Chapter 5
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Review for second exam:
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
... valence electrons for main group elements alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases metals, nonmetals, metalloids (semimetals); general properties and location Effective nuclear charge, Zeff; approximate value for Zeff, calculation and interpretation Zeff and Coulomb’s law Trends in ...
Exam Review – Part 1
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
Solution - ZOMUedu
... ○ Stock solution = a solution of known concentration that is used to make more dilute solutions Precipitation ○ Precipitation = when aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are poured together and a solid forms (solid = precipitate) ○ We can predict the products ■ The anion and cation switch partners ■ ...
... ○ Stock solution = a solution of known concentration that is used to make more dilute solutions Precipitation ○ Precipitation = when aqueous solutions of ionic compounds are poured together and a solid forms (solid = precipitate) ○ We can predict the products ■ The anion and cation switch partners ■ ...
General Chemistry (C) Sept
... Q1: What is a covalent bond? Q2: What compounds are formed with covalent bond? Molecular compounds and network compounds Localized electron-sharing model Bond Energy Bond strength and bond length Covalent radii Dipole moment and Polar bonds Multiple bonds:-bond, -bond, etc. Resonance and Electron ...
... Q1: What is a covalent bond? Q2: What compounds are formed with covalent bond? Molecular compounds and network compounds Localized electron-sharing model Bond Energy Bond strength and bond length Covalent radii Dipole moment and Polar bonds Multiple bonds:-bond, -bond, etc. Resonance and Electron ...
Chemical Bonds
... • Forces holding atoms or ions together • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bondi ...
... • Forces holding atoms or ions together • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bondi ...
Midterm Review 1
... 4. Which of the following are isotopes of the same element? 9Y 9Y 10Y 5. Describe Rutherford's experiment: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... 4. Which of the following are isotopes of the same element? 9Y 9Y 10Y 5. Describe Rutherford's experiment: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... Ionic compound -a compound composed entirely of ions formed by the gaining and losing of valence electrons Ionic Bonding - a positively charged ion is attracted to a negatively charge ion. ...
... Ionic compound -a compound composed entirely of ions formed by the gaining and losing of valence electrons Ionic Bonding - a positively charged ion is attracted to a negatively charge ion. ...
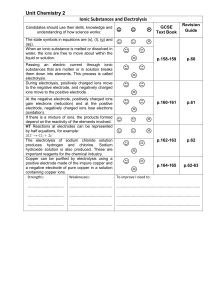
Unit_Chemistry_2_Ionic_Substances_and_Electrolysis
... Ionic Substances and Electrolysis Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: ...
... Ionic Substances and Electrolysis Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: ...
Honors Chemistry - Stout Middle School
... form an ionic compound (which is neutral in charge). 6. Know why transition elements can have more than one oxidation number. 7. Know the four elements, outside groups 1 and 2, that have only one oxidation number and know these elements oxidation numbers. 8. Know what an ionic compound is and what f ...
... form an ionic compound (which is neutral in charge). 6. Know why transition elements can have more than one oxidation number. 7. Know the four elements, outside groups 1 and 2, that have only one oxidation number and know these elements oxidation numbers. 8. Know what an ionic compound is and what f ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
... There are many types of chemical reactions. Five of the most common are: synthesis: two or more reactants combine to form a single product. A+BC decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atom ...
Ionic Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions. ...
... one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions. ...
Lectures 1-6 - TCD Chemistry
... Know about the main types of intermolecular forces. {London (dispersion), dipole-dipole, ion-dipole, hydrogen-bonding) ...
... Know about the main types of intermolecular forces. {London (dispersion), dipole-dipole, ion-dipole, hydrogen-bonding) ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... periodic trends (atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity) review of Bohr-Rutherford diagram ionic compounds (properties, formation, structure, naming, and bonding) molecular element molecular compound (properties, drawing, bonding, naming) nomenclature (i ...
... periodic trends (atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity) review of Bohr-Rutherford diagram ionic compounds (properties, formation, structure, naming, and bonding) molecular element molecular compound (properties, drawing, bonding, naming) nomenclature (i ...
S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
Chapter 9 Review quizdom
... b. cobalt(I) chloride c. cobalt(II) chlorate d. cobalt(II) chloride ...
... b. cobalt(I) chloride c. cobalt(II) chlorate d. cobalt(II) chloride ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... Compounds come in two basic types: covalent and ionic. To determine whether a compound is covalent or ionic, the periodic table is required. ...
... Compounds come in two basic types: covalent and ionic. To determine whether a compound is covalent or ionic, the periodic table is required. ...
CHAPTER 7 READING GUIDE – IONIC COMPOUNDS AND METALS
... 9. Although the formation of an ________________ is the most stable electron configuration, other electron configurations can provide some ________________. 10. ____________________, which are located on the right side of the periodic table, easily gain _________________ to attain a stable outer ele ...
... 9. Although the formation of an ________________ is the most stable electron configuration, other electron configurations can provide some ________________. 10. ____________________, which are located on the right side of the periodic table, easily gain _________________ to attain a stable outer ele ...
Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing
... masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
1.5.16(Chem) - mrcarlsonschemistryclass
... • Atoms bonded together with an IONIC bond are called ionic compounds. • An ionic bond is a METAL bonded with a NONMETAL. • Draw the crystal lattice structure for sodium chloride: ...
... • Atoms bonded together with an IONIC bond are called ionic compounds. • An ionic bond is a METAL bonded with a NONMETAL. • Draw the crystal lattice structure for sodium chloride: ...
Writing Formulas
... Binary compounds consist of two elements that may be ionic or covalent. The general rule is to put the least electronegative element first, the more electronegative element second and balance the charges to zero. ...
... Binary compounds consist of two elements that may be ionic or covalent. The general rule is to put the least electronegative element first, the more electronegative element second and balance the charges to zero. ...
bonding notes for votech
... Attraction between + nucleus and e- or between + and – ions Only valence e- involved in bonding Bonding occurs to have complete outermost energy levels – to become like noble gases ...
... Attraction between + nucleus and e- or between + and – ions Only valence e- involved in bonding Bonding occurs to have complete outermost energy levels – to become like noble gases ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.