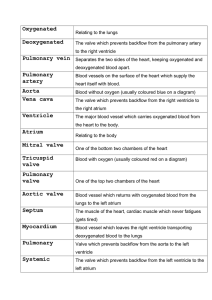
Q1-3 Circulatory System
... 2. Arteries – lead away from heart/ smooth muscles allow stretching/ *pulse – stretching arteries 3. Blood Pressure – force of blood against artery walls a. Systolic Pressure – upper number (120mmHg) Pressure when ventricles contract b. Diastolic Pressure – ventricles relaxed (70mmHg) c. Hypertensio ...
... 2. Arteries – lead away from heart/ smooth muscles allow stretching/ *pulse – stretching arteries 3. Blood Pressure – force of blood against artery walls a. Systolic Pressure – upper number (120mmHg) Pressure when ventricles contract b. Diastolic Pressure – ventricles relaxed (70mmHg) c. Hypertensio ...
Linda Bracken DEHF F
... During the relaxation phase of the heart beat (diastole) the left atria fills and blood passes through the Mitral valve (one way doorway) into the left ventricle (next room) and the mitral valve closes behind it ...
... During the relaxation phase of the heart beat (diastole) the left atria fills and blood passes through the Mitral valve (one way doorway) into the left ventricle (next room) and the mitral valve closes behind it ...
Heart Notes
... pulmonary veins; to LV through mitral valve; to body via aortic valve then aorta ...
... pulmonary veins; to LV through mitral valve; to body via aortic valve then aorta ...
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
... the study of the heart the "bishop's hat" valve the arteries regularly carry … blood exception to # 3 the veins regularly carry … blood exception to # 5 the largest veins and arteries are closest to / furthest from the heart 8. a persistent chest pain is called 9. a benign tumor of a blood vessel is ...
... the study of the heart the "bishop's hat" valve the arteries regularly carry … blood exception to # 3 the veins regularly carry … blood exception to # 5 the largest veins and arteries are closest to / furthest from the heart 8. a persistent chest pain is called 9. a benign tumor of a blood vessel is ...
Cardiopmyopathy
... The heart muscles can enlarge when being strained either by heart valves that don’t function properly or by high blood pressure. This will make the heart walls thicken and beat stronger but it can obstruct blood flow. ...
... The heart muscles can enlarge when being strained either by heart valves that don’t function properly or by high blood pressure. This will make the heart walls thicken and beat stronger but it can obstruct blood flow. ...
Este - Delmar
... Baroreceptors Baroreceptors, located in the carotid sinus, sense fluctuations in blood pressure and initiate compensatory responses (changes in heart rate, vasoconstriction). ...
... Baroreceptors Baroreceptors, located in the carotid sinus, sense fluctuations in blood pressure and initiate compensatory responses (changes in heart rate, vasoconstriction). ...
File
... __________________________ and contract to prevent ______________________________ of these valves ...
... __________________________ and contract to prevent ______________________________ of these valves ...
THE HEART THE VALVES
... ventricle, as well as through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. ...
... ventricle, as well as through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. ...
Printable Version
... 6. As you complete the lab, Review the "Lab Objectives" from the handout and write a synopsis of the lab addressing the first objective. Focus on the relationship between parts as they pertain to blood flow. Pay attention to oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow. ...
... 6. As you complete the lab, Review the "Lab Objectives" from the handout and write a synopsis of the lab addressing the first objective. Focus on the relationship between parts as they pertain to blood flow. Pay attention to oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flow. ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... more muscular side… to whole body • Aorta • Inferior vena cava – receives blood from the trunk to RA • * RV and LV pump at same time, same amount ...
... more muscular side… to whole body • Aorta • Inferior vena cava – receives blood from the trunk to RA • * RV and LV pump at same time, same amount ...
Chemistry
... You must answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper in complete sentences! 1. Describe the flow of blood through both the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits. a. As you describe the blood flow, you must name each chamber, valve, artery and vein in the heart that blood travels through. 2. Explai ...
... You must answer these questions on a separate sheet of paper in complete sentences! 1. Describe the flow of blood through both the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits. a. As you describe the blood flow, you must name each chamber, valve, artery and vein in the heart that blood travels through. 2. Explai ...
Quiz: The Circulatory System. - year22011-2012
... 1- How many chambers does the heart have? a. Six. b. Five. c. Four. d. Three. 2- The movement of blood through the heart and body is called: a. Circulation. b. Locomotion. c. Ventriculation. d. Heart pump. 3- The beating sound your heart makes comes from: a. Blood going in the wrong direction. b. Va ...
... 1- How many chambers does the heart have? a. Six. b. Five. c. Four. d. Three. 2- The movement of blood through the heart and body is called: a. Circulation. b. Locomotion. c. Ventriculation. d. Heart pump. 3- The beating sound your heart makes comes from: a. Blood going in the wrong direction. b. Va ...
CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM The system which is related with the
... `When the heart rate is greater then 100bpm it is called Tachycardia’ Due to-Excessive water intake -Mental hasitation -Exercise -Disease condition (fever, rheumatic fever, arthritis) ...
... `When the heart rate is greater then 100bpm it is called Tachycardia’ Due to-Excessive water intake -Mental hasitation -Exercise -Disease condition (fever, rheumatic fever, arthritis) ...
Heart Physiology
... Ventricles contract, increasing pressure A-V valves close Atria begin filling with blood ...
... Ventricles contract, increasing pressure A-V valves close Atria begin filling with blood ...
Components of S2 - University Health
... • The pressure & its rate of development across the closed semilunar valves – The greater the rate of development of the pressure gradient (rapid ventricular relaxation), the more rapid the velocity of valve vibration and the louder the sound produced ...
... • The pressure & its rate of development across the closed semilunar valves – The greater the rate of development of the pressure gradient (rapid ventricular relaxation), the more rapid the velocity of valve vibration and the louder the sound produced ...
LECTURE # 23 – Friday OCTOBER 25, 2001 Outline
... –Prevent BACKFLOW of blood from the ventricles to atria when ventricles CONTRACT ...
... –Prevent BACKFLOW of blood from the ventricles to atria when ventricles CONTRACT ...
Name: Class: ______ Date: Sheep Heart Dissection Student
... 12. Using words, describe blood flow through the major blood vessels and heart, starting with deoxygenated blood that has been returned from the body. ...
... 12. Using words, describe blood flow through the major blood vessels and heart, starting with deoxygenated blood that has been returned from the body. ...
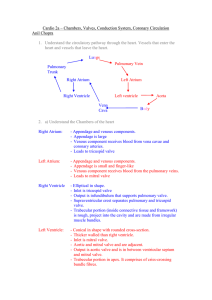
Chambers Valves, Conduction System, Coronary Circulation
... Ventricular septum: runs obliquely between left and right ventricles. It is mainly muscular but also contains Purkinje Fibres. A small part of the ventricular septum is membranous. c) Understand the components of heart valves. Atrioventricular Valves: between atria and ventricles. prevent backfl ...
... Ventricular septum: runs obliquely between left and right ventricles. It is mainly muscular but also contains Purkinje Fibres. A small part of the ventricular septum is membranous. c) Understand the components of heart valves. Atrioventricular Valves: between atria and ventricles. prevent backfl ...
Structure of the Cardiovascular System
... heart supplying vital organs and tissues* - Remember ‘A’ = ‘A’way • Thicker, muscular wall to allow blood to be shunted around the body • Dealing with blood under high pressure * except for the pulmonary artery - transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs ...
... heart supplying vital organs and tissues* - Remember ‘A’ = ‘A’way • Thicker, muscular wall to allow blood to be shunted around the body • Dealing with blood under high pressure * except for the pulmonary artery - transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs ...
Slide ()
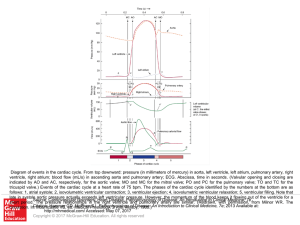
... tricuspid valve.) Events of the cardiac cycle at a heart rate of 75 bpm. The phases of the cardiac cycle identified by the numbers at the bottom are as follows: 1, atrial systole; 2, isovolumetric ventricular contraction; 3, ventricular ejection; 4, isovolumetric ventricular relaxation; 5, ventricul ...
... tricuspid valve.) Events of the cardiac cycle at a heart rate of 75 bpm. The phases of the cardiac cycle identified by the numbers at the bottom are as follows: 1, atrial systole; 2, isovolumetric ventricular contraction; 3, ventricular ejection; 4, isovolumetric ventricular relaxation; 5, ventricul ...
The Heart
... inferior vena cava and superior vena cava. 2. Blood passes through the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle. 3. Blood passes through the pulmonary valve to enter the pulmonary artery. ...
... inferior vena cava and superior vena cava. 2. Blood passes through the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle. 3. Blood passes through the pulmonary valve to enter the pulmonary artery. ...
Heart 4: Fibrous Skeleton of the Heart
... In addition to cardiac muscle tissue, the heart wall also contains a dense connective tissue network forming the fibrous skeleton of the heart that reinforces the myocardium internally and anchors the cardiac muscle fibers. This network of collagen and elastin fibres is thicker in some areas than ot ...
... In addition to cardiac muscle tissue, the heart wall also contains a dense connective tissue network forming the fibrous skeleton of the heart that reinforces the myocardium internally and anchors the cardiac muscle fibers. This network of collagen and elastin fibres is thicker in some areas than ot ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.