* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart - Dr Magrann
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
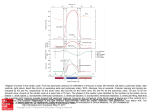
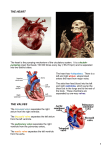
Heart STRUCTURES TO KNOW ON THE HEART • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1. apex and base 2. right and left atrium 3. right and left ventricle 4. interventricular septum 5. mitral valve (bicuspid valve) 6. tricuspid valve 7. pulmonary semilunar valve 8. aortic semilunar valve 9. papillary muscles 10. chordae tendinae 11. SA node 12. AV node 13. superior vena cava 14. inferior vena cava 15. pulmonary trunk (branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries) 16. pulmonary arteries (right and left) 17. pulmonary vein 18. aorta 19. right and left coronary artery 20. coronary sinus 21. ductus arteriosis 22. foramen ovale fossa ovale 23. ligamentum arteriosum Layers of the Heart Epicardium (outer layer of heart) AKA visceral layer of serous pericardium It’s the shiny surface on outside of heart Myocardium (contains cardiac muscle) Endocardium (lines the inside of heart) Arteries and Veins ARTERY Carries blood AWAY from the heart. VEIN Carries blood TO the heart. Base Atrial septum Right atrium Right ventricle Apex Ventricular septum Left atrium Left ventricle Apex Blood Flow Deoxygenated blood goes to the heart via the superior and inferior vena cavae, which empty into the right atria. Blood goes from the right atria into the right ventricle by going through the tricuspid valve. It then goes into the lungs to get oxygen. Blood Flow Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins and enters into the left atria. It goes into the left ventricle by passing through the bicuspid (mitral) valve. If this valve is blocked, blood will get backed up into the pulmonary circulation. Blood goes from the left ventricle into the aorta, where it is sent to the body. Blood Flow Because there is high pressure in the ventricles, there are semilunar valves between the ventricles and the great arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta). The heart sounds (lub-dub) are caused from the vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut. Heart Valves Bicuspid (Mitral) valve Tricuspid valve Between right atrium and right ventricle Aortic semilunar valve between left atrium and left ventricle Between left ventricle and aorta Pulmonary semilunar valve Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery NOTE: The semilunar valves are between the ventricles and the great arteries Heart Valves To keep the valves from prolapsing (turning inside out), they are tied down by cords, called cordae tendonae. The cordae tendonae are anchored to papillary muscles embedded in the myocardium. Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Apex Left atrium Mitral (bicuspid) valve Left ventricle Aortic semilunar valve Mitral (bicuspid) valve Trabeculae carnae Pectinate muscles Cordae tendonae Coronary Arteries The heart itself needs oxygen, too. Right and left coronary arteries come off the aorta and circle the outside of the heart to supply the heart tissue. When they are clogged, they may need a coronary bypass surgery. The saphenous vein (from the leg) is the vessel most often used to replaced the damaged coronary artery. Coronary Sinus This is the largest of the coronary veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart tissue back to the right atrium. Left coronary artery Heart Beat The heart contracts because of electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node (SA node) and the atrioventricular node (AV node). The SA node is the pacemaker. It signals the atria to contract. The AV node causes the ventricles to contract. SA node Right atrium AV node Bundle of His Bundle branches Purkinje fibers Superior vena cavae Aorta Pulmonary trunk SA Node AV Node Right Atrium Left Atrium Cordae tendonae Interventricular septum Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Papillary muscles Trabeculae carnae Superior vena cavae Aorta Pulmonary trunk Tricuspid valve Right Atrium Left Atrium Bicuspid (Mitral) valve Cordae tendonae Papillary muscles Aortic semilunar valve Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Superior vena cavae Pulmonary trunk Aorta Right coronary artery Right Atrium Left Atrium Left coronary artery Posterior view of heart Trachea Superior vena cavae Aorta Pulmonary veins Coronary sinus Left Atrium Right Atrium Inferior vena cavae Left Atrium Right Atrium Pulmonary semilunar valve Left ventricle (the wall is thicker) Right ventricle Fetal Heart The fetus has no need to use its pulmonary circulation since it gets oxygen from the placenta. Therefore, blood flows from the pulmonary artery right back into the aorta. Fetal Heart The fetus also has an opening between the right and left atria so blood can be sent to the body faster. Fetal Heart Foramen Ovale An opening between the right and left atrium in a fetus, allows fetal blood to bypass the lungs. At birth, it should close, leaving a bit of fibrous tissue there called the Fossa Ovalis. Ductus Arteriosis A connection in the fetus between the pulmonary artery and the aorta. At birth, it should close, leaving a bit of fibrous tissue there called the Ligamentum arteriosum. Heart problems in newborn Fetal Circulation Umbilical Vein This is an example where a vein carries oxygenated blood (in the fetus). Umbilical Artery This artery has a mixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (in the fetus). Umbilical cord Placenta Umbilical artery (blue; carries mixed blood) Umbilical vein (red; carries oxygenated blood) Arteries and Veins ARTERY Carries blood AWAY from the heart. They USUALLY carry oxygen, but not always. VEIN Carries blood TO the heart. They USUALLY are not oxygenated, but sometimes they are. Blood Vessels Arterial walls are thicker than venous walls because they are under higher pressure. Arteries have more elastin than veins. The saphenous vein is often used to bypass a damaged coronary artery during a coronary bypass surgery. ARTERY MEDIUM POWER ARTERIOLE HIGH POWER VEIN VENUOLE CAPILLARY HIGH POWER