Ms - cloudfront.net
... c. Using the previous information, how many grams of Fe3(PO4)2 precipitate can be formed? 47. Quicklime (CaO) can be prepared by roasting limestone (CaCO3). When 2.00 x 103g of CaCO3 are heated, the actual yield of CaO is 1.50 x 103g. What is the percent yield? CaCO3 CaO + CO2 48. If 1.85g of Alum ...
... c. Using the previous information, how many grams of Fe3(PO4)2 precipitate can be formed? 47. Quicklime (CaO) can be prepared by roasting limestone (CaCO3). When 2.00 x 103g of CaCO3 are heated, the actual yield of CaO is 1.50 x 103g. What is the percent yield? CaCO3 CaO + CO2 48. If 1.85g of Alum ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER 2016
... a. F2 b. Cl2 c. C d. NaCl e. KF f. CO2 g. H2 h. Ag i. Rust (Fe2O3) j. MgO k. O2 l. I2 m.CO n. K2CO3 ...
... a. F2 b. Cl2 c. C d. NaCl e. KF f. CO2 g. H2 h. Ag i. Rust (Fe2O3) j. MgO k. O2 l. I2 m.CO n. K2CO3 ...
Chemical Formulas
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
TEK 8.5D: Chemical Formulas
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
... Scientists use chemical formulas such as NaCl instead of common names (table salt) or chemical names (sodium chloride) because it is shorter, more accurate, and universally understood. ...
Chapter 6 review
... 23. Which family of elements includes inert (nonreactive) gases that glow when energized with electricity? _____________________________________________________ 24. The first periodic table was published by ______________________ in _______________. 25. Dimitri Mendeleev’s periodic table was arrange ...
... 23. Which family of elements includes inert (nonreactive) gases that glow when energized with electricity? _____________________________________________________ 24. The first periodic table was published by ______________________ in _______________. 25. Dimitri Mendeleev’s periodic table was arrange ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... f) hydrofluoric acid 15. A binary compound of zinc and sulfur contains 67.1% zinc by mass. What is the ratio of zinc and sulfur atoms in the compound? 16. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, 10B (19.9%), with an atomic mass of 10.0129, and 11B (80.1%) with an atomic mass of 11.00931. ...
... f) hydrofluoric acid 15. A binary compound of zinc and sulfur contains 67.1% zinc by mass. What is the ratio of zinc and sulfur atoms in the compound? 16. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, 10B (19.9%), with an atomic mass of 10.0129, and 11B (80.1%) with an atomic mass of 11.00931. ...
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best
... ______ 5. Nonmetallic elements in Group 17 that react with most metals to form salts are a. alkali metals. b. halogens. c. lanthanides. d. noble gases. ______ 6. The outer-level electron configuration of a neutral alkaline-earth metal atom consists of a. one electron in the s orbital. b. two electro ...
... ______ 5. Nonmetallic elements in Group 17 that react with most metals to form salts are a. alkali metals. b. halogens. c. lanthanides. d. noble gases. ______ 6. The outer-level electron configuration of a neutral alkaline-earth metal atom consists of a. one electron in the s orbital. b. two electro ...
Mr. Trachtenberg`s Big Chemistry Test Review Part I of III 20pts
... 11.) Elements in the upper right-‐hand corner of the Periodic Table have the highest electronegativies and ionization energies. 12.) Moving down a group atoms get larger 13.) Moving from l ...
... 11.) Elements in the upper right-‐hand corner of the Periodic Table have the highest electronegativies and ionization energies. 12.) Moving down a group atoms get larger 13.) Moving from l ...
All you need to know about Additional Science
... If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
... If we have a solution containing 100 g of sodium hydroxide, how much chlorine gas should we pass through the solution to make bleach? Too much, and some chlorine will be wasted, too little and not all of the sodium hydroxide will react. ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
How is the periodic table organized?
... silvery in their pure form and are highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
... silvery in their pure form and are highly reactive. This group includes the elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K). ...
