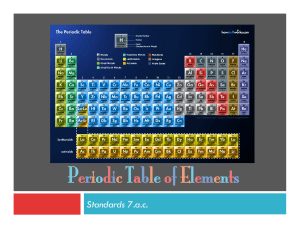
The Periodic Table
... Patterns, atomic number and electrons The periodic table shows that patterns in the properties of elements are linked to atomic number. atomic number = number of protons number of protons = number of electrons atomic number = number of electrons Therefore, as atomic number increases by one, the num ...
... Patterns, atomic number and electrons The periodic table shows that patterns in the properties of elements are linked to atomic number. atomic number = number of protons number of protons = number of electrons atomic number = number of electrons Therefore, as atomic number increases by one, the num ...
Chapter 6
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
... • Atoms get smaller as you go bottom to top on the periodic table because as you travel up a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you travel left to right across the periodic table because the number of protons in the nucleus increases. • As the number of pr ...
Chapter 6 Periodic Table Lecture Notes
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
Unit Expectations – Periodic Table
... SWBAT - Identify the number of valence electrons, whether the elements would gain or lose electrons and give the oxidation number / charge. Students will also be able to differentiate between oxidation number and charge in words and through symbols using elements.; C4.9x Electron Energy Levels The r ...
... SWBAT - Identify the number of valence electrons, whether the elements would gain or lose electrons and give the oxidation number / charge. Students will also be able to differentiate between oxidation number and charge in words and through symbols using elements.; C4.9x Electron Energy Levels The r ...
5.3 Representative Groups PPT
... n Relate the number of valence electrons to groups in the periodic table and to properties of elements in those groups. n Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. n Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
... n Relate the number of valence electrons to groups in the periodic table and to properties of elements in those groups. n Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. n Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
Chapter 7 The Development of the Periodic Table
... electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
... electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
The Periodic Table
... Elements in the same family have similar properties because their outer electron configurations are the same ...
... Elements in the same family have similar properties because their outer electron configurations are the same ...
The Modern Periodic Table (cont.)
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
ch 6 ppt - Madison County Schools
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
Chapter 6 PP
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
D. - Telluride Middle/High School
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
Document
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
ch3 - sscyr11chemistry
... Magnesium and phosphorus, with outer electrons in the third shell, are in the same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a n ...
... Magnesium and phosphorus, with outer electrons in the third shell, are in the same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a n ...
ch3 - ChemistryVCE
... Magnesium and phosphorus, with outer electrons in the third shell, are in the same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a n ...
... Magnesium and phosphorus, with outer electrons in the third shell, are in the same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a n ...
periods - Madeira City Schools
... electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in the outer energy levels are attracted to the nucleus. ...
... electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in the outer energy levels are attracted to the nucleus. ...
Learning Guide 3
... 4. As you go down a group the elements may change from nonmetal metalloid metal. 5. The metallic characteristics increase as you go down a group. 6. As you go left to right metallic characteristics ...
... 4. As you go down a group the elements may change from nonmetal metalloid metal. 5. The metallic characteristics increase as you go down a group. 6. As you go left to right metallic characteristics ...
Chapter 6 the Periodic Table
... Valence electrons and group number • A main group (representative) element and the number of valence electrons it contains are related. • Group 1 has one valence electron, Group 2 has 2 valence electrons and so on. ( Exception He is in group 18, but ...
... Valence electrons and group number • A main group (representative) element and the number of valence electrons it contains are related. • Group 1 has one valence electron, Group 2 has 2 valence electrons and so on. ( Exception He is in group 18, but ...
Chapter 1 - Study Guide Solutions
... Example: the following diagram is a representation of the oxygen atom according to the Rutherford-Bohr model. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 therefore this element is represented by 8 protons (positive charges) in the nucleus and 8 electrons (negative charges) that are distributed as ...
... Example: the following diagram is a representation of the oxygen atom according to the Rutherford-Bohr model. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 therefore this element is represented by 8 protons (positive charges) in the nucleus and 8 electrons (negative charges) that are distributed as ...
Periodic Table Presentation Lesson
... Nonmetals are dull and poor conductors of heat and electric current. The solid nonmetals tend to be brittle and unmalleable. The most reactive of the nonmetals are found on the far right of the periodic table (group 17). ...
... Nonmetals are dull and poor conductors of heat and electric current. The solid nonmetals tend to be brittle and unmalleable. The most reactive of the nonmetals are found on the far right of the periodic table (group 17). ...
Chem Periodicity, Reactivity, Redox 2009 Yingxin
... @ Most reactive non-metals @ Fluorine is the most reactive element in the periodic table @ Hence, they are powerful oxidizing agents @ React vigorously with most metals to form ionic salts @ Reactivity decreases down group @ Decreased oxidizing power, less ability to gain electrons due to more shell ...
... @ Most reactive non-metals @ Fluorine is the most reactive element in the periodic table @ Hence, they are powerful oxidizing agents @ React vigorously with most metals to form ionic salts @ Reactivity decreases down group @ Decreased oxidizing power, less ability to gain electrons due to more shell ...
Document
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
... • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. • The periodic table organizes the elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns); elements with similar properties are in the same ...
Periodic Table 2015
... • 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electr ...
... • 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (F I). • 3.2.3 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electr ...
c1l2ch06
... nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
... nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...
... Where were the elements made? There are 92 naturally-occurring elements and about 15 artificially-produced elements. Elements were originally made in stars. In the early stages of a star’s life, light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are formed. These fused together to make heavier elements s ...