE IS IT???? Absolute Location –describes an exact place on earth. It requires latitude and longitude coordinates. -It can give you a global location (using latitude and longitude) or a local location (street address). -longitude, latitude, continent, hemispheres, continent, country, or state Example: Springs School Address – 48 School Street East Hampton NY 11937 LOCATION – RELATIVE LOCATION WHAT IS AROUND YOU? Relative Location: describes the position of a place in relation to another place. -The position can be described using landmarks, directions, time or distance from one place to another What countries are neighbors of the country? Example: Canada is north of America Example: giving directions to your house Continent – one of the seven large land masses in the world ITEMS YOU NEED TO KNOW TO FIND A LOCATION Prime Meridian – An imaginary line of longitude running from the north pole to the south pole. It divides the globe into eastern and western hemispheres Hemisphere – One of the two shapes made by cutting a sphere in half Look at p. 10. Label if the cities/countries are in the eastern or western Hemisphere Latitude: Runs East to West but measures North and South of the equator (horizontal) CAN I FIND YOU? Put your finger on 30 degrees north latitude. Where are you? ARE YOU IN. . . YOU NEED TO ADD LONGITUDE Longitude: Runs North and South but runs East and West of prime meridian (vertical) Where are you if you are on 30 degrees north latitude and 120 east longitude? YOU NEED TO PUT LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE TOGETHER. . . Where are you if you are on 30 degrees north latitude and 60 east longitude? NOW LET’S PUT LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE TOGETHER. . . Where are you if you are on 30 degrees north latitude 135 degrees west longitude? LABEL: PRIME MERIDIAN AND EQUATOR PLACE NATURAL AND HUMAN FEATURES THAT MAKE ONE PLACE DIFFERENT FROM EVERY OTHER - Landforms, climate, plants, animals, people, language, or culture Describe the place (size, shape). What is the climate (temperature, rainfall)? What kinds of physical features are there (mountains, rivers, deserts)? Describe the people who live there (nationalities, traditions, etc.) Human Features: culture, food, religion, clothing, ethnicity, customs HUMAN-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTIONS RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PEOPLE AND THE ENVIRONMENT - Effects how people live, work, travel, dress, and communicate How do people use the land (farming, herding, mining, industry)? How have people changed the land? Where do most people live (near a river or coastline, in the mountains)? Why do you think people settled there (water, safety, food, natural beauty)? HUMAN-ENVIRONMENT INTERACTIONS Environment – everything that surrounds us -- Climate -- Air we breath -- Water we drink Natural resources – Items a country posses that help it function -Oil -Water -Forests -Minerals Conserve/Conservation – to save or to preserve something such as fuel, natural resources (trees/water) LISTEN THE BOOK: THE LORAX Listen for examples of Human Environment Interaction MOVEMENT “HOW DO PEOPLE, GOODS, AND IDEA MOVE FROM PLACE TO PLACE?” - What happens in one place affects what happened in another How will you travel to the place (route, drive, fly, walk)? Does the country export goods to other places? If so, what and where? Does the country import goods from other places? If so, what and from where? Why would people leave or move to the country (jobs, family, climate, war)? MOVEMENT 2.0 REGIONS AN AREA OF LAND AND DESCRIBED BY THE FEATURES THAT MAKE IT UNIQUE -Share at least one common feature --Country, state, cities, political regions -What are the political divisions of the country (states, provinces, republics)? -How is the country similar to any of its neighbors (traditions, language, climate)? -What language(s) do people speak? REGIONS Physical Characteristics The features of a place that Climate – The weather help us recognize and describe conditions of an area, including winds, temperature, it. They may include mountains, valleys, plains, forests, deserts, and precipitation or bodies of water HOW DO I READ A MAP? -Locate and read the title Locate and read the key -Identify the symbols -Make sure you are “going” in the right direction -Find the compass rose and read it clockwise -Remember Never Eat Sour Watermelons TYPES OF MAPS Political Maps--Show man made features such as boundaries, cities, capitals TYPES OF MAPS Physical Maps Shows elevation and physical features such as mountains, lakes, and rivers TYPES OF MAPS Climate Maps: gives general information about the climate & precipitation of region. TYPES OF MAPS Linguistic/language Map: Shows the geographic distribution of a language, or a dialect. TYPES OF MAPS Road Map: A map, especially one for motorists, showing and designating the roads of a region. WHAT MAP SHOULD I USE????? Which map would you use if I: Want to find out the height of a certain mountain? Wanted to move to a place that had mild winters, what kind of map would help you to decide? Want to figure out which state has the hottest summers, Arizona or North Carolina? Wanted to figure out which states made up the New England colonies? Wanted to figure out which map would help you find the land height above sea level of a certain area? Wanted to plan a hiking trip, which map do I want to use? Wanted to make sure I can communicate with the native people, which map do I use? Wanted to locate the boundaries and capital city of Michigan? Wanted to figure out which interstate highway runs north and south through Mississippi?