* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy and Physiology
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
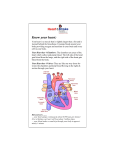
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 20: The Heart Introduction • • • • • • • Heart beat 100,000X / day ( moves 8000L) Muscle is never at rest Pulmonary circuit goes to heart from lungs Systemic circuit goes to heart from body Arteries (afferent) – away from the heart Veins (efferent) – toward the heart Capillaries – exchange vessels 20.1 Anatomy of the Heart • • • • • • Tilts to left of sternum Between intercostal spaces 3 and 5 Associated with lots of fatty tissue Pericardial sac – protects and lubricates (fluid) Myocardium = heart muscle Coronary arteries = supply blood to heart muscle itself ( these are “bypassed”) Chambers and vessels • Superior vena cava – blood from head/neck/limbs to RA • Right Atrium – receives blood from body • Right ventricle – pump * / to lungs • Left Atrium– from lungs • Left ventricle – pump * / to body through; thicker more muscular side… to whole body • Aorta • Inferior vena cava – receives blood from the trunk to RA • * RV and LV pump at same time, same amount Chambers, vessels and valves • RA and RV separated by tricuspid valve • Cusps anchored to chordae tendineae that tug flaps down to prevent backflow • LA receives blood through mitral valve • LV is associated with semilunar valve 20.2 Generation of Action Potentials • Muscle cells in conducting system coordinate beat • Contractile cells contract to propel blood • Electrocardiograph (ECG, EKG) shows electrical events of heart beat • App called cardiograph • Sinoatrial (SA) node in RA ▫ Spontaneous depolarization without neural or hormonal ▫ 80 – 100 action potentials per minute ▫ Pacemaker cells • Atrioventricular (AV) node between A and V ▫ 50 msec from SA to AV ▫ Delay at AV node so atria finish contracting before ventricles • Conducting cells with internodal pathways do not have stable resting potential; drift toward threshold • Purkinje fibers ▫ Rapid conduction of action potentials ventricular myocardium Energy • Heart muscles have lots of mitochondria that break down both fatty acids and glucose (stored as glycogen) • Have heme units (part of hemoglobin) stored as myoglobin so they can have access to lots of O2 – very aerobic • Calcium ions are very important to the conduction of action potentials in the cardiac muscle cells