* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE HEART THE VALVES
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
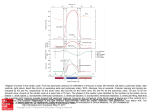
THE HEART The heart is the pumping mechanism of the circulatory system. It is a double pumping organ that beats ~90 000 times every day (~6570 bpm) and is separated into two distinct sides. The heart has 4 chambers. There is a left and right atrium, where blood enters the heart from major veins. The atria then feed blood into the left and right ventricles, which pump the blood out to the lungs and to the rest of the body. These chambers are separated by oneway valves. THE VALVES The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. The bicuspid valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle. The pulmonary valve separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary artery. The aortic valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta. 1 OTHER MAJOR PARTS The largest artery in the body is called the aorta. It has 3 superior branches and a descending portion to the lower body. The largest vein in the body is called the vena cava. It has a superior portion and an inferior portion. The heart comes to a point at the bottom, called the apex, and the left and right sides of the heart are separated by a thick wall called the septum. 2 3 PATHWAY OF BLOOD Blood enters the heart from the superior and inferior vena cava. This is deoxygenated blood as it is coming back to the heart to replenish the oxygen it dispersed to the cells. The blood pools in the right atrium. At the same time as this, oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the heart through the pulmonary veins and pools in the left atrium. When the atria contract, blood is forced through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, as well as through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. When the ventricles contract, deoxygenated blood is forced through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which takes blood to the lungs to pick up new oxygen. This blood will REENTER the heart in the left atrium. At the same time, oxygenated blood is pumped through the aortic valve into the aorta, which takes blood into the systemic system to provide oxygen to somatic cells. This blood will REENTER the heart in the right atrium, starting the entire process over again. *** Which chamber(s) do you think have the thickest walls? *** 4