Unit 3 Review Notes - Brinkmann chapter7_and_8_review1
... – Ionic compounds form solids at ordinary temperatures. High mp and bp. – Good conductors of heat and electricity – Ionic compounds organize in a characteristic crystal lattice of alternating positive and negative ions. – generally soluble as a ...
... – Ionic compounds form solids at ordinary temperatures. High mp and bp. – Good conductors of heat and electricity – Ionic compounds organize in a characteristic crystal lattice of alternating positive and negative ions. – generally soluble as a ...
FALL Final Review KEY
... 25. The modern periodic table is organized by ATOMIC NUMBER = PROTONS 26. All atoms of the same element have the same number of PROTONS 27. (1) A and D; Period 3 (2) B and C; Group 1A ...
... 25. The modern periodic table is organized by ATOMIC NUMBER = PROTONS 26. All atoms of the same element have the same number of PROTONS 27. (1) A and D; Period 3 (2) B and C; Group 1A ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Formulas
... number of atoms in the molecule. The only exception is that if the first atom in the molecule has only one atom, the mono prefix is dropped (understood) ex. CO is carbon monoxide CO2 is carbon dioxide ...
... number of atoms in the molecule. The only exception is that if the first atom in the molecule has only one atom, the mono prefix is dropped (understood) ex. CO is carbon monoxide CO2 is carbon dioxide ...
Multivalent Ionic Compounds
... 12. Draw Lewis Diagrams for the atoms and ions of the first 18 elements in the Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to crea ...
... 12. Draw Lewis Diagrams for the atoms and ions of the first 18 elements in the Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to crea ...
3(aq)
... Reactions that form water • Base: substances that have a bitter taste, and are slippery to the touch (like soap) 1. are also called “alkaline” solutions 2. they are substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved into water. 3. bases are considered “strong” bases are those that easily d ...
... Reactions that form water • Base: substances that have a bitter taste, and are slippery to the touch (like soap) 1. are also called “alkaline” solutions 2. they are substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved into water. 3. bases are considered “strong” bases are those that easily d ...
File
... All are solids at SATP (Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure) of 25 oC and 100 kPa. ...
... All are solids at SATP (Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure) of 25 oC and 100 kPa. ...
Objective: The objective of the lab is to study the types of reactions
... cramping of the muscle. When salt is put in water it dissolves into sodium and chloride ions that are too small to be seen. However, the effect can be seen by observing any electric current that can be produced. This is a common test to see if a material is an electrolyte (a compound that can be spl ...
... cramping of the muscle. When salt is put in water it dissolves into sodium and chloride ions that are too small to be seen. However, the effect can be seen by observing any electric current that can be produced. This is a common test to see if a material is an electrolyte (a compound that can be spl ...
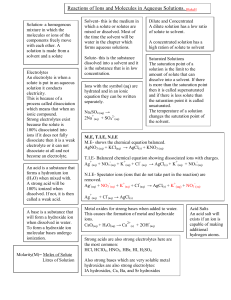
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. The solvent is present in greatest abundance. All other substances are solutes. ...
... Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. The solvent is present in greatest abundance. All other substances are solutes. ...
Aqueous chemistry is a very important component to laboratory
... The partially negative oxygen atom in water will surround the positive cations, while the partially positive hydrogen atoms will surround the negative anions. If two electrodes (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solut ...
... The partially negative oxygen atom in water will surround the positive cations, while the partially positive hydrogen atoms will surround the negative anions. If two electrodes (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solut ...
anna-chrobok-silesian-university-of-technology
... - Diels-Alder reaction, - oxidation of alcohols and ketones. IONIC LIQUIDS as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts Recycling of ionic liquids prevents them from: - ending up in the aquatic environment, - release into the atmosphere (low volatility). ...
... - Diels-Alder reaction, - oxidation of alcohols and ketones. IONIC LIQUIDS as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts Recycling of ionic liquids prevents them from: - ending up in the aquatic environment, - release into the atmosphere (low volatility). ...
Worksheet on Ionic and Atomic Size Trends
... 12. The sodium ion is smaller than the atom, because when sodium loses its valence electron to form an ion, it also loses its 3rd energy level. 13. The chlorine ion is larger than the chlorine atom, because adding an additional electron to the 3 rd energy level causes the energy level to expand beca ...
... 12. The sodium ion is smaller than the atom, because when sodium loses its valence electron to form an ion, it also loses its 3rd energy level. 13. The chlorine ion is larger than the chlorine atom, because adding an additional electron to the 3 rd energy level causes the energy level to expand beca ...
s - chem116
... To write a net ionic equation from the newly created ionic equation: Na+ + Cl- + Ag+ + NO3- Na+ + NO3- + AgCl Simply eliminate any ion that appears on both the reactant and product side of the equation (shown in orange). ...
