* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH. 13 Cardio Notes
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
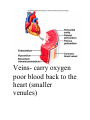
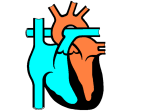
Ch. 13: Cardiovascular System -includes pump and blood vessels -carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes wastes -adult heart 14cm x 9 cm Pericardium-sac enclosing the heart, several layers Layers of heart wallsouter epicardium, middle myocardium, inner endocardium Veins- carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart (smaller venules) Arteries-carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (smaller arterioles) Capillariessmallest—connect smallest arterioles with smallest venules Oxygen poor blood travels from body parts to Inferior--Superior Vena Cava to Right Atrium—Tricuspid Valve—Right Ventricle--Pulmonary Artery— Lungs (picks up O2)—Pulmonary Veins—Left Atrium—Bicuspid (mitral)Valve--Left Ventricle—Aorta— Body Cardiac cycle- a heartbeat http://msjensen.cehd.umn.edu/1135/links/animations/Flash/0028-swf_the_cardiac_cy.swf Atria relax-blood flows in them and then into ventricles, atria contract (Systole), then atria relax (Diastole) and Ventricles contract (Systole—Lubb), then relax (Diastole—Dupp) Blood pressure-force blood exerts in arteries Systolic pressure/diastolic pressure— Pulse-expanding and recoiling of arterial wall Videos: http://www.mayoclini c.com/health/what-isbloodpressure/MM00783 http://www.mayoclini c.com/health/how-tomeasure-bloodpressure/MM00784 Hypertensionpersistently elevated arterial pressure Caused by: kidney disease, high sodium, obesity, stress, arteriosclerosis (decreased elasticity of artery walls and narrowed arteries) Consequences: Enlarges heart, heart muscle weakens/can die, atherosclerosis, thrombus or embolism…stroke Cardiac Conduction System-areas that initiate and distribute impulses SA (sinoatrial)nodespecialized tissue that acts as the pacemaker Heart Sounds Lubb-during ventricular contraction, when AV valves are closing Dupp-during ventricular relaxation, when pulmonary and aortic valves are closing Sheep Heart dissection http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio202/cyberheart/suphrt. htm http://www.hometrainingtools.com/heart-dissectionproject/a/1318/ Factors affecting blood flow: Heart action-pressure cardiac output Blood volume-lower blood volume, lower pressure Resistance-Friction hinders blood flow Viscosity-greater viscosity, greater resistance—blood pressure rises