File - eScience@Kings
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
... • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
Periodic Table
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
Atomic structure and Periodic table revision guide File
... called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. The boiling points of the noble gases increase wi ...
... called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. The boiling points of the noble gases increase wi ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
File - dr. stephen alfred
... Atoms will often take, give, or share electrons with other atoms in order to have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level. Elements whose atoms undergo such processes are called Reactive and can combine to form compounds. Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the sam ...
... Atoms will often take, give, or share electrons with other atoms in order to have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level. Elements whose atoms undergo such processes are called Reactive and can combine to form compounds. Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the sam ...
05 sg Periodic Law
... led to the development of many chemistry-based industries (e.g., dyes, soaps, petrochemicals & fertilizers) helped fuel the discovery of new elements. By the 1860’s, more than 60 elements were known. With the relatively large number of known elements, scientists began to search for a systematic unde ...
... led to the development of many chemistry-based industries (e.g., dyes, soaps, petrochemicals & fertilizers) helped fuel the discovery of new elements. By the 1860’s, more than 60 elements were known. With the relatively large number of known elements, scientists began to search for a systematic unde ...
Periodic classificatiion of elements
... the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a group? A. Down the group the effective nuclear charge experience by valence electrons is decrea ...
... the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a group? A. Down the group the effective nuclear charge experience by valence electrons is decrea ...
Study Guide for Electrons Mini-Test - seys
... Chemical Interactions - 1.2 - Elements make up the periodic table Elements can be organized by similarities: one way of organizing elements: - masses of their atoms - not all the atoms of an element have the same atomic mass number = isotopes - when finding mass of an atom = finding the average mass ...
... Chemical Interactions - 1.2 - Elements make up the periodic table Elements can be organized by similarities: one way of organizing elements: - masses of their atoms - not all the atoms of an element have the same atomic mass number = isotopes - when finding mass of an atom = finding the average mass ...
lanthanides - schultz915
... The d-block elements are also known as __________ ___________. a. Noble gases b. Alkali metals c. transition metals d. Alkaline earth metals ...
... The d-block elements are also known as __________ ___________. a. Noble gases b. Alkali metals c. transition metals d. Alkaline earth metals ...
Ex. 41 Answer
... b) The boiling point of an element depends on the strength of attractions between its particles. Silicon has a giant covalent structure. A lot of heat is needed to overcome the strong covalent bonds between the atoms. Molecules in phosphorus are attracted to one another by weak van der Waals’ forces ...
... b) The boiling point of an element depends on the strength of attractions between its particles. Silicon has a giant covalent structure. A lot of heat is needed to overcome the strong covalent bonds between the atoms. Molecules in phosphorus are attracted to one another by weak van der Waals’ forces ...
worksheet i—extra credit
... The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is known as the ____________________ energy. This quantity generally _________________________ as you move left to right across a period. The size of an ion depends on whether the atom from which it formed gained or lost an _____________________ ...
... The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is known as the ____________________ energy. This quantity generally _________________________ as you move left to right across a period. The size of an ion depends on whether the atom from which it formed gained or lost an _____________________ ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... Properties such as density, atomic radius, oxidation numbers, ionization energy, and e- affinity can be ...
... Properties such as density, atomic radius, oxidation numbers, ionization energy, and e- affinity can be ...
The d-and f-Block Elements
... Due to the similar sizes of the lanthanides, it is difficult to separate them but due to lanthanide contraction their properties slightly vary (such as ability to form complexes). The variation in the properties is utilized to separate them. 2. Basic Strength of Hydroxide : Due to the lanthanide con ...
... Due to the similar sizes of the lanthanides, it is difficult to separate them but due to lanthanide contraction their properties slightly vary (such as ability to form complexes). The variation in the properties is utilized to separate them. 2. Basic Strength of Hydroxide : Due to the lanthanide con ...
Name Pre-Test : Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 2. The __________________is the center of the atom. 3. The atomic number is the number of __________________in an atom. 4. Protons have a __________________charge. 5. __________________are atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons. 6. The electron __________________is the space in ...
... 2. The __________________is the center of the atom. 3. The atomic number is the number of __________________in an atom. 4. Protons have a __________________charge. 5. __________________are atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons. 6. The electron __________________is the space in ...
Instructional-Objectives
... Describe the place of metals, metalloids and nonmetals in the periodic table. 3.6 Electron Arrangements within Atoms State the basic postulates of Bohr's theory. Describe the first model, the Bohr model of arrangement of electrons in shells (orbits) around a nucleus of an atom. Describe how Bo ...
... Describe the place of metals, metalloids and nonmetals in the periodic table. 3.6 Electron Arrangements within Atoms State the basic postulates of Bohr's theory. Describe the first model, the Bohr model of arrangement of electrons in shells (orbits) around a nucleus of an atom. Describe how Bo ...
Instructional Objectives 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Describe the place of metals, metalloids and nonmetals in the periodic table. 3.6 Electron Arrangements within Atoms • State the basic postulates of Bohr's theory. • Describe the first model, the Bohr model of arrangement of electrons in shells (orbits) around a nucleus of an atom. • Describe how Bo ...
... Describe the place of metals, metalloids and nonmetals in the periodic table. 3.6 Electron Arrangements within Atoms • State the basic postulates of Bohr's theory. • Describe the first model, the Bohr model of arrangement of electrons in shells (orbits) around a nucleus of an atom. • Describe how Bo ...
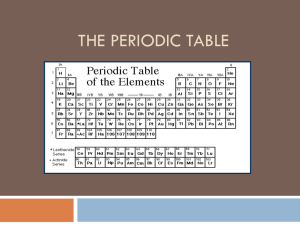
Periodic Table
... main body of the periodic table to their current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
... main body of the periodic table to their current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
Periodic Table
... main body of the periodic table to their current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
... main body of the periodic table to their current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
Chapter 5 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... At the completion of chapter 13 you should be able to... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Ex ...
... At the completion of chapter 13 you should be able to... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Ex ...
03 Chapter 2 Atomic Structure Power point Periodic Table
... • 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electr ...
... • 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electr ...
Daily Inquiry: 10-31-2011
... increasing atomic numbers, elements with similar chemical and physical properties occur at regular intervals. • Today the periodic table arranges elements by groups and periods. • Group – vertical column of elements – also known as families • Period – horizontal row of elements ...
... increasing atomic numbers, elements with similar chemical and physical properties occur at regular intervals. • Today the periodic table arranges elements by groups and periods. • Group – vertical column of elements – also known as families • Period – horizontal row of elements ...