Unit 3.pmd
... Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers which is related to the electronic configuration. Depending upon the type of orbitals receiving the last electron, the elements in the periodic t ...
... Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers which is related to the electronic configuration. Depending upon the type of orbitals receiving the last electron, the elements in the periodic t ...
Chp4Sec1and2
... Atomic theory grew as a series of models that developed from experimental evidence. As more evidence was collected, the theory and models were revised. ...
... Atomic theory grew as a series of models that developed from experimental evidence. As more evidence was collected, the theory and models were revised. ...
Periodic Table
... Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table The f-block elements are wedged between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity ...
... Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table The f-block elements are wedged between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity ...
Discovering Elements
... directly to the filling of the shells. They give the table its periodic nature, as elements with similar electron configurations fall into columns called groups. Group 1, the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr), all have 1 outer electron, and Group 7, the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), all have 7 oute ...
... directly to the filling of the shells. They give the table its periodic nature, as elements with similar electron configurations fall into columns called groups. Group 1, the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr), all have 1 outer electron, and Group 7, the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I, At), all have 7 oute ...
Isotopes and the Electron Configuration of the Blocks in the Periodic
... It is known that elements of the Periodic Table of Elements have fractional numerical values of atomic masses. This is because the elements consists of, as regularly, a mix of inborn (native) isotopes. For this reason we conclude that the average weighted atomic mass of all stable isotopes of any el ...
... It is known that elements of the Periodic Table of Elements have fractional numerical values of atomic masses. This is because the elements consists of, as regularly, a mix of inborn (native) isotopes. For this reason we conclude that the average weighted atomic mass of all stable isotopes of any el ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND
... ATOMIC RADIUS- The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electrons in the atom of any element is called its atomic radius. Periodicity- (a) In period- Atomic radius of elements decreases from left to right in a period. (b) In Group- Atomic radius of elements increases ...
... ATOMIC RADIUS- The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electrons in the atom of any element is called its atomic radius. Periodicity- (a) In period- Atomic radius of elements decreases from left to right in a period. (b) In Group- Atomic radius of elements increases ...
10TH CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CHEMISRY As a large
... With the developments in the field of Chemistry, various scientists attempted to classify the known elements of their times so that their study may become easier and more informative. Some of the attempts are mentioned as under: i) Division of elements into metals and non-metals: Earlier chemists re ...
... With the developments in the field of Chemistry, various scientists attempted to classify the known elements of their times so that their study may become easier and more informative. Some of the attempts are mentioned as under: i) Division of elements into metals and non-metals: Earlier chemists re ...
Organizing the periodic table
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
... The vertical columns of the periodic table are known as a group. Another name for each group is a “family”. Each group is filled with atoms which have similar characteristics. There are eighteen groups in the periodic table. The lanthanides and actinides do not fit in the periodic table because the ...
Introduction to Atoms
... a. Each is a good conductor of electricity. b. They are never found uncombined in nature. c. They lose two electrons in chemical reactions. d. They are much less reactive than most metals. ...
... a. Each is a good conductor of electricity. b. They are never found uncombined in nature. c. They lose two electrons in chemical reactions. d. They are much less reactive than most metals. ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
Patterns in The Periodic Table
... calcium (Ca) helps to build strong bones and teeth. Similarly, strontium (Sr) builds a strong shell in coral. Many substances composed of alkaline earth metals burn with bright, colourful flames. As a result of this property, alkaline earth metals such as magnesium are used in fireworks. ...
... calcium (Ca) helps to build strong bones and teeth. Similarly, strontium (Sr) builds a strong shell in coral. Many substances composed of alkaline earth metals burn with bright, colourful flames. As a result of this property, alkaline earth metals such as magnesium are used in fireworks. ...
Periodicity - ilc.edu.hk
... are great ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling >> melting Particles are completely separated on boiling For Gp4A elements, the differences between m.p. and b.p. are relatively small ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling melting ...
... are great ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling >> melting Particles are completely separated on boiling For Gp4A elements, the differences between m.p. and b.p. are relatively small ∵ extent of bond breaking : boiling melting ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
... discovered at that time. Mendeléev named them by prefixing a Sanskrit numeral, Eka (one) to the name of preceding element in the same group. It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respective ...
xi_chem_ch3_classification of elements
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
Periodic Table Packet
... 1. malleable - can be rolled or hammered into sheets 2. ductile - can be drawn into wires " are solids at room . temperature except for mercury 9. Nonmetals a. Chemical properties - tend to gain electrons i. have high electron affinities ii. produce covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other non ...
... 1. malleable - can be rolled or hammered into sheets 2. ductile - can be drawn into wires " are solids at room . temperature except for mercury 9. Nonmetals a. Chemical properties - tend to gain electrons i. have high electron affinities ii. produce covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other non ...
"Part 1" Resource
... Alexander, Roy. “The History of the Periodic Table." allperiodictables.com, 2011. Web. 28 Nov. 2011. ...
... Alexander, Roy. “The History of the Periodic Table." allperiodictables.com, 2011. Web. 28 Nov. 2011. ...
What is the PERIODIC TABLE?
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
d) Ramsay. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table
... The ionization energies for removing successive electrons from sodium are 496 kJ/mol, 4562 kJ/mol, 6912 kJ/mol, and 9544 kJ/mol. The great jump in ionization energy after the first electron is removed indicates that a) sodium has four or five electrons. ...
... The ionization energies for removing successive electrons from sodium are 496 kJ/mol, 4562 kJ/mol, 6912 kJ/mol, and 9544 kJ/mol. The great jump in ionization energy after the first electron is removed indicates that a) sodium has four or five electrons. ...
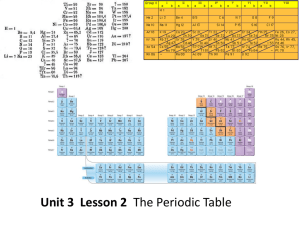
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
... Each jump in the line marks the beginning of a new period (row) in the periodic table 4) What trends to you observe about the relationship between atomic radius and the atomic number? The value for atomic radii generally decrease across a period and increase down a group. 5) Based on the trends, wha ...
... Each jump in the line marks the beginning of a new period (row) in the periodic table 4) What trends to you observe about the relationship between atomic radius and the atomic number? The value for atomic radii generally decrease across a period and increase down a group. 5) Based on the trends, wha ...
History of Periodic Table
... Broke the trend of arranging elements solely by their atomic mass Wanted to keep elements with similar properties in the same columns Left gaps in his early tables; predicted elements that had not been discovered would fill in those gaps - Ekasilicon Germanium - Germanium was discovered in 1886 ...
... Broke the trend of arranging elements solely by their atomic mass Wanted to keep elements with similar properties in the same columns Left gaps in his early tables; predicted elements that had not been discovered would fill in those gaps - Ekasilicon Germanium - Germanium was discovered in 1886 ...
Electrons in Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... An element has the electron configuration [Kr] 5s24d4. Without looking at the periodic table, identify the period, block, and group in which this element is located. Then, consult the periodic table to identify this element and the others in its group ...
... An element has the electron configuration [Kr] 5s24d4. Without looking at the periodic table, identify the period, block, and group in which this element is located. Then, consult the periodic table to identify this element and the others in its group ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
Chapter 5
... • Compare the periodic trends of atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity, and state the reasons for these variations. • Define valence electrons, and state how many are present in atoms of each main-group element. • Compare the atomic radii, ionization energies, and electronegativitie ...
... • Compare the periodic trends of atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity, and state the reasons for these variations. • Define valence electrons, and state how many are present in atoms of each main-group element. • Compare the atomic radii, ionization energies, and electronegativitie ...