module-21 (worksheet-1)
... 6) Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of Periodic Table. (a) The elements become less metallic in nature. (b) The number of valence electrons increases. (c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily. (d) The ...
... 6) Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of Periodic Table. (a) The elements become less metallic in nature. (b) The number of valence electrons increases. (c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily. (d) The ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table - Scotch Plains
... activity increases down a group because the electrons become more shielded by inner shells, making it harder to hold onto the valence electrons. ...
... activity increases down a group because the electrons become more shielded by inner shells, making it harder to hold onto the valence electrons. ...
18HYD13_F_Layout 1
... same slot, but also put some unlike elements in the same plot. (ii) Electronic configuration of hydrogen resembles that of alkaline earth metals. (iii The term atomic size refers to the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the penultimate sh,ell of an isolated atom. (iv) In the Modern peri ...
... same slot, but also put some unlike elements in the same plot. (ii) Electronic configuration of hydrogen resembles that of alkaline earth metals. (iii The term atomic size refers to the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the penultimate sh,ell of an isolated atom. (iv) In the Modern peri ...
CBSE Class 10 Physics Periodic classification of elements Notes
... a. The law was applicable to elements upto calcium (Ca) only b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two element ...
... a. The law was applicable to elements upto calcium (Ca) only b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two element ...
Unit 4 Pack
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
Table The Discussion
... table so the table wouldn’t be so wide. The elements in each of these two periods share many properties. The lanthanides are shiny and reactive. The actinides are all radioactive and are therefore unstable. Elements 95 through 103 do not exist in nature but have been manufactured in the lab. ...
... table so the table wouldn’t be so wide. The elements in each of these two periods share many properties. The lanthanides are shiny and reactive. The actinides are all radioactive and are therefore unstable. Elements 95 through 103 do not exist in nature but have been manufactured in the lab. ...
Periodic Classification of Elements
... Question 5: Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two) Answer: Scandium and germanium Question 6: What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table? Answer: Mendeleev’s periodic table was based o ...
... Question 5: Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two) Answer: Scandium and germanium Question 6: What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table? Answer: Mendeleev’s periodic table was based o ...
File - the prayas tutorial
... He could not assign a correct position to hydrogen because hydrogen resembles alkali metals in electronic configuration and also resembles halogens because of its existence as a diatomic molecule. It reacts with metals as well as non-metals to form covalent compounds. The elements were arranged in t ...
... He could not assign a correct position to hydrogen because hydrogen resembles alkali metals in electronic configuration and also resembles halogens because of its existence as a diatomic molecule. It reacts with metals as well as non-metals to form covalent compounds. The elements were arranged in t ...
questions on periodic classification of elements
... of the bond formed between them? To which period of the Modern periodic table do these two elements belong? 11. The elements Li, Be, B , C ,N, O ,F and Ne are present in the second period . How many valence electrons do these elements have? Classify them as metals and non metals. 12. An atom ‘X’ has ...
... of the bond formed between them? To which period of the Modern periodic table do these two elements belong? 11. The elements Li, Be, B , C ,N, O ,F and Ne are present in the second period . How many valence electrons do these elements have? Classify them as metals and non metals. 12. An atom ‘X’ has ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
... In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
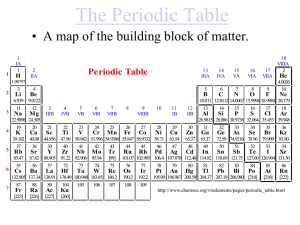
Elements are the building blocks of matter.
... 4. Is there a link between the group number (ie. 1 - 18) and the number of valence electrons an atom has? How are they related? 5. What do you notice about the location of valence electrons for elements belonging to the same period (horizontal row)? 6. Is there a link between the period number and t ...
... 4. Is there a link between the group number (ie. 1 - 18) and the number of valence electrons an atom has? How are they related? 5. What do you notice about the location of valence electrons for elements belonging to the same period (horizontal row)? 6. Is there a link between the period number and t ...
Ch. 5.1 History of the periodic table ppt.
... When he arranged elements by increasing atomic weights, he noticed that similar elements occurred at regular intervals. ...
... When he arranged elements by increasing atomic weights, he noticed that similar elements occurred at regular intervals. ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
Physical Science
... Scientists use the periodic table to explain the chemical behavior of different groups of elements. • The discovery of scandium (Sc) in 1879 and the discovery of germanium (Ge) in 1886 ...
... Scientists use the periodic table to explain the chemical behavior of different groups of elements. • The discovery of scandium (Sc) in 1879 and the discovery of germanium (Ge) in 1886 ...
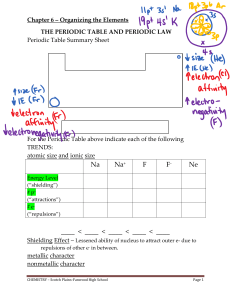
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
... The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
Periodic Table Student Outline
... Group 1 Alkali metals very reactive … become more reactive as you go down the group … always occur combined with nonmetals in nature Group 2 Alkaline Earth Metals also reactive (not as reactive as group 1) Group 17 Halogens- all diatomic, contain elements in all 3 phases of matter. Group18 N ...
... Group 1 Alkali metals very reactive … become more reactive as you go down the group … always occur combined with nonmetals in nature Group 2 Alkaline Earth Metals also reactive (not as reactive as group 1) Group 17 Halogens- all diatomic, contain elements in all 3 phases of matter. Group18 N ...
IT`S ATOMIC
... considered to be nonmetals. Metals and nonmetals have very different properties. As a result, metals and nonmetals will combine to form Group Figure 1 new substances. In addition to the zigzag line, the periodic table contains vertical columns of elements as well as horizontal rows of elements. The ...
... considered to be nonmetals. Metals and nonmetals have very different properties. As a result, metals and nonmetals will combine to form Group Figure 1 new substances. In addition to the zigzag line, the periodic table contains vertical columns of elements as well as horizontal rows of elements. The ...
File u1 sec2.2 slide show
... Chemical Family – Noble Gases Noble Gases (Column 18) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn The most stable and unreactive elements At room temperature, they are colourless, odourless gases. ...
... Chemical Family – Noble Gases Noble Gases (Column 18) He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn The most stable and unreactive elements At room temperature, they are colourless, odourless gases. ...
D. - Taylor County Schools
... • The two rows under the periodic table are called the inner transition metals. ...
... • The two rows under the periodic table are called the inner transition metals. ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
... The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
General Structure of the Periodic Table
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
... In the sixty-seven years from Dalton's formulation of atomic weight to Mendeleyev's periodic table many scientists had tried to create a working organizational structure for the elements. Mendeleyev succeeded where others failed because he realized that there existed a number of as yet unknown eleme ...
The Periodic Table
... Elements in Group 6 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 7 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
... Elements in Group 6 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 7 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
CSCOPE Periodic Table Powerpoint
... Elements in Group 16 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 17 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
... Elements in Group 16 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 17 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
MENDELEEV AND THE ATOMIC TABLE Dmitri Ivanovich
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...