periodic classification - cpprashanths Chemistry
... 4.Similar elements placed separately:-Li , Na K,Rb and Cs present in IA are quite different from coinage metals Cu ,Ag Au present in IB. 5.Dissimilar elements placed together:-Cu and Hg with many similar properties but Cu is placed in IB while Hg is placed in Group II B. 6.Uncertianty in prediction ...
... 4.Similar elements placed separately:-Li , Na K,Rb and Cs present in IA are quite different from coinage metals Cu ,Ag Au present in IB. 5.Dissimilar elements placed together:-Cu and Hg with many similar properties but Cu is placed in IB while Hg is placed in Group II B. 6.Uncertianty in prediction ...
7-1 Notes: Arranging the Elements
... and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are __________. Metals are found to the _______ ...
... and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are __________. Metals are found to the _______ ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
The Periodic Table - Prairie Rose School Division No. 8
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
KS4 Chemistry The Periodic Table 1 of 47 © Boardworks Ltd 2005
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
KS4 The Periodic Table 3548KB
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
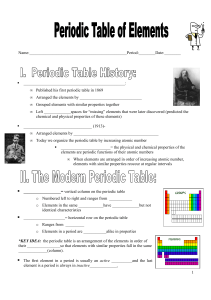
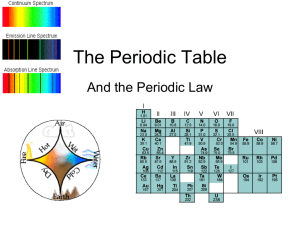
History of the Periodic Table
... The familiar periodic table that adorns many science classrooms is based on a number of early efforts to identify and classify the elements. In the 1790’s, one of the first lists of elements and their compounds was compiled by French chemist Antioine-Laurent Lavioser. It was Lavoisier who divided th ...
... The familiar periodic table that adorns many science classrooms is based on a number of early efforts to identify and classify the elements. In the 1790’s, one of the first lists of elements and their compounds was compiled by French chemist Antioine-Laurent Lavioser. It was Lavoisier who divided th ...
Mendeleef`s Periodic Table
... With the discovery of a large number of elements, it became difficult to study the elements individually, so classification of elements was done to make the study easier. Earlier Attempts to Classify Elements Many attempts were made to classify the known elements from time to time. The earlier attem ...
... With the discovery of a large number of elements, it became difficult to study the elements individually, so classification of elements was done to make the study easier. Earlier Attempts to Classify Elements Many attempts were made to classify the known elements from time to time. The earlier attem ...
Period
... 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and period 4? __________ 6. What element is in group 12 and p ...
... 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and period 4? __________ 6. What element is in group 12 and p ...
Chemical Periodicity
... Low density, weak, brittle (non-malleable), poor conductor of heat. metalloids or semimetals High density, in between strong and weak, brittle, fair conductors of heat. 2 Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his contribution to chemistry? He was a chemist who worked on trying to figure out the ...
... Low density, weak, brittle (non-malleable), poor conductor of heat. metalloids or semimetals High density, in between strong and weak, brittle, fair conductors of heat. 2 Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his contribution to chemistry? He was a chemist who worked on trying to figure out the ...
Inorganic Chemistry ELEMENTS AND
... Chemical Bond : Chemical bond may be defined as the attractive force that binds together the constituent atoms in a molecule. Following are some different types of chemical bonds which usually occur in various molecules. (i) Electrovalent bond (Ionic bond) : This type of bond is formed by transfer o ...
... Chemical Bond : Chemical bond may be defined as the attractive force that binds together the constituent atoms in a molecule. Following are some different types of chemical bonds which usually occur in various molecules. (i) Electrovalent bond (Ionic bond) : This type of bond is formed by transfer o ...
Chapter 5
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
Document
... transition metals and inner transition metals. • The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
... transition metals and inner transition metals. • The two sets of inner transition metals are called the lanthanide series and actinide series and are located at the bottom of the periodic table. ...
TEST-Periodic Table
... a. Rb is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of elements in Group 1A increases from top to bottom. b. Li is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of ...
... a. Rb is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of elements in Group 1A increases from top to bottom. b. Li is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of ...
