TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND SOLUTION CHEMISTRY
... assumed to react completely with any weak acid it encounters. 11. An acid-base reaction is often called a ______________________________. When just enough base is added with the acid in a solution, we say the acid has been neutralized. ***** What volume of 0.250 M KOH will react completely with 25.0 ...
... assumed to react completely with any weak acid it encounters. 11. An acid-base reaction is often called a ______________________________. When just enough base is added with the acid in a solution, we say the acid has been neutralized. ***** What volume of 0.250 M KOH will react completely with 25.0 ...
Chapter3 Solutions
... separate and the elements are gases. Another factor that contributes is the fact that the elements are relatively light, compared to iodine, for example. 11. Ionic compounds do not contain molecules, since one ion is bound to several other ions of opposite charge in a lattice. To speak of intermolec ...
... separate and the elements are gases. Another factor that contributes is the fact that the elements are relatively light, compared to iodine, for example. 11. Ionic compounds do not contain molecules, since one ion is bound to several other ions of opposite charge in a lattice. To speak of intermolec ...
chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ...
... Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ...
Pre-AP Chemistry - Simple Rules for Electron Exchange Simple
... Tracking how they change as each chemical species goes from reactants to products helps us keep track of which species loses and which species gains electrons. You will note that oxidation numbers (or “oxidation states” for groups of like atoms) are similar, but not identical to, formal ionic charge ...
... Tracking how they change as each chemical species goes from reactants to products helps us keep track of which species loses and which species gains electrons. You will note that oxidation numbers (or “oxidation states” for groups of like atoms) are similar, but not identical to, formal ionic charge ...
Chemical Bonding
... Covalent Bonding Example 3 Seven of the elements have such high attraction for electrons that they will never exist as individual, unattached atoms. Anytime these elements are present in pure form they will bond to other atoms of the same element. For example a fluorine atom will readily bond to a ...
... Covalent Bonding Example 3 Seven of the elements have such high attraction for electrons that they will never exist as individual, unattached atoms. Anytime these elements are present in pure form they will bond to other atoms of the same element. For example a fluorine atom will readily bond to a ...
SC-Database
... • An edited sub-set of SC-Database has been prepared and is included with SCDatabase and with Sol-Eq.(Solution Equilibria; principles and applications). And other packages. • Ionic strength corrections using Specific Interaction Theory have been added. ...
... • An edited sub-set of SC-Database has been prepared and is included with SCDatabase and with Sol-Eq.(Solution Equilibria; principles and applications). And other packages. • Ionic strength corrections using Specific Interaction Theory have been added. ...
Dissociation
... — Learn to use your reference tables — it’s fun and if you take advantage of this special limited time offer, it’s absolutely free — The guidelines are useful in helping to predict what will happen if the solutions of two different soluble compounds are mixed — If the mixing results in a combination ...
... — Learn to use your reference tables — it’s fun and if you take advantage of this special limited time offer, it’s absolutely free — The guidelines are useful in helping to predict what will happen if the solutions of two different soluble compounds are mixed — If the mixing results in a combination ...
acids: bases - IDS-chem2-Rn-10
... small amounts to a solution so that the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. ...
... small amounts to a solution so that the pH (acidity or basicity) of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. ...
Activities 2
... E) Covalent bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. 4) Which bond or interaction between atoms would be most difficult to disrupt when the interacting atoms are put into water and heated slightly? A) covalent bond B) hydrogen ...
... E) Covalent bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. 4) Which bond or interaction between atoms would be most difficult to disrupt when the interacting atoms are put into water and heated slightly? A) covalent bond B) hydrogen ...
Topic Book periodicity
... together. Increases across the period while following elements which exhibit metallic bonding (due to increased strength following increased number of valence e-.) Highest m.p. of period lies with macromolecular covalent structure (with very strong bonds). Sharp decrease in m.p. with elements that e ...
... together. Increases across the period while following elements which exhibit metallic bonding (due to increased strength following increased number of valence e-.) Highest m.p. of period lies with macromolecular covalent structure (with very strong bonds). Sharp decrease in m.p. with elements that e ...
