AS Unit F321 Unit 1 Side A check list
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, 2ulphuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pot ...
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, 2ulphuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pot ...
CHEM104 Examlette 1 – ANSWERS TOTAL POINTS = 94 Multiple
... b) some of the salt has precipitated c) there is some association between ions d) all of the above 6. a) Name the categories of solids (5 pts): metals, ionic solids, molecular solids, network solids, amorphous solids b) Pick two from the list in (a) and describe in what ways these two solids types a ...
... b) some of the salt has precipitated c) there is some association between ions d) all of the above 6. a) Name the categories of solids (5 pts): metals, ionic solids, molecular solids, network solids, amorphous solids b) Pick two from the list in (a) and describe in what ways these two solids types a ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... salts apart. Ions have charges and attract the opposite charges on the water molecules. ...
... salts apart. Ions have charges and attract the opposite charges on the water molecules. ...
Module 8 - Brookville Local Schools
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
Ch 6 Jeopardy Review
... In these bonds valence electrons are able to freely move between a cation lattice. ...
... In these bonds valence electrons are able to freely move between a cation lattice. ...
Zumdahl Chapter
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
... First Year Chemistry Podcast DVD Featuring Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams from Peak Educational Consulting LLC All Rights Reserved © This is an interactive page that allows you to get to all of the content on this DVD. Click to each unit packet or podcast. The podcasts require Quicktime and the pa ...
First, there are several issues regarding this course need to be
... In order to apply the Born equation (10.2), we need to know the radius of the corresponding ions. These numbers can be obtained from Table 23.3 r(Br-) = 196 pm; r(Cl-) = 181 pm; thus ∆solvGө(Br-, aq) - ∆solvGө (Cl-, aq) = - (1/196 – 1/181)*6.86*104 kJ mol-1 = 29.00 kJ mol-1 (The calculated result is ...
... In order to apply the Born equation (10.2), we need to know the radius of the corresponding ions. These numbers can be obtained from Table 23.3 r(Br-) = 196 pm; r(Cl-) = 181 pm; thus ∆solvGө(Br-, aq) - ∆solvGө (Cl-, aq) = - (1/196 – 1/181)*6.86*104 kJ mol-1 = 29.00 kJ mol-1 (The calculated result is ...
Unit 4 - Dorman High School
... V. Ionic Bonding and Structures of Ionic Compounds When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can ...
... V. Ionic Bonding and Structures of Ionic Compounds When an ionic compound is formed the bond is extremely strong. We write the formulas for these compounds, but they are empirical formulas because the compound is composed of a very tightly packed and ordered arrangement of ions. Ionic compounds can ...
Pre- AP & NET IONIC EQUATIONS
... 3. an excess of ammonia gas is bubbled through a solution saturated with silver chloride --which reactant acts as a Lewis base? explain 2 NH3 + AgCl → [Ag(NH3)2] + + Cl--the NH3 donates electron pairs to the silver ion and is thus a Lewis base 4. a concentrated solution of ammonia is added to a susp ...
... 3. an excess of ammonia gas is bubbled through a solution saturated with silver chloride --which reactant acts as a Lewis base? explain 2 NH3 + AgCl → [Ag(NH3)2] + + Cl--the NH3 donates electron pairs to the silver ion and is thus a Lewis base 4. a concentrated solution of ammonia is added to a susp ...
Science 1206 Unit 3 Part 1
... c. Silicon trifluoride d. Hexaphosphorus pentachloride Worksheet #2 ...
... c. Silicon trifluoride d. Hexaphosphorus pentachloride Worksheet #2 ...
Science 9
... the outer shell of an atom or ion. 2. ___________________ is an atom with a positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. 3. ___________________ is the attraction between positive and negative ions. 4. ___________________ is any of the group 2 elements beryllium, magnesium, calci ...
