9/98 scerri 7p dom - PubContent test page
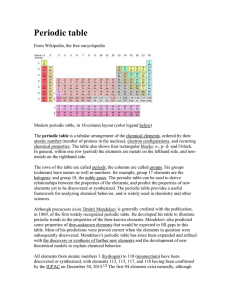
... to classify all the elements correctly. But the table did not appear in print until 1870 because of a publisher’s delay—a factor that contributed to an acrimonious dispute for priority that ensued between Lothar Meyer and Mendeleev. Around the same time, Mendeleev assembled his own periodic table wh ...
... to classify all the elements correctly. But the table did not appear in print until 1870 because of a publisher’s delay—a factor that contributed to an acrimonious dispute for priority that ensued between Lothar Meyer and Mendeleev. Around the same time, Mendeleev assembled his own periodic table wh ...
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
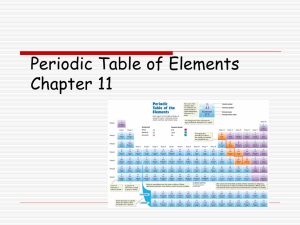
2 Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... valence electrons does each one have? (One) In a similar way, have students name the elements and numbers of valence electrons in a few examples in Groups 2 and 13 through 18. Instruct students to look at Figure 10 if they are unsure to which group any of the elements belong. Apply After students ha ...
... valence electrons does each one have? (One) In a similar way, have students name the elements and numbers of valence electrons in a few examples in Groups 2 and 13 through 18. Instruct students to look at Figure 10 if they are unsure to which group any of the elements belong. Apply After students ha ...
Question Bank Periodic Table and Periodic Properties
... _________. Ans. (i) increases, (ii) increases (o) Increase in nuclear charge of an atom _________ the tendency of atoms to lose electrons. Ans. decreases. (p) An atom with a small atomic radii takes up electrons _________ readily than an atom with large radii. Ans. more. (q) If the combining atoms o ...
... _________. Ans. (i) increases, (ii) increases (o) Increase in nuclear charge of an atom _________ the tendency of atoms to lose electrons. Ans. decreases. (p) An atom with a small atomic radii takes up electrons _________ readily than an atom with large radii. Ans. more. (q) If the combining atoms o ...
4 PERIODIC TABLE AND ATOMIC PROPERTIES W
... In 1863, J.A.R. Newlands, developed a system of classification of elements and entitled it as Law of Octaves. He arranged the elements is such a way that every eighth element had similar properties, like the notes of music. The law could not apply to a large number of known elements. However, the la ...
... In 1863, J.A.R. Newlands, developed a system of classification of elements and entitled it as Law of Octaves. He arranged the elements is such a way that every eighth element had similar properties, like the notes of music. The law could not apply to a large number of known elements. However, the la ...
Periodic Table ppt
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
Organizing the periodic table
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
Periodic_table_questions
... The table below shows the elements on the third period. Sample of each of the elements were burnt in oxygen and the oxides formed were tested to see whether they were acids or bases. ...
... The table below shows the elements on the third period. Sample of each of the elements were burnt in oxygen and the oxides formed were tested to see whether they were acids or bases. ...
OXIDATION AND REDUCTION
... Oxidation Number is the valency of an atom in a molecule or ion which is assigned the sign either + or -. It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compo ...
... Oxidation Number is the valency of an atom in a molecule or ion which is assigned the sign either + or -. It may be (i)electrovalency or (ii)covalency . When the proper sign is associated with valency it becomes oxidation number(ON). It is mostly a theoretical concept particularly for covalent compo ...
Periodic Table Notes
... electrons as easily as Groups 1 and 2 Good conductors of heat and electricity Some are used for jewelry The transition metals are able to hold up to 32 electrons in their second to last shell. Can bond with many elements in a variety of shapes. ...
... electrons as easily as Groups 1 and 2 Good conductors of heat and electricity Some are used for jewelry The transition metals are able to hold up to 32 electrons in their second to last shell. Can bond with many elements in a variety of shapes. ...
Valence Electrons - Warren County Public Schools
... •I can predict chemical reactivity for an element based on its number of valence electrons and location on periodic table. •I can predict the charge for an element (ion) to reach maximum stability. •I can distinguish between metallic and non-metallic properties. •I can understand how the periodic ta ...
... •I can predict chemical reactivity for an element based on its number of valence electrons and location on periodic table. •I can predict the charge for an element (ion) to reach maximum stability. •I can distinguish between metallic and non-metallic properties. •I can understand how the periodic ta ...
Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Chapter 5
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN
... Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration. (i) ns2np4 for n = 3, (ii) (n – 1) d2ns2 for n = 4, and (iii) (n – 2) f7 (n – 1) d1ns2 for n = 6, in the periodic ...
... Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration. (i) ns2np4 for n = 3, (ii) (n – 1) d2ns2 for n = 4, and (iii) (n – 2) f7 (n – 1) d1ns2 for n = 6, in the periodic ...
periodic table
... – Each period ends with a completely filled outer shell that has the maximum number of electrons for that shell. – The number identifying the “A” families identifies the number of electrons in the outer shell, except helium – The outer shell electrons are responsible for chemical ...
... – Each period ends with a completely filled outer shell that has the maximum number of electrons for that shell. – The number identifying the “A” families identifies the number of electrons in the outer shell, except helium – The outer shell electrons are responsible for chemical ...
Placing Elements on the Periodic Table
... electrons as easily as Groups 1 and 2 Good conductors of heat and electricity Some are used for jewelry The transition metals are able to hold up to 32 electrons in their second to last shell. Can bond with many elements in a variety of shapes. ...
... electrons as easily as Groups 1 and 2 Good conductors of heat and electricity Some are used for jewelry The transition metals are able to hold up to 32 electrons in their second to last shell. Can bond with many elements in a variety of shapes. ...
virtual lab- Atoms on periodic table student
... 2. How is the current periodic table ordered? (This one is not in the reading). 3. On what side of the periodic table are the metals? 4. On what side of the periodic table are the nonmetals? 5. How would you describe the properties of metalloids? In this Virtual Lab, your will explore the relationsh ...
... 2. How is the current periodic table ordered? (This one is not in the reading). 3. On what side of the periodic table are the metals? 4. On what side of the periodic table are the nonmetals? 5. How would you describe the properties of metalloids? In this Virtual Lab, your will explore the relationsh ...
Chemistry A- Periodic Table Packet
... members touch the zigzag line are called metalloids because they have both metallic and nonmetallic properties. NEW: The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. Groups (vertical, “up and down”) – ...
... members touch the zigzag line are called metalloids because they have both metallic and nonmetallic properties. NEW: The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. Groups (vertical, “up and down”) – ...
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
Presentation
... period, Scandium has larger atomic radius , hence it has lowest density (d = 3.0g/cm3) c. Scandium Ans. c ...
... period, Scandium has larger atomic radius , hence it has lowest density (d = 3.0g/cm3) c. Scandium Ans. c ...
Question (1): Explain `Dobereiner`s Triads and its drawback. Answer
... 2) Halogens are 'salt producers'. They are elements of group VIIA and have seven electrons in their valence shell. They are typical non-metals. Examples: F, Cl, Br and I are halogens. Question (34): Why are alkali metals not found in the free state? Answer: Alkali metals are very reactive in nature. ...
... 2) Halogens are 'salt producers'. They are elements of group VIIA and have seven electrons in their valence shell. They are typical non-metals. Examples: F, Cl, Br and I are halogens. Question (34): Why are alkali metals not found in the free state? Answer: Alkali metals are very reactive in nature. ...
2. Classification of Elements and periodicity in properties
... ¾ Zn, Cd and Hg are not considered to be transition elements as their atoms and Ions have completed d-orbitals. ¾ Small atomic size, high nuclear charge, and unpaired d-electrons give characteristic properties to transition elements. ¾ Transition elements are hard and dense metals. ¾ They have high ...
... ¾ Zn, Cd and Hg are not considered to be transition elements as their atoms and Ions have completed d-orbitals. ¾ Small atomic size, high nuclear charge, and unpaired d-electrons give characteristic properties to transition elements. ¾ Transition elements are hard and dense metals. ¾ They have high ...
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Law
... Break-up of the Periodic Table Within the groups and periods there is further classification: Metals – located on the left, center and bottom of the periodic table. Non-metals – located on the right side of the table. Metalloids – located on the “staircase” seen in the periodic table. ...
... Break-up of the Periodic Table Within the groups and periods there is further classification: Metals – located on the left, center and bottom of the periodic table. Non-metals – located on the right side of the table. Metalloids – located on the “staircase” seen in the periodic table. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Nonmetals occupy the upper right side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are generally gases and include groups such as the carbon group (group 14), the nitrogen group (group 15), the oxygen group (group 16), the halogens (group 17), and the noble gases (group 18). Characteristics shared amongst nonme ...
... Nonmetals occupy the upper right side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are generally gases and include groups such as the carbon group (group 14), the nitrogen group (group 15), the oxygen group (group 16), the halogens (group 17), and the noble gases (group 18). Characteristics shared amongst nonme ...