Chapter 4 Stoichiometry Power Point
... Hydration Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive (H atoms) and negative (O atoms) region, or “positive and negative poles”. This is why water is called a polar solvent. When an ionic compound, such as NaCl, dissol ...
... Hydration Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive (H atoms) and negative (O atoms) region, or “positive and negative poles”. This is why water is called a polar solvent. When an ionic compound, such as NaCl, dissol ...
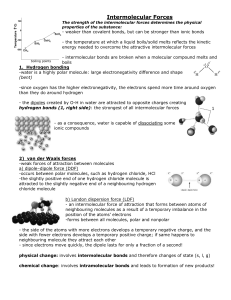
Intermolecular Forces
... - intermolecular bonds are broken when a molecular compound melts and boils 1. Hydrogen bonding -water is a highly polar molecule: large electronegativity difference and shape (bent) boiling points ...
... - intermolecular bonds are broken when a molecular compound melts and boils 1. Hydrogen bonding -water is a highly polar molecule: large electronegativity difference and shape (bent) boiling points ...
Matter and Measurement
... reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is t ...
... reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is t ...
FORMULA WRITNG
... 1) Write balanced equations (molecular, total ionic, and net ionic) for the reaction between each of the following solutions. If no reaction occurs, write “NR” for No Reaction. a. barium nitrate and sodium phosphate molecular: total ionic: net ionic: b. silver nitrate and sodium sulfide molecular: t ...
... 1) Write balanced equations (molecular, total ionic, and net ionic) for the reaction between each of the following solutions. If no reaction occurs, write “NR” for No Reaction. a. barium nitrate and sodium phosphate molecular: total ionic: net ionic: b. silver nitrate and sodium sulfide molecular: t ...
Factors Affecting Solubility PPT
... Polar solutes are soluble in polar solvents. Nonpolar solutes are soluble in nonpolar solvents. If two liquids: miscible or immiscible ...
... Polar solutes are soluble in polar solvents. Nonpolar solutes are soluble in nonpolar solvents. If two liquids: miscible or immiscible ...
H 2 SO 4
... Hydration Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive (H atoms) and negative (O atoms) region, or “positive and negative poles”. This is why water is called a polar solvent. When an ionic compound, such as NaCl, dissol ...
... Hydration Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive (H atoms) and negative (O atoms) region, or “positive and negative poles”. This is why water is called a polar solvent. When an ionic compound, such as NaCl, dissol ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... Example: 1.5 moles of NaCl are dissolved to make 250mL aqueous solution. ...
... Example: 1.5 moles of NaCl are dissolved to make 250mL aqueous solution. ...
Reaction types summary
... In reality ions in solution are not related to one another and so no such movement takes place. The collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be ...
... In reality ions in solution are not related to one another and so no such movement takes place. The collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be ...
iClicker PARTICIPATION Question: Development of the Modern
... The periodic table can help us to determine what the charge on ions will be. ...
... The periodic table can help us to determine what the charge on ions will be. ...
4.4 Oxidation Reduction Redox An introduction to
... In reality ions in solution are not related to one another and so no such movement takes place. The collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be ...
... In reality ions in solution are not related to one another and so no such movement takes place. The collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be ...
topic-2.doc
... 2. Ionic bond: bond formed by the electrostatic attraction after the complete transfer of an electron from a donor atom to an acceptor o Ion: charged atom or molecule o Anion: a negatively charged ion o Cation: a positively charged ion o ionic compounds are called salts (e.g. NaCl or table salt) ...
... 2. Ionic bond: bond formed by the electrostatic attraction after the complete transfer of an electron from a donor atom to an acceptor o Ion: charged atom or molecule o Anion: a negatively charged ion o Cation: a positively charged ion o ionic compounds are called salts (e.g. NaCl or table salt) ...
Different kinds of defects are possible in the regular and orderly
... Defects in solid state Different kinds of defects are possible in crystalline solids. There exist three main groups with additional subgroups. The main groups are point defects, extended defects and dislocations. Point defects: - Schottky defect: This means, that an equal number ob cations and anion ...
... Defects in solid state Different kinds of defects are possible in crystalline solids. There exist three main groups with additional subgroups. The main groups are point defects, extended defects and dislocations. Point defects: - Schottky defect: This means, that an equal number ob cations and anion ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.