CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
... 27 Why is cryolite, Na3AlF6, used in the extraction of aluminium from aluminium oxide? A ...
... 27 Why is cryolite, Na3AlF6, used in the extraction of aluminium from aluminium oxide? A ...
AP_chemistry_Summer_Assignment_2014
... B. K 5. A cylinder rod formed from silicon is 46.0 cm long and has a mass of 3.00 kg. The density of silicon is 2.33 g/cm3. What is the diameter of the cylinder? (the volume of cylinder is given by ∏ r2h, where r is the radius and h is the length) 6. How many significant figures are in each of the f ...
... B. K 5. A cylinder rod formed from silicon is 46.0 cm long and has a mass of 3.00 kg. The density of silicon is 2.33 g/cm3. What is the diameter of the cylinder? (the volume of cylinder is given by ∏ r2h, where r is the radius and h is the length) 6. How many significant figures are in each of the f ...
Chemical Reactions - Mr. Brown`s Science Town
... Example: Chromium (III) sulfite Cr+3SO3-2 = Cr2(SO3)3 d. Molecular Compounds – Prefixes = Subscripts ...
... Example: Chromium (III) sulfite Cr+3SO3-2 = Cr2(SO3)3 d. Molecular Compounds – Prefixes = Subscripts ...
IGCSE Revision document
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
2009-10 Chemistry 1st Semester Final Exam Topics and Review
... 35. Write and balance the chemical equations for the following reactions. Include the physical states (aq, s, l, g) of the reactants and products. a. When zinc metal and sulfur powder are heated, they form solid zinc sulfide. b. When sodium metal is placed in a beaker of water, hydrogen gas and sodi ...
... 35. Write and balance the chemical equations for the following reactions. Include the physical states (aq, s, l, g) of the reactants and products. a. When zinc metal and sulfur powder are heated, they form solid zinc sulfide. b. When sodium metal is placed in a beaker of water, hydrogen gas and sodi ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
Name: Date: AP Chemistry/Chemistry 145 Summer Assignment
... 16. Limestone, coral, and seashells are composed primarily of solid calcium carbonate. The test for the identification of a carbonate is to use a few drops of aqueous hydrochloric acid. Solid ...
... 16. Limestone, coral, and seashells are composed primarily of solid calcium carbonate. The test for the identification of a carbonate is to use a few drops of aqueous hydrochloric acid. Solid ...
Chemistry for Changing Times
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
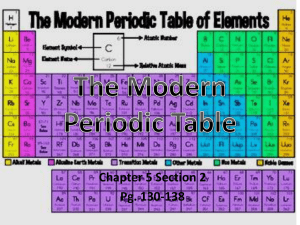
PERIODIC TABLE - WordPress.com
... Read pages 64-69 from your textbook [Chapter 3. Elements and Compounds, Section 3.1] and answer the following questions: 1. Which property of elements did Mendeleev use to arrange elements in his periodic table? 2. State three physical properties of metals. 3. What is atomic number? 4. What are the ...
... Read pages 64-69 from your textbook [Chapter 3. Elements and Compounds, Section 3.1] and answer the following questions: 1. Which property of elements did Mendeleev use to arrange elements in his periodic table? 2. State three physical properties of metals. 3. What is atomic number? 4. What are the ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... b. is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. c. generally decreases from top to bottom within a group. d. is generally higher for metals than for nonmetals. ...
... b. is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. c. generally decreases from top to bottom within a group. d. is generally higher for metals than for nonmetals. ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
CML738 Elias 2017 fluorine chemistry
... application is non-stick cookware. Other fluoropolymers tend to have similar properties to PTFE—high chemical resistance and good dielectric properties—which leads to use in the chemical process industry and electrical insulation. They are easier to work with (to form into complex shapes), but are m ...
... application is non-stick cookware. Other fluoropolymers tend to have similar properties to PTFE—high chemical resistance and good dielectric properties—which leads to use in the chemical process industry and electrical insulation. They are easier to work with (to form into complex shapes), but are m ...
Periodic Table Trends
... non-metals in Group VII therefore increases as one moves up the group as does their non-metallic nature. Fluorine (F) is the most reactive element and astatine (At) is the least reactive element in Group VII. ...
... non-metals in Group VII therefore increases as one moves up the group as does their non-metallic nature. Fluorine (F) is the most reactive element and astatine (At) is the least reactive element in Group VII. ...
Document
... Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Answer all questions. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. A copy of the Periodic Table is printed on page 16. ...
... Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid. Answer all questions. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. A copy of the Periodic Table is printed on page 16. ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate par ...
... 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate par ...
(periods) to
... sometimes shown as having a coordinate bond between sulfur and oxygen or they are show as having double between the sulfur and the oxygen. Both are acceptable. ...
... sometimes shown as having a coordinate bond between sulfur and oxygen or they are show as having double between the sulfur and the oxygen. Both are acceptable. ...
The Periodic Table
... Said properties of unknown elements could be predicted by the properties of elements around the missing element ...
... Said properties of unknown elements could be predicted by the properties of elements around the missing element ...
5 - BrainMass
... 5.72) Using the values from Thermodynamics Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25°C), calculate the value of ΔH° for each of the following reactions: a. N2O4 (g) + 4 H2 (g) N2 (g) + 4 H2O (g) b. 2 KOH(s) + CO2 (g) K2CO3(s) + H2O (g) c. SO2 (g) + 2 H2S (g) 3/8 S8(s) + 2 H2O (g) d. F ...
... 5.72) Using the values from Thermodynamics Quantities for Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25°C), calculate the value of ΔH° for each of the following reactions: a. N2O4 (g) + 4 H2 (g) N2 (g) + 4 H2O (g) b. 2 KOH(s) + CO2 (g) K2CO3(s) + H2O (g) c. SO2 (g) + 2 H2S (g) 3/8 S8(s) + 2 H2O (g) d. F ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review Worksheet Part 1
... b. Students know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many ...
... b. Students know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many ...
The Mole Ratio · the ratio between the molar amounts of any two
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
20161025140773
... that scientists work with contain trillions of atoms – To have a convenient way to compare the masses of atoms, scientists chose one isotope to serve as a standard – An atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom ...
... that scientists work with contain trillions of atoms – To have a convenient way to compare the masses of atoms, scientists chose one isotope to serve as a standard – An atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as one twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom ...
Unit 2 Test Review - Liberty High School
... 15. During a chemical reaction, 2.445 g of carbon reacts with 3.257 g of oxygen to form carbon monoxide gas. How many grams of carbon monoxide are formed in this reaction? 16. Ibuprofen has the chemical formula C13H18O2. It is 75.69% carbon, 8.80% hydrogen, and 15.51% oxygen. How many mg of carbon d ...
... 15. During a chemical reaction, 2.445 g of carbon reacts with 3.257 g of oxygen to form carbon monoxide gas. How many grams of carbon monoxide are formed in this reaction? 16. Ibuprofen has the chemical formula C13H18O2. It is 75.69% carbon, 8.80% hydrogen, and 15.51% oxygen. How many mg of carbon d ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...