1st Semester Exam in High School Chemistry
... A. dihydrogen monoxide B. hydrogen oxide C. hydrogen oxalate D. hydrogen dioxide ...
... A. dihydrogen monoxide B. hydrogen oxide C. hydrogen oxalate D. hydrogen dioxide ...
Chapter 8
... A substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat. Reactive elements combine with oxygen ...
... A substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light and heat. Reactive elements combine with oxygen ...
Semester 2 review questions
... of increasing mass and noticed a pattern in physical and chemical properties. 2. ____________________ was a British physicist who determined the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus)of the atoms of elements and then arranged the elements according to their atomic number. 3. _____(T/F) The ...
... of increasing mass and noticed a pattern in physical and chemical properties. 2. ____________________ was a British physicist who determined the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus)of the atoms of elements and then arranged the elements according to their atomic number. 3. _____(T/F) The ...
educator exam series
... Mathematical tables and electronic calculations may be used All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary For examiner’s use only: Questions Max. score Candidates score ...
... Mathematical tables and electronic calculations may be used All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary For examiner’s use only: Questions Max. score Candidates score ...
CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME
... N2O5 __________________________________ NO ____________________________________ CBr4 ___________________________________ CO ________________________________________ N2O4 _______________________________________ SO3 ________________________________________ IF7 _____________________________________ NH3 ...
... N2O5 __________________________________ NO ____________________________________ CBr4 ___________________________________ CO ________________________________________ N2O4 _______________________________________ SO3 ________________________________________ IF7 _____________________________________ NH3 ...
MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
1044771584 - Papacambridge
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Unit 10: Chemical Periodicity
... s, p, d, and f block and what other names these areas are called (transition, inner transition, representative elements, etc) (also alkali, alkaline earth, halogen, noble gas locations) vertical = groups (families), horizontal = periods, and how these are numbered where electrons are lost from ...
... s, p, d, and f block and what other names these areas are called (transition, inner transition, representative elements, etc) (also alkali, alkaline earth, halogen, noble gas locations) vertical = groups (families), horizontal = periods, and how these are numbered where electrons are lost from ...
Chemistry2 Midterm Review 2012 – Tuesday
... 29. Determine the molar mass of each of the following compounds: a. N2O5 b. FeCO3 c. Ca(C2H3O2)2 30. Calculate the percentage by mass of oxygen in the following compounds: a. NO2 b. CH3COOCH3 c. Cr(NO3)3 31. The molecular formula of allicin, the compound responsible for the smell of garlic, is C6H10 ...
... 29. Determine the molar mass of each of the following compounds: a. N2O5 b. FeCO3 c. Ca(C2H3O2)2 30. Calculate the percentage by mass of oxygen in the following compounds: a. NO2 b. CH3COOCH3 c. Cr(NO3)3 31. The molecular formula of allicin, the compound responsible for the smell of garlic, is C6H10 ...
Periodicity review handout
... 10. In each of the following pairs, which element is the most electronegative? a. Cl ...
... 10. In each of the following pairs, which element is the most electronegative? a. Cl ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... What will be the temperature when the volume increases to (60 mL) and the pressure to (2280 mmHg)? a- 1638ºC b- 1968ºC c- 1638K d- 45.5ºC ...
... What will be the temperature when the volume increases to (60 mL) and the pressure to (2280 mmHg)? a- 1638ºC b- 1968ºC c- 1638K d- 45.5ºC ...
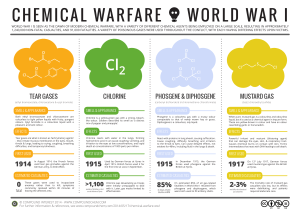
chemical warfare world war i
... liquid, but it’s used as a chemical agent in impure form. These are yellow-brown in colour and have an odour resembling garlic or horseradish. ...
... liquid, but it’s used as a chemical agent in impure form. These are yellow-brown in colour and have an odour resembling garlic or horseradish. ...