* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Geography Study Guide
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Major explorations after the Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
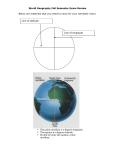
# Social Studies Study Guide Chapter 1: Introduction to Geography Name______________________ Date ______________________ 1. Define Geography: The study of the Earth and people and their interactions 2. Define the five themes of geography A. Location- Where something is on Earth B. Place- the location of something C. Regions-areas on Earth with features that make them different from other areas D. Movement- how ideas and products get from place to place…. Television, radio, computers, telephones, and transportation E. Human-Environment Interactions-how humans affect the environment Such as litter, air pollution and how the environment affects humans Such as climate, hurricanes, tornadoes 3. Name the 5 regions of the United States: A. Northeast B. Southeast C. West D. Mid west E. Southwest 4. Physical Features: give 2 examples natural resources or landforms found in a place: mountains, rivers, forest 5. Human Features: give 2 examples features built by humans, such as Buildings, roads, farms, bridges 6. Define Culture: people ways of life 7. Define Heritage: a culture that comes from the past and continues today Page 2 8. Give an example of a Primary Source: records made by people who took part or saw an event: diaries, photographs, artifacts 9. Give an example of a Secondary Source: a record of an event by someone who was not at an event at the time it happened *****Map Skills***** Define the following terms: 1. Absolute Location: the exact location on Earth….the use of longitude and latitude lines 2. Relative Location: the location of something in relation to some other place 3. Map Scale: compares the distance on a map to the distance of the real world 4. Inset Map: a smaller map inside a larger map 5. Locator: a picture of a globe which shows where the main map is located within the state, country, or continent 6. Map Key: explains what the symbols are the map stand for 7 Grid System: pattern of squares formed by the lines of latitude and longitude 8. Lines of Latitude: the east and west lines on a map called parallels 9 Lines of Longitude: North and south lines on a map called Meridians 10. Equator: the parallel marked 0 degrees divides the northern and southern hemispheres 11. Prime Meridian: the meridian marked 0 degrees divides the western and eastern hemispheres # Social Studies Study Guide Chapter 1: Introduction to Geography Page 3 Name______________________ Date ______________________ Label and Name each continent and ocean. Name the two main lines on the map 1. North America 8. Pacific Ocean 2. South America 9. Atlantic Ocean 3. Africa 10. Indian Ocean 4. Europe 11. Arctic Ocean 5. Asia 12. Prime Meridian 6. Australia 13. Equator 7. Antarctica