Asperger`s Syndrome
... – A discrete period of intense fear or discomfort in which the following symptoms may develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes ...
... – A discrete period of intense fear or discomfort in which the following symptoms may develop abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes ...
Risk Factors in the Individual
... – information about degree of self-worth – same sources may both increase and lower sense of self-worth ...
... – information about degree of self-worth – same sources may both increase and lower sense of self-worth ...
Reactive Attachment Disorder
... In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual IV-TR (DSM IV-TR, 2000) Reactive Attachment Disorder is defined as a condition of “markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate social relatedness in most contexts; symptoms begin before age 5 years and are associated with grossly pathological care” ( ...
... In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual IV-TR (DSM IV-TR, 2000) Reactive Attachment Disorder is defined as a condition of “markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate social relatedness in most contexts; symptoms begin before age 5 years and are associated with grossly pathological care” ( ...
Clinical Guidelines Series, 2009: Reactive Attachment Disorder March 16, 2009
... In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual IV-TR (DSM IV-TR, 2000) Reactive Attachment Disorder is defined as a condition of “markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate social relatedness in most contexts; symptoms begin before age 5 years and are associated with grossly pathological care” ( ...
... In the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual IV-TR (DSM IV-TR, 2000) Reactive Attachment Disorder is defined as a condition of “markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate social relatedness in most contexts; symptoms begin before age 5 years and are associated with grossly pathological care” ( ...
Psych Disorders Review Sheet
... men outnumbering women five to one); and mood disorder (with women outnumbering men two to one). Poverty is a predictor of mental illness but it can also be the result of mental illness due to inability to function effectively in society and thus being driven into poverty. ...
... men outnumbering women five to one); and mood disorder (with women outnumbering men two to one). Poverty is a predictor of mental illness but it can also be the result of mental illness due to inability to function effectively in society and thus being driven into poverty. ...
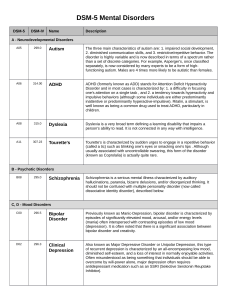
DSM V Mental Disorders
... detachment from oneself combined with an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from a third person perspective. However, unlike in psychosis, the indivi ...
... detachment from oneself combined with an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from a third person perspective. However, unlike in psychosis, the indivi ...
Mood Disorders
... Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) an anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to a terrifying event or ordeal in which grave physical harm occurred or was threatened Traumatic events that may trigger PTSD include violent personal assaults, natural or humancaused disasters, accidents, or ...
... Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) an anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to a terrifying event or ordeal in which grave physical harm occurred or was threatened Traumatic events that may trigger PTSD include violent personal assaults, natural or humancaused disasters, accidents, or ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... have a stable and rewarding relationships based on the internalization (a process closely related to introjection as described above) of the early childhood representations of others in the form of “objects.” However, internalization of these objects is not a mere imitation. Filtered by the child’s ...
... have a stable and rewarding relationships based on the internalization (a process closely related to introjection as described above) of the early childhood representations of others in the form of “objects.” However, internalization of these objects is not a mere imitation. Filtered by the child’s ...
Disruptive, Impulse-Control and Conduct Disorders
... Other Specified Disruptive, ImpulseControl, and Conduct Disorder This category applies to presentations in which symptoms characteristic of a disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorder that cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas ...
... Other Specified Disruptive, ImpulseControl, and Conduct Disorder This category applies to presentations in which symptoms characteristic of a disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorder that cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas ...
Psychological Disorders
... If depression is the common cold of psychological disorders, schizophrenia is the cancer. ...
... If depression is the common cold of psychological disorders, schizophrenia is the cancer. ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... based on operant conditioning principles Reinforcement for behaving appropriately ...
... based on operant conditioning principles Reinforcement for behaving appropriately ...
Separation Anxiety Disorder
... conditions, which can be present from an early age or begin suddenly after a triggering event. They are prone to flare up at times of high stress. ...
... conditions, which can be present from an early age or begin suddenly after a triggering event. They are prone to flare up at times of high stress. ...
sample abstract, spr panel
... Bulimia Trial, CBT was superior to PPT in relieving symptoms in bulimic clients. However, with clients with preoccupied attachment states of mind the two therapy types had results that were more comparable. This paper provides a qualitative exploration of PPT cases with go ...
... Bulimia Trial, CBT was superior to PPT in relieving symptoms in bulimic clients. However, with clients with preoccupied attachment states of mind the two therapy types had results that were more comparable. This paper provides a qualitative exploration of PPT cases with go ...
PS1000: Introduction to Abnormal Psychology Mood disorders and
... Intrusive thoughts - normal But, why are they persistent in OCD to cause distress Thought suppression? ...
... Intrusive thoughts - normal But, why are they persistent in OCD to cause distress Thought suppression? ...
DSM-V: Trauma-and Stressor-Related Disorders
... According to NCPTSD: “National estimates of PTSD prevalence suggest that DSM-5 rates were slightly lower than DSM-IV. … Revision of Criterion A1 in DSM-5 narrowed qualifying traumatic events such that the unexpected death of family or a close friend due to natural causes is no longer included. Resea ...
... According to NCPTSD: “National estimates of PTSD prevalence suggest that DSM-5 rates were slightly lower than DSM-IV. … Revision of Criterion A1 in DSM-5 narrowed qualifying traumatic events such that the unexpected death of family or a close friend due to natural causes is no longer included. Resea ...