... the outer shell of an atom or ion. 2. ___________________ is an atom with a positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. 3. ___________________ is the attraction between positive and negative ions. 4. ___________________ is any of the group 2 elements beryllium, magnesium, calci ...
File
... A reversible reaction. The reaction can occur in both directions. Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because its ionization in water is incomplete. ...
... A reversible reaction. The reaction can occur in both directions. Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte because its ionization in water is incomplete. ...
Net ionic equation
... Soluble only means greater than 0.01 moles dissolve in 1 L of solution 1. All nitrates, acetates, ammonium and Group 1 salts are soluble 2. Solubility of chlorides, bromides and iodides (all soluble except Ag+ Pb2+ and Hg22+) 3. Hydroxides (all insoluble except rule 1, Ca, Sr, Ba) ...
... Soluble only means greater than 0.01 moles dissolve in 1 L of solution 1. All nitrates, acetates, ammonium and Group 1 salts are soluble 2. Solubility of chlorides, bromides and iodides (all soluble except Ag+ Pb2+ and Hg22+) 3. Hydroxides (all insoluble except rule 1, Ca, Sr, Ba) ...
Review Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + energy The release of energy is shown as a product in the equation. We can show this in an energy level diagram: ...
... CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + energy The release of energy is shown as a product in the equation. We can show this in an energy level diagram: ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
Chemistry 3202 Name: Acid-base Theory Problems Assignment 1
... from a hydrochloric acid solution. Label the reactants as acids or bases. ...
... from a hydrochloric acid solution. Label the reactants as acids or bases. ...
Chemical Properties of Water - Part 2
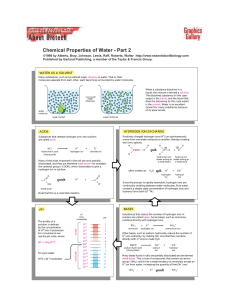
... WATER AS A SOLVENT Many substances, such as household sugar, dissolve in water. That is, their molecules separate from each other, each becoming surrounded by water molecules. ...
... WATER AS A SOLVENT Many substances, such as household sugar, dissolve in water. That is, their molecules separate from each other, each becoming surrounded by water molecules. ...
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
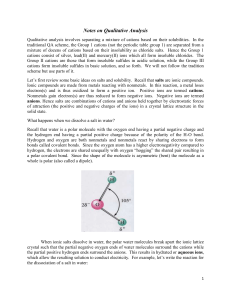
... cations consist of silver, lead(II) and mercury(II) ions which all form insoluble chlorides. The Group II cations are those that form insoluble sulfides in acidic solution, while the Group III cations form insoluble sulfides in basic solution, and so forth. We will not follow the tradition scheme bu ...
... cations consist of silver, lead(II) and mercury(II) ions which all form insoluble chlorides. The Group II cations are those that form insoluble sulfides in acidic solution, while the Group III cations form insoluble sulfides in basic solution, and so forth. We will not follow the tradition scheme bu ...
Chapter 8
... Covalent bonds are not as strong as ionic bonds. – Melting temperature of salt is 801 degrees C, sugar is 185 degrees C. ...
... Covalent bonds are not as strong as ionic bonds. – Melting temperature of salt is 801 degrees C, sugar is 185 degrees C. ...
Chemical and Molecular Formulas PPT
... more than one chemical compound? A: Letters of the alphabet can be combined in many different ways to form words, the atoms of 2 or more elements can also be combined in different ways to form more than one type of compound • consider elements A&B: AB, A2B2, AB2 … • what does the subscript 2 represe ...
... more than one chemical compound? A: Letters of the alphabet can be combined in many different ways to form words, the atoms of 2 or more elements can also be combined in different ways to form more than one type of compound • consider elements A&B: AB, A2B2, AB2 … • what does the subscript 2 represe ...
Gas-forming Reactions
... methanol (CH3OH) do not form ions in solution and thus do not conduct electricity. ...
... methanol (CH3OH) do not form ions in solution and thus do not conduct electricity. ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.