Name_____________________________________ Per_____
... Page 679: External Anatomy of the HEART Page 681: Internal Anatomy of the HEART 1. Page 682 – 684 / Pathway of BLOOD Trace a drop of blood from inferior vena cava, through heart, and to aorta. ...
... Page 679: External Anatomy of the HEART Page 681: Internal Anatomy of the HEART 1. Page 682 – 684 / Pathway of BLOOD Trace a drop of blood from inferior vena cava, through heart, and to aorta. ...
Biology 12 Name: Quiz #14 Match each term in the left
... 1. Match each term in the left-hand column with the best definition from the right-hand column. Please put the letter of the best definition beside the appropriate term. (1 mark each = 9 marks) ...
... 1. Match each term in the left-hand column with the best definition from the right-hand column. Please put the letter of the best definition beside the appropriate term. (1 mark each = 9 marks) ...
ekg jeopardy review game for exam #1
... What is the minimum amount of points that may be connected by electrical leads to produce an EKG? ...
... What is the minimum amount of points that may be connected by electrical leads to produce an EKG? ...
Position of the Heart
... P= wave from SA node through atria QRS = ventricular depolarization T wave = ventricular repolarization P-Q interval = time from atria contraction to beginning of ventricular contraction. Q-T interval = ventricular depolarization to repolarization. ...
... P= wave from SA node through atria QRS = ventricular depolarization T wave = ventricular repolarization P-Q interval = time from atria contraction to beginning of ventricular contraction. Q-T interval = ventricular depolarization to repolarization. ...
Heart Damage
... Some cancer treatments can damage the heart in different locations and in a variety of ways. ...
... Some cancer treatments can damage the heart in different locations and in a variety of ways. ...
the chemokine receptor cxcr7 functions in endocardial
... Cardiac disease is the number one killer in developed countries and congenital heart diseases are the most common birth defects worldwide. The heart supplies nutrients and oxygen to the entire body, therefore the proper development and function of the heart is essential for survival of an organism. ...
... Cardiac disease is the number one killer in developed countries and congenital heart diseases are the most common birth defects worldwide. The heart supplies nutrients and oxygen to the entire body, therefore the proper development and function of the heart is essential for survival of an organism. ...
17. CV II - EKG-mechanical
... QRS Wave or Complex: caused by depolarization of ventricles (atrial repolarization masked by this) T Wave: caused by repolarization of ventricles PR Interval: time elapsed between start of P wave and R wave (period of delay at AV node) (called PQ interval in text) • ECG Leads (12 combinations of ele ...
... QRS Wave or Complex: caused by depolarization of ventricles (atrial repolarization masked by this) T Wave: caused by repolarization of ventricles PR Interval: time elapsed between start of P wave and R wave (period of delay at AV node) (called PQ interval in text) • ECG Leads (12 combinations of ele ...
The Bodies Transport System 14.1
... ________________ carry blood away from the heart. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ are tiny vessels that bring blood to every cell. ...
... ________________ carry blood away from the heart. ________________ carry blood back to the heart. ________________ are tiny vessels that bring blood to every cell. ...
1-coronary valve
... In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds often described as lub and dub , that occur in sequence with each heart beat. These are the first heart sound (S1) and second heart sound (S2), produced by the closing of the aortic valves and semilunar valves respectively. In addition to these n ...
... In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds often described as lub and dub , that occur in sequence with each heart beat. These are the first heart sound (S1) and second heart sound (S2), produced by the closing of the aortic valves and semilunar valves respectively. In addition to these n ...
Sheep Heart Dissection
... 5. Look for major blood vessels bringing blood into and out of the heart. Snip away and extraneous tissue, potentially from the pericardial sac. Identify ventricles and atria. 6. Orient the heart identifying right and left side and the anterior/ventral and posterior/dorsal sides. 7. Find the pulmona ...
... 5. Look for major blood vessels bringing blood into and out of the heart. Snip away and extraneous tissue, potentially from the pericardial sac. Identify ventricles and atria. 6. Orient the heart identifying right and left side and the anterior/ventral and posterior/dorsal sides. 7. Find the pulmona ...
