Lecture 2 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... to add necessary to neutralize a strong base or acid, you’ll need to know what? ...
... to add necessary to neutralize a strong base or acid, you’ll need to know what? ...
Study Guide for Test 2: Chapters 3 & 4... This is NOT a complete list of what will be... Revised March 4, 2014
... excess reactant, actual yield, theoretical yield, percent yield, solute, solvent, solution, Molarity (M), concentrated solution, diluted solution, concentration, making a solution by dilution method, electrolyte, nonelectrolyte, strong electrolyte, strong acid, weak electrolyte, weak acid, soluble, ...
... excess reactant, actual yield, theoretical yield, percent yield, solute, solvent, solution, Molarity (M), concentrated solution, diluted solution, concentration, making a solution by dilution method, electrolyte, nonelectrolyte, strong electrolyte, strong acid, weak electrolyte, weak acid, soluble, ...
Solutions Intro
... If we add more solvent to a solution we are diluting it. We lower its concentration of solute. In other words, a given amount of solution we will find less solute and more solvent. Before venturing more deeply into concentration, let’s explain what happens when a substance dissolves in water. Why is ...
... If we add more solvent to a solution we are diluting it. We lower its concentration of solute. In other words, a given amount of solution we will find less solute and more solvent. Before venturing more deeply into concentration, let’s explain what happens when a substance dissolves in water. Why is ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_old
... What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show how they interact with each other to form ionic com ...
... What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show how they interact with each other to form ionic com ...
Electrochem 1 - GCG-42
... Electron transfer reactions are oxidation-reduction or redox reactions. Therefore, this field is often called ELECTROCHEMISTRY. ...
... Electron transfer reactions are oxidation-reduction or redox reactions. Therefore, this field is often called ELECTROCHEMISTRY. ...
SNC2D – Science 10 Tuesday April 26th, 2010 Mr. Sourlis and Mr
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
Lesson 2: Electrolytes
... 3 conditions must be met in order for an electric current to flow: 1. Electric charges (ions) must be present ions are found in ionic compounds 2. These charges must be mobile when dissolved in water, the ions are pulled apart and are free to conduct electricity 3. The charges must move in a par ...
... 3 conditions must be met in order for an electric current to flow: 1. Electric charges (ions) must be present ions are found in ionic compounds 2. These charges must be mobile when dissolved in water, the ions are pulled apart and are free to conduct electricity 3. The charges must move in a par ...
2011 Spring 1 key
... conversion of reactants to products and products to reactants, the reaction never proceeds completely to products. (2) It is common, especially in reactions involving organic compounds, to have side reactions. These reactions form products other than the desired product. (3) Sometimes a reaction is ...
... conversion of reactants to products and products to reactants, the reaction never proceeds completely to products. (2) It is common, especially in reactions involving organic compounds, to have side reactions. These reactions form products other than the desired product. (3) Sometimes a reaction is ...
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
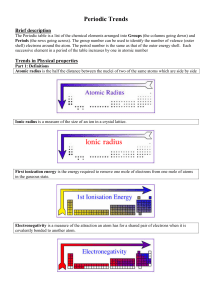
... The atomic radius decreases going across a period because, although the number of protons increases, the electrons are being added to the same energy shell. This means the electrostatic attraction between nucleus and valence electrons increases and the radius decreases. The ionic radius generally de ...
... The atomic radius decreases going across a period because, although the number of protons increases, the electrons are being added to the same energy shell. This means the electrostatic attraction between nucleus and valence electrons increases and the radius decreases. The ionic radius generally de ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... a. Has the highest melting point? b. Has the lowest melting point? c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the f ...
... a. Has the highest melting point? b. Has the lowest melting point? c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the f ...
(activity) of hydrogen ions
... (1) A known amount of acid is pipetted into a conical flask and universal indicator added. (2-3) The acid is titrated with the alkali in the burette until the indicator turns green and the volume of alkali noted. (1-3) are repeated with both known volumes mixed together BUT without the contaminatin ...
... (1) A known amount of acid is pipetted into a conical flask and universal indicator added. (2-3) The acid is titrated with the alkali in the burette until the indicator turns green and the volume of alkali noted. (1-3) are repeated with both known volumes mixed together BUT without the contaminatin ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1411
... This compound is composed of two parts – cationic part that is identified as Cu ion. The ...
