Metals and Non
... Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temperature; bromine is a liquid; iodine is a solid Bromine vaporizes easily Iodine sublimes easily upon heating Very reactive nonmetals Fluorine is the most electronegative and the most reactive element known Strongest elemental oxidizing agents; gain one ele ...
... Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temperature; bromine is a liquid; iodine is a solid Bromine vaporizes easily Iodine sublimes easily upon heating Very reactive nonmetals Fluorine is the most electronegative and the most reactive element known Strongest elemental oxidizing agents; gain one ele ...
ExamView - chemistry chapter 6 test.tst
... ____ 34. To what category of elements does an element belong if it is a poor conductor of electricity? a. metalloids c. metals b. nonmetals d. transition elements ____ 35. Alkali metals are extremely reactive because they a. have two valence electrons that form compounds with calcium and magnesium. ...
... ____ 34. To what category of elements does an element belong if it is a poor conductor of electricity? a. metalloids c. metals b. nonmetals d. transition elements ____ 35. Alkali metals are extremely reactive because they a. have two valence electrons that form compounds with calcium and magnesium. ...
Lab 18
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
students - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Hint: Start with most complicated substances first and leave simplest substances for last. solid sodium reacts w/oxygen to form solid sodium oxide ...
... Hint: Start with most complicated substances first and leave simplest substances for last. solid sodium reacts w/oxygen to form solid sodium oxide ...
Topic 3 - periodicity
... the distance between two bonded atoms. For this reason noble gases are given no value as they do not bond with other atoms. On descending a group, the atomic radius increase. This is because the outer electrons are getting further from the nucleus. This applies for both alkali metals and halogens. ...
... the distance between two bonded atoms. For this reason noble gases are given no value as they do not bond with other atoms. On descending a group, the atomic radius increase. This is because the outer electrons are getting further from the nucleus. This applies for both alkali metals and halogens. ...
2016
... f. Krypton g. Fluorine h. Scandium I. Arsenic J. Potassium K. Sodium l. chloride m. Iron n. Zinc o. tin 10. Write the latin names for each of the elements symbols: a. Na b. Au c. Ag d. Sn e. Fe f. Hg ...
... f. Krypton g. Fluorine h. Scandium I. Arsenic J. Potassium K. Sodium l. chloride m. Iron n. Zinc o. tin 10. Write the latin names for each of the elements symbols: a. Na b. Au c. Ag d. Sn e. Fe f. Hg ...
MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW! Unit 1 Convert the following: 1.) 2.02 x
... * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese ...
... * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or physical changes. 14.) Shredding cheese 15.) Melting cheese 16.) Digesting cheese ...
Atomic structure 1 and 2 Lankani Wijesinghe
... • Silvery metals • Less reactive than alkali metals • Produces H2 when reacted with water ...
... • Silvery metals • Less reactive than alkali metals • Produces H2 when reacted with water ...
Who`s in this family?
... Halogens Make up group 17 in the periodic table Who’s in this family? Most reactive group of nonmetals They have 7 valence electrons (Halogens react with most metals to produce salts • They have a wide range of physical properties: • Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temp. • Bromine is a liqu ...
... Halogens Make up group 17 in the periodic table Who’s in this family? Most reactive group of nonmetals They have 7 valence electrons (Halogens react with most metals to produce salts • They have a wide range of physical properties: • Fluorine and chlorine are gases at room temp. • Bromine is a liqu ...
Document
... hydrochloric acid in an open beaker. The mass of the products was found to be less than the total mass of the reactants. How should the students have conducted their experiment to reflect the law of conservation of mass? A the students should have used a less reactive metal in their experiment. B Th ...
... hydrochloric acid in an open beaker. The mass of the products was found to be less than the total mass of the reactants. How should the students have conducted their experiment to reflect the law of conservation of mass? A the students should have used a less reactive metal in their experiment. B Th ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
File
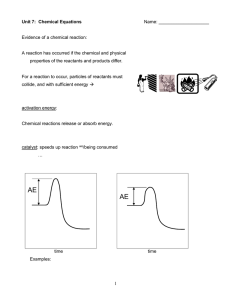
... “Exothermic” means that heat is released during the reaction. This often results in the reaction container feeling warm to the touch (heat is given off). Reactants Products + HEAT (heat on product side because released) “Endothermic” means that heat is absorbed during the reaction. This often resu ...
... “Exothermic” means that heat is released during the reaction. This often results in the reaction container feeling warm to the touch (heat is given off). Reactants Products + HEAT (heat on product side because released) “Endothermic” means that heat is absorbed during the reaction. This often resu ...
graphing atomic properties
... 5. Circle the atom with the largest atomic radius (size) in each group: a. aluminum, sulfur, phosphorus b. arsenic, bismuth, nitrogen c. iron, lithium, silicon d. barium, beryllium, bromine 6. Circle the atom that would require the LEAST amount of energy to remove an ea. magnesium, chlorine, silicon ...
... 5. Circle the atom with the largest atomic radius (size) in each group: a. aluminum, sulfur, phosphorus b. arsenic, bismuth, nitrogen c. iron, lithium, silicon d. barium, beryllium, bromine 6. Circle the atom that would require the LEAST amount of energy to remove an ea. magnesium, chlorine, silicon ...
Nomenclature Notes
... Step 1: Use the periodic table to identify the symbols of the elements (note that the second elements’ ending is –ide meaning, for example, that bromide is actually bromine). Step 2: Determine what number the prefix stands for and write this number as a subscript after the symbol. The number one (1) ...
... Step 1: Use the periodic table to identify the symbols of the elements (note that the second elements’ ending is –ide meaning, for example, that bromide is actually bromine). Step 2: Determine what number the prefix stands for and write this number as a subscript after the symbol. The number one (1) ...
Chem Reactions (and Balancing Equations)
... All chemical reactions: • have two parts • Reactants - the substances you start with • Products- the substances you end up with • The reactants turn into the products. • Reactants ...
... All chemical reactions: • have two parts • Reactants - the substances you start with • Products- the substances you end up with • The reactants turn into the products. • Reactants ...
4-3 Families of Elements
... iii. All elements with atomic numbers greater than 92 are man-made III. Nonmetals a. Carbon is found in three different forms and can also form many compounds i. Carbon can be in the form of graphite (pencil "lead"), diamonds, or fullerenes ii. Carbon can combine with other elements to form millions ...
... iii. All elements with atomic numbers greater than 92 are man-made III. Nonmetals a. Carbon is found in three different forms and can also form many compounds i. Carbon can be in the form of graphite (pencil "lead"), diamonds, or fullerenes ii. Carbon can combine with other elements to form millions ...
Section 2.5 Molecules and Ions
... Write the names for the three isotopes of hydrogen. Identify whether an element is a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. Classify elements as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, or noble gases. List several examples of diatomic molecules. Classify ions in terms of monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, catio ...
... Write the names for the three isotopes of hydrogen. Identify whether an element is a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. Classify elements as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, or noble gases. List several examples of diatomic molecules. Classify ions in terms of monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, catio ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Homework Booklet Unit 1 Feb14
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Chemistry Midterm Exam Review Sheet
... 35. Why do elements lose or gain electrons? 36. Why do ions have a + or – charge? 37. How many electrons are lost or gained if an ion has the following charge: a. +1 ...
... 35. Why do elements lose or gain electrons? 36. Why do ions have a + or – charge? 37. How many electrons are lost or gained if an ion has the following charge: a. +1 ...