Q. State the procedure that you followed to expose a semilunar valve.
... Q. State one factor that decreases heart rate. A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. What is the fun ...
... Q. State one factor that decreases heart rate. A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? A. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Q. What is the fun ...
International School of Tianjin Digestion and Transport
... epithelial layer / lining / epithelium; microvilli; goblet cells; ...
... epithelial layer / lining / epithelium; microvilli; goblet cells; ...
Heart Anatomy and Physiology Presentation
... • occurs after ventricular contraction • semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
... • occurs after ventricular contraction • semilunar valves closing Murmur – abnormal heart sound ...
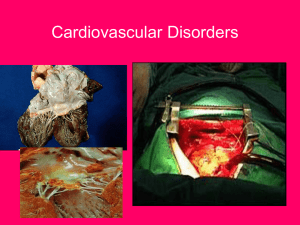
Cardiovascular Disorders/homeostatic Imbalances
... valve stretches and bulges into left atrium during ventricular contraction • Blood can regurgitate into the left atrium • Palpitations, fatigue, anxiety, chest pains • associated with arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation) that may ...
... valve stretches and bulges into left atrium during ventricular contraction • Blood can regurgitate into the left atrium • Palpitations, fatigue, anxiety, chest pains • associated with arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation) that may ...
Grade 11 Biology Worksheet -2 ( Circulatory system) a)Give one
... 3) Ventricle relaxes as a closed chamber in the early phase of its diastole. 4) You can palpate the pulse on an artery in each heart beat. 5) There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the human heart. 6) Atria have thinner walls than ventricles 7) Blood flows under pressure in the a ...
... 3) Ventricle relaxes as a closed chamber in the early phase of its diastole. 4) You can palpate the pulse on an artery in each heart beat. 5) There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the human heart. 6) Atria have thinner walls than ventricles 7) Blood flows under pressure in the a ...
Hollywood Squares Circulatory (6-8)
... This is composed of the heart & blood vessels including arteries, veins & capillaries. ...
... This is composed of the heart & blood vessels including arteries, veins & capillaries. ...
Mnstrviola`s SSSS Anatomy Practice Test KEY 2014-2015
... In the systemic circuit, blood travels from the left atrium through the mitrial valve into the left ventricle. It then goes through the aortic valve, into the aorta and then to various parts of the body. When blood returns from the body, it enters from the vena cava into the right atrium. It then g ...
... In the systemic circuit, blood travels from the left atrium through the mitrial valve into the left ventricle. It then goes through the aortic valve, into the aorta and then to various parts of the body. When blood returns from the body, it enters from the vena cava into the right atrium. It then g ...
CDVD Handout Stage C - Veterinary Cardiology Specialists
... left side of the heart becomes leaky from old age, degenerative changes. The green circles in all the images represent the left atrial chamber. The shortest arrow in the upper photo to the right, labeled “A”, represents the direction of normal blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricula ...
... left side of the heart becomes leaky from old age, degenerative changes. The green circles in all the images represent the left atrial chamber. The shortest arrow in the upper photo to the right, labeled “A”, represents the direction of normal blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricula ...
Cardiovascular System 1
... of diaphragm, posterior of sternum, vertebral column, and large blood vessels attached to heart ...
... of diaphragm, posterior of sternum, vertebral column, and large blood vessels attached to heart ...
Introduction to Physiology
... • Parietal pericardium – not a heart wall layer but is continuous serous membrane with visceral pericardium. Pericardial cavity – between the Epicardium (visceral) and the parietal pericardium. Contains serous ...
... • Parietal pericardium – not a heart wall layer but is continuous serous membrane with visceral pericardium. Pericardial cavity – between the Epicardium (visceral) and the parietal pericardium. Contains serous ...
Interferences to Oxygen: congenital anomalies and cardiovascular
... Improved function of valve Less problem with complications ...
... Improved function of valve Less problem with complications ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.