Document
... • The – side of the H2O dipole is attracted to the Na+ ions while the + side of the H2O dipole heads for the Cl- ions. • The H2O molecules surround and carry off each ion, until the crystal is completely dissolved. ...
... • The – side of the H2O dipole is attracted to the Na+ ions while the + side of the H2O dipole heads for the Cl- ions. • The H2O molecules surround and carry off each ion, until the crystal is completely dissolved. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Atoms tend to lose, gain, or ___________ electrons to complete their valence shells. When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it fills its valence shell forming a negative chloride________. Whenever ionic solids are formed, __________ is involved. An ionic material is composed of positive ions bonded ...
... Atoms tend to lose, gain, or ___________ electrons to complete their valence shells. When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it fills its valence shell forming a negative chloride________. Whenever ionic solids are formed, __________ is involved. An ionic material is composed of positive ions bonded ...
Ch. 6 - Chemical Bonds I. Why Atoms Combine
... yes no (solution or liquid) crystal lattice of ions, molecules, odorous liquids & gases crystalline solids ...
... yes no (solution or liquid) crystal lattice of ions, molecules, odorous liquids & gases crystalline solids ...
Summer Assignment 2015
... 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the atomic weight) of chlorine. 7. Write the empirical formulas for the following molecules: (a) glucose, a sub ...
... 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the atomic weight) of chlorine. 7. Write the empirical formulas for the following molecules: (a) glucose, a sub ...
Ionic Bonding
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
AP Chemistry Stoichiometry Review UNIT 1
... Write the formulas of your six strong acids and your six strong bases. Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 acidic ionic compounds (salts). Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 basic ionic compounds. Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 neutral ionic compounds. Name these ...
... Write the formulas of your six strong acids and your six strong bases. Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 acidic ionic compounds (salts). Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 basic ionic compounds. Name these compounds. Write the formulas of 4 neutral ionic compounds. Name these ...
Test - Chemical Bonding- Practice Test
... 21) _____________- Typically solids at room temperature 22) _____________- Usually have high melting and boiling points 23) _____________ -Bonding occurs when there is a transfer valence electrons 24) _____________- Bonding occurs between nonmetals and metals 25) _____________- Compounds have relati ...
... 21) _____________- Typically solids at room temperature 22) _____________- Usually have high melting and boiling points 23) _____________ -Bonding occurs when there is a transfer valence electrons 24) _____________- Bonding occurs between nonmetals and metals 25) _____________- Compounds have relati ...
Chapt3
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
Chemical Stability
... 1) Metals form ionic bonds with nonmetals. 2) Metal form ionic bonds with polyatomic ions. 3) Polyatomic ions form ionic bonds with each other. ...
... 1) Metals form ionic bonds with nonmetals. 2) Metal form ionic bonds with polyatomic ions. 3) Polyatomic ions form ionic bonds with each other. ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
Formulas of Compounds
... IUPAC- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry set the ground rules for naming ...
... IUPAC- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry set the ground rules for naming ...
NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY – UNIT 1 – CHEMICAL CHANGES AND
... Ionic bonds are the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Ionic compounds form lattice structures of oppositely charged ions. Ionic compound have high melting and boiling points because strong ionic bonds must be broken in order to break down the lattice. Dissolving also break ...
... Ionic bonds are the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Ionic compounds form lattice structures of oppositely charged ions. Ionic compound have high melting and boiling points because strong ionic bonds must be broken in order to break down the lattice. Dissolving also break ...
Challenge - ChemistryIBWYA
... indicates a strong electrolyte. Some molecular compounds, notably acids and bases, can also form solutions with high conductivity, because when dissolved they react with the solvent to form ions. Instead of a simple dissociation, the chemical reaction produces the charged particles. A solution of hy ...
... indicates a strong electrolyte. Some molecular compounds, notably acids and bases, can also form solutions with high conductivity, because when dissolved they react with the solvent to form ions. Instead of a simple dissociation, the chemical reaction produces the charged particles. A solution of hy ...
Ionic Bonding
... another electron from the Na+ ion? Since the Na+ ion has a noble gas electron configuration, stripping away the next electron from this stable arrangement would take far more energy than what is released during lattice formation (Sodium I2 = 4,560 kJ/mol). Thus, sodium is present in ionic compounds ...
... another electron from the Na+ ion? Since the Na+ ion has a noble gas electron configuration, stripping away the next electron from this stable arrangement would take far more energy than what is released during lattice formation (Sodium I2 = 4,560 kJ/mol). Thus, sodium is present in ionic compounds ...
6.7 – Ionic Compounds
... Ionic Compounds Ionic Compounds – A metal and nonmetal that has transferred electrons. A cation (positively charged ion) and an anion (negatively charged ion) that has a force of attraction in order to become a neutral charge overall. Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystall ...
... Ionic Compounds Ionic Compounds – A metal and nonmetal that has transferred electrons. A cation (positively charged ion) and an anion (negatively charged ion) that has a force of attraction in order to become a neutral charge overall. Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystall ...
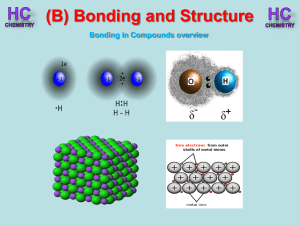
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
... - non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions - electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals ...
Ion Exchange
... (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix normally in the form of small (1–2 mm diameter) beads fabricated from an organic polymer ...
... (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix normally in the form of small (1–2 mm diameter) beads fabricated from an organic polymer ...
Presentation
... how to write formulas and names for three different types of chemical compounds: • 1. IONIC COMPOUNDS • 2. MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS • 3. ACIDS *Each type will have a set of rules that we must follow to correctly represent the substance. ...
... how to write formulas and names for three different types of chemical compounds: • 1. IONIC COMPOUNDS • 2. MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS • 3. ACIDS *Each type will have a set of rules that we must follow to correctly represent the substance. ...
Ch. 9
... – For metals that can have more than one charge, the name of the metal is succeeded by the valency in capital Roman numerals in () parentheses OR by using the suffix –ous for the lowest valency & -ic for the highest valency ...
... – For metals that can have more than one charge, the name of the metal is succeeded by the valency in capital Roman numerals in () parentheses OR by using the suffix –ous for the lowest valency & -ic for the highest valency ...
Honors Chemistry
... For double replacement reactions, use a solubility table and the following rules: 1. If one of the products formed is water, the reaction happens. 2. If a gas is formed, the reaction happens. 3. If an insoluble product forms (I or Ss), the reaction happens (actually a reaction may happen when two so ...
... For double replacement reactions, use a solubility table and the following rules: 1. If one of the products formed is water, the reaction happens. 2. If a gas is formed, the reaction happens. 3. If an insoluble product forms (I or Ss), the reaction happens (actually a reaction may happen when two so ...
Student Learning Map
... How are the different types of intermolecular forces explained (dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, induced dipoles, London dispersion forces)? ...
... How are the different types of intermolecular forces explained (dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, induced dipoles, London dispersion forces)? ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... modern chemical science. These solvents should possess such properties like low volatility, low to no toxicity, non-flammable, as well as high thermal stability, all in accordance with both ecological and safety rules. Meanwhile, such solvents should have good solvation ability and selectivity for sp ...
... modern chemical science. These solvents should possess such properties like low volatility, low to no toxicity, non-flammable, as well as high thermal stability, all in accordance with both ecological and safety rules. Meanwhile, such solvents should have good solvation ability and selectivity for sp ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.