* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
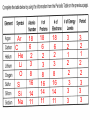
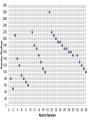
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are elements arranged on the periodic table? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p170 Get Organized! What are elements? • By the 1860s, scientists considered there to be at least 60 different basic substances, or elements. • Scientists found that many of these elements have similar properties and began classifying them. Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table What are elements? p170 Get Organized! dull, nonmetal, brittle, odor Solid, shiny, metal gas, nonmetal, yellow liquid, shiny, metal metal, shiny Liquid, nonmetal Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p171 How are the elements organized? • Dmitri Mendeleev first organized the elements by arranging them in order of increasing atomic mass. • He observed that the properties of those elements were in a periodic, or regularly repeating, pattern. Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p171 How are the elements organized? • Mendeleev’s arrangement of the elements became known as the periodic table. • Henry Moseley reorganized Mendeleev’s periodic table in order of increasing number of protons, or atomic number. • The periodic table is useful because it makes clear many patterns among the elements’ properties. 6) Explain Henry Moseley arranged the elements on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table P172-173 How are the elements organized? 8) 3 9) 6 Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p174 Making Arrangements What information is contained in each square on the periodic table? • Each square contains an element’s chemical name, atomic number, chemical symbol, and average atomic mass. • The atomic number is placed at the top of each square. • The chemical symbol is an abbreviation for the element’s name. • The first letter of the chemical symbol is always capitalized, and any other letter is lowercase. • The name of the element is written under the symbol. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company p174 Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p174 What information is contained in each square on the periodic table? • All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but the number of neutrons can vary. • The average atomic mass of an atom is the weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. • Average atomic mass is reported in atomic mass units (u). Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p175 How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • A zigzag line on the periodic table divides the three major categories of elements: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. • Metals are elements that are shiny and conduct heat and electricity well. • Elements to the left of the zigzag line are metals, except for hydrogen. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p175 How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • The elements to the right of the zigzag line are nonmetals. • Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity, and are often dull and brittle. • Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and nonmetals. They border the zigzag line. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p175 How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • List three metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p176 How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons participate in chemical bonding. Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table p177 How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each horizontal row of elements on the periodic table is called a period. • Physical and chemical properties of elements change in predictable ways from one end of the period to the other. • Elements in the same period have the same number of energy levels •Atomic number increases as you move from left to right •Number of energy levels increase by 1 as you go down the periodic table •Number of Valence Electrons increase and you go from left to right on the periodic table •Atomic size decreases as you move from left to right •Atomic number increases as you move from left to right •Number of energy levels increase by 1 as you go down the periodic table •Number of Valence Electrons increase and you go from left to right on the periodic table •Atomic size decreases as you move from left to right across a period. Al 13 13 13 Atomic number and # of p+ are equal e- and # of p+ are equal 2 Protons Electrons Atomic Number 3 3 How many energy levels are in the atom Ar C He Li O S Si Na 18 6 2 3 8 16 14 11 18 6 2 3 8 16 14 11 18 6 2 3 8 16 14 11 3 2 1 2 2 3 3 3 3 2 1 2 2 3 3 3 2 1 2 3 3 2 1 2 3 3 4 2 1 4 1 18 14 18 1 14 1 Same number of valence electrons Same number of energy levels or shells 17 2 3 3 7 17 2 3 6 1 group period Atomic Number Protons Valence electrons Energy levels (shells) Down Across Vertical Horizontal 2) Describe the pattern you see in the graph The line drops steadily and then jumps and begins to drop again in a diagonal line pattern 3) Compare your graph to the periodic table of elements. How does the pattern relate to the structure in the periodic table? The diagonal line in the graph relate to the periods (rows) in the periodic table. Each jump in the line marks the beginning of a new period (row) in the periodic table 4) What trends to you observe about the relationship between atomic radius and the atomic number? The value for atomic radii generally decrease across a period and increase down a group. 5) Based on the trends, what are approximate values of the atomic radii of 10, 18, and 31 50, 90, 150