... This compound is composed of two parts – cationic part that is identified as Cu ion. The ...
Chemical Bonding Review
... represented by two or three lines between atoms. For dot diagrams, two or three pairs of dots are between the elements. ...
... represented by two or three lines between atoms. For dot diagrams, two or three pairs of dots are between the elements. ...
Review Package
... 5. Ionic Compounds (Textbook p. 139-146; 148-149) Terminology (ion, cation, anion, ionic charge/combining capacity, valence electron, stable octet, polyatomic ion, binary compound, ternary compound, ionic bond) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams/Lewis Dot structures to show the formation of ionic com ...
... 5. Ionic Compounds (Textbook p. 139-146; 148-149) Terminology (ion, cation, anion, ionic charge/combining capacity, valence electron, stable octet, polyatomic ion, binary compound, ternary compound, ionic bond) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams/Lewis Dot structures to show the formation of ionic com ...
Nomenclature
... Forming NaCl from Na and Cl2 • A metal atom can transfer an electron to a nonmetal. • The resulting cation and anion are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. ...
... Forming NaCl from Na and Cl2 • A metal atom can transfer an electron to a nonmetal. • The resulting cation and anion are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. ...
Solute - St John Brebeuf
... THINK ABOUT THIS For solutions to form, and to mix chemical compounds together when adding a solute to a solvent to make a solution…bonds need to break and new bonds need to form! So, we need to remember the intermolecular forces that hold molecules together…. ...
... THINK ABOUT THIS For solutions to form, and to mix chemical compounds together when adding a solute to a solvent to make a solution…bonds need to break and new bonds need to form! So, we need to remember the intermolecular forces that hold molecules together…. ...
Instructions for AP/IB 2 Chem Summer Assignment Note
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
Final Review: L17-25
... Na+ and Cl- appear on both sides of the equation. They are spectator ions. Spectator ions are in the solution, but do not participate in the overall reaction. ...
... Na+ and Cl- appear on both sides of the equation. They are spectator ions. Spectator ions are in the solution, but do not participate in the overall reaction. ...
Chapter 12: Basic Review Worksheet
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
... as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and even petrol. Another fuel ,coal, can be changed into coke which, when mixed with iron ore and heated results in the production of iron and steel. Even seemingly useless materials such as ...
... as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and even petrol. Another fuel ,coal, can be changed into coke which, when mixed with iron ore and heated results in the production of iron and steel. Even seemingly useless materials such as ...
PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... expected to be soluble in water, and the solubility rules confirm this. • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) ha ...
... expected to be soluble in water, and the solubility rules confirm this. • b) Glycine (H2NCH2COOH) is a covalent compound, but it contains polar N–H and O–H bonds. This would make the molecule interact well with polar water molecules, and make it likely that it would be soluble. c) Pentane (C5H12) ha ...
Test 2 - Northwest Florida State College
... excess reactant, actual yield, theoretical yield, percent yield, solute, solvent, solution, Molarity (M), concentrated solution, diluted solution, concentration, making a solution by dilution method, electrolyte, nonelectrolyte, strong electrolyte, strong acid, weak electrolyte, weak acid, soluble, ...
... excess reactant, actual yield, theoretical yield, percent yield, solute, solvent, solution, Molarity (M), concentrated solution, diluted solution, concentration, making a solution by dilution method, electrolyte, nonelectrolyte, strong electrolyte, strong acid, weak electrolyte, weak acid, soluble, ...
Chapter 2
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are n ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) Elements are made up of atoms 2) Atoms of each element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. 3) Compounds are formed when atoms combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are n ...
Chemistry Review
... 9. What type of bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal? A nonmetal and a nonmetal? 10. When is an atom with 3 energy levels considered stable? 11. Which type of bond forms water? 12. What type of compound produces hydrogen ions in solution? 13. What is a radioactive isotope? ...
... 9. What type of bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal? A nonmetal and a nonmetal? 10. When is an atom with 3 energy levels considered stable? 11. Which type of bond forms water? 12. What type of compound produces hydrogen ions in solution? 13. What is a radioactive isotope? ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.