How the Periodic Table Works
... outermost s orbital and the inner d orbital can participate in chemical reactions. They include elements that we usually think of as metals, like iron, nickel, chromium and precious metals such as gold, copper, silver and platinum. Metals are located mostly in group 13 (IIIA) and some in groups 141 ...
... outermost s orbital and the inner d orbital can participate in chemical reactions. They include elements that we usually think of as metals, like iron, nickel, chromium and precious metals such as gold, copper, silver and platinum. Metals are located mostly in group 13 (IIIA) and some in groups 141 ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Spring Packet
... Follow the directions below to complete the periodic table: 1. Label each group and period with the appropriate numbers. 2. Fill in the elements for Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18 and provide the names for each family, for example alkaline earth, noble gases, etc (see pg 513-514, 522 – 525 ...
... Follow the directions below to complete the periodic table: 1. Label each group and period with the appropriate numbers. 2. Fill in the elements for Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18 and provide the names for each family, for example alkaline earth, noble gases, etc (see pg 513-514, 522 – 525 ...
Chapter 5 The Periodic Table
... • The Alkaline Earth Metals-Group 2A Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Have 2 valence electrons Harder than Group 1A metals Key Concept: Differences in reactivity among the alkaline earth metals are shown by the ways they react with water (ex. Ca, Sr, Ba-cold water) and (Mg-hot water) Mg & Ca-essential for bio ...
... • The Alkaline Earth Metals-Group 2A Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Have 2 valence electrons Harder than Group 1A metals Key Concept: Differences in reactivity among the alkaline earth metals are shown by the ways they react with water (ex. Ca, Sr, Ba-cold water) and (Mg-hot water) Mg & Ca-essential for bio ...
... because they are farther from the nucleus. viii. Which element will have the smallest ionization energy in this period? Why? Answers will vary for each period. Electrons are harder to remove from small atoms because they are closer to the nucleus. ix. Which element will have the largest ionization e ...
Week 9 (wk9) - Riverside Local Schools
... which the single electron is lost helps make the Group 1 metal 4. The elements of Group 1 of the periodic table are known as… 5. In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are… 6. The elements of Group 2 of the periodic table are called… 7. The Group 2 metals are har ...
... which the single electron is lost helps make the Group 1 metal 4. The elements of Group 1 of the periodic table are known as… 5. In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are… 6. The elements of Group 2 of the periodic table are called… 7. The Group 2 metals are har ...
Reactions of Main Group ...ith Nitrogen - Chemwiki
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... • Because of the decrease in unpaired electrons, the bonds that the atoms can form with each other become weaker. • As a result, these elements have lower melting and boiling points. • In Period 6, Cesium, Cs, has low melting and boiling points because it has only one valence electron to use for bon ...
... • Because of the decrease in unpaired electrons, the bonds that the atoms can form with each other become weaker. • As a result, these elements have lower melting and boiling points. • In Period 6, Cesium, Cs, has low melting and boiling points because it has only one valence electron to use for bon ...
The Periodic Table
... Valence electrons and group number • A main group (representative) element and the number of valence electrons it contains are related. • Group 1 has one valence electron, Group 2 has 2 valence electrons and so on. ( Exception He is in group 18, but ...
... Valence electrons and group number • A main group (representative) element and the number of valence electrons it contains are related. • Group 1 has one valence electron, Group 2 has 2 valence electrons and so on. ( Exception He is in group 18, but ...
Chapter 6 - HCC Learning Web
... subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. • Recently, several compounds of xenon and krypton have been made and the term noble gases or rare gases is currently used. Chapter 6 ...
... subsequently discovered in the next 5 years. • They were originally called the inert gases. • Recently, several compounds of xenon and krypton have been made and the term noble gases or rare gases is currently used. Chapter 6 ...
Describe the Periodic Table
... History of the Periodic Table • In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev listed all the elements known at the time in order of their atomic weight. He arranged the list into a table of rows and columns. • In Mendeleev’s day, there were 63 known elements. Today, we know of almost 100 elements that can be found in ...
... History of the Periodic Table • In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev listed all the elements known at the time in order of their atomic weight. He arranged the list into a table of rows and columns. • In Mendeleev’s day, there were 63 known elements. Today, we know of almost 100 elements that can be found in ...