A Proposal for Research - Adult Survivors CAN Sustain Recovery
... Wherever possible “real” – those individuals in Dunedin or Christchurch wishing to personally present for interview / assessment will be recruited for participation. However, experience to date suggests these will be few. Real participants will complete a similar procedure to other participants, as ...
... Wherever possible “real” – those individuals in Dunedin or Christchurch wishing to personally present for interview / assessment will be recruited for participation. However, experience to date suggests these will be few. Real participants will complete a similar procedure to other participants, as ...
1 DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria for Communication and Other
... The fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) was released by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) in May 2013. The DSM provides diagnostic criteria for mental disorders and is widely used by different professionals in clinical and community settings in ...
... The fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) was released by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) in May 2013. The DSM provides diagnostic criteria for mental disorders and is widely used by different professionals in clinical and community settings in ...
WHAT IS Autism Spectrum Disorder?
... Then significant loss of previously acquired skills in at least 2 of the following areas(language, social skills, adaptive behavior, bowel or bladder control, play, or motor skills) before the age of 10 Entered into the DSM IV in 1994 ...
... Then significant loss of previously acquired skills in at least 2 of the following areas(language, social skills, adaptive behavior, bowel or bladder control, play, or motor skills) before the age of 10 Entered into the DSM IV in 1994 ...
An attachment perspective on psychopathology
... extent to which attachment insecurities are a sufficient cause of mental disorders. In our view, beyond disorders such as separation anxiety and pathological grief, in which attachment injuries are the main causes and themes, attachment insecurities per se are unlikely to be sufficient causes of men ...
... extent to which attachment insecurities are a sufficient cause of mental disorders. In our view, beyond disorders such as separation anxiety and pathological grief, in which attachment injuries are the main causes and themes, attachment insecurities per se are unlikely to be sufficient causes of men ...
psychotic - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Per DSM-IV – These disorders “are all characterized by having psychotic symptoms as the defining feature…The term psychotic has historically received a number of different definitions, none of which has achieved universal acceptance. The narrowest definition of psychotic is restricted to delusions ...
... • Per DSM-IV – These disorders “are all characterized by having psychotic symptoms as the defining feature…The term psychotic has historically received a number of different definitions, none of which has achieved universal acceptance. The narrowest definition of psychotic is restricted to delusions ...
Module 8 Complete Slide Presentation PDF
... psychosocial interventions, even without medications – High rates of “relapse” ...
... psychosocial interventions, even without medications – High rates of “relapse” ...
Reactive attachment disorder

Reactive attachment disorder (RAD) is described in clinical literature as a severe and relatively uncommon disorder that can affect children. RAD is characterized by markedly disturbed and developmentally inappropriate ways of relating socially in most contexts. It can take the form of a persistent failure to initiate or respond to most social interactions in a developmentally appropriate way—known as the ""inhibited form""—or can present itself as indiscriminate sociability, such as excessive familiarity with relative strangers—known as the ""disinhibited form"". The term is used in both the World Health Organization's International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) and in the DSM-IV-TR, the revised fourth edition of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). In ICD-10, the inhibited form is called RAD, and the disinhibited form is called ""disinhibited attachment disorder"", or ""DAD"". In the DSM, both forms are called RAD; for ease of reference, this article will follow that convention and refer to both forms as reactive attachment disorder.RAD arises from a failure to form normal attachments to primary caregivers in early childhood. Such a failure could result from severe early experiences of neglect, abuse, abrupt separation from caregivers between the ages of six months and three years, frequent change of caregivers, or a lack of caregiver responsiveness to a child's communicative efforts. Not all, or even a majority of such experiences, result in the disorder. It is differentiated from pervasive developmental disorder or developmental delay and from possibly comorbid conditions such as intellectual disability, all of which can affect attachment behavior. The criteria for a diagnosis of a reactive attachment disorder are very different from the criteria used in assessment or categorization of attachment styles such as insecure or disorganized attachment. DSM-5, the fifth revised edition published in 2013, separates RAD into two separate disorders: reactive attachment disorder (previously referred to as the ""inhibited"" form), and social engagement disorder.Children with RAD are presumed to have grossly disturbed internal working models of relationships which may lead to interpersonal and behavioral difficulties in later life. There are few studies of long-term effects, and there is a lack of clarity about the presentation of the disorder beyond the age of five years. However, the opening of orphanages in Eastern Europe following the end of the Cold War in the early-1990s provided opportunities for research on infants and toddlers brought up in very deprived conditions. Such research broadened the understanding of the prevalence, causes, mechanism and assessment of disorders of attachment and led to efforts from the late-1990s onwards to develop treatment and prevention programs and better methods of assessment. Mainstream theorists in the field have proposed that a broader range of conditions arising from problems with attachment should be defined beyond current classifications.Mainstream treatment and prevention programs that target RAD and other problematic early attachment behaviors are based on attachment theory and concentrate on increasing the responsiveness and sensitivity of the caregiver, or if that is not possible, placing the child with a different caregiver. Most such strategies are in the process of being evaluated. Mainstream practitioners and theorists have presented significant criticism of the diagnosis and treatment of alleged reactive attachment disorder or attachment disorder within the controversial field commonly known as attachment therapy. Attachment therapy has a scientifically unsupported theoretical base and uses diagnostic criteria or symptom lists unrelated to criteria under ICD-10 or DSM-IV-TR, or to attachment behaviors. A range of treatment approaches are used in attachment therapy, some of which are physically and psychologically coercive, and considered to be antithetical to attachment theory.