... To write a net ionic equation from the newly created ionic equation: Na+ + Cl- + Ag+ + NO3- Na+ + NO3- + AgCl Simply eliminate any ion that appears on both the reactant and product side of the equation (shown in orange). ...
CH 4 Notes
... Example: For a 1.0 M solution of NaCl: The solution is 1.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in Cl1- ions. Example: For a 1.0 M solution of Na2SO4: The solution is 2.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in SO42- ions. ...
... Example: For a 1.0 M solution of NaCl: The solution is 1.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in Cl1- ions. Example: For a 1.0 M solution of Na2SO4: The solution is 2.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in SO42- ions. ...
AP Chemistry: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... electricity. Example: NaCl If a substance dies not form ions in solution, the substance is a nonelectrolyte, and the solution does not conduct electricity. Example: sugar Ionic Compounds in Water When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions dissociate. This means that in solution the solid ...
... electricity. Example: NaCl If a substance dies not form ions in solution, the substance is a nonelectrolyte, and the solution does not conduct electricity. Example: sugar Ionic Compounds in Water When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions dissociate. This means that in solution the solid ...
CHEM1405 2005-J-3 June 2005 • Ammonia (NH 3) has a boiling
... much larger atom that H or C and hence has more electrons and these are held further from the nucleus. The electron cloud in I2 is, therefore, much more polarisable leading to stronger dispersion forces in I2. and a higher melting point. NaCl has relatively strong ionic bonds between all of the Na+ ...
... much larger atom that H or C and hence has more electrons and these are held further from the nucleus. The electron cloud in I2 is, therefore, much more polarisable leading to stronger dispersion forces in I2. and a higher melting point. NaCl has relatively strong ionic bonds between all of the Na+ ...
The Copper Cycle
... phones to the thousands of processes occurring within our bodies. We cannot even begin to identify the millions of chemical reactions occurring around us all the time; yet, most of these reactions can be classified into one of three main types of chemical reactions: precipitation reactions, acid-bas ...
... phones to the thousands of processes occurring within our bodies. We cannot even begin to identify the millions of chemical reactions occurring around us all the time; yet, most of these reactions can be classified into one of three main types of chemical reactions: precipitation reactions, acid-bas ...
+2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 1. Write formulas for the binary ionic compounds formed between the following elements: a. potassium and iodine b. magnesium and chlorine c. sodium and sulfur d. aluminum and sulfur e. aluminum and nitrogen 2. Name the binary ionic compounds indicated by the following formulas: a. AgCl ...
... 1. Write formulas for the binary ionic compounds formed between the following elements: a. potassium and iodine b. magnesium and chlorine c. sodium and sulfur d. aluminum and sulfur e. aluminum and nitrogen 2. Name the binary ionic compounds indicated by the following formulas: a. AgCl ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.2 - reich
... • 1-Berylium chloride and aluminum react together. What is the reaction type? Balance the chemical reaction. • 2-Magnesium chloride and sodium phosphate undergo a double displacement reaction. Go through all the steps to show the net ionic equation. • 3- When you cook with a propane grill you burn p ...
... • 1-Berylium chloride and aluminum react together. What is the reaction type? Balance the chemical reaction. • 2-Magnesium chloride and sodium phosphate undergo a double displacement reaction. Go through all the steps to show the net ionic equation. • 3- When you cook with a propane grill you burn p ...
Determination of electrochemical equivalent of copper and
... Nd – the number of dissociated particles N – overall number of dissolved particles If 0,8 < α < 1 the electrolyte is called strong and it means that almost all dissolved particles were dissociated. For middle electrolytes α = 0,5 and the number of particles dissociated and not dissociated is similar ...
... Nd – the number of dissociated particles N – overall number of dissolved particles If 0,8 < α < 1 the electrolyte is called strong and it means that almost all dissolved particles were dissociated. For middle electrolytes α = 0,5 and the number of particles dissociated and not dissociated is similar ...
Fundamentals of General Chemistry and Physical Chemistry for
... In solution, the immediate neighborhood of any positive ion tends to have more negative than positive ions, whereas that of a negative ion tends to have more positive than negative ions. If an electric potential is applied, a positive ion moves toward the negative electrode, and vice versa, and its ...
... In solution, the immediate neighborhood of any positive ion tends to have more negative than positive ions, whereas that of a negative ion tends to have more positive than negative ions. If an electric potential is applied, a positive ion moves toward the negative electrode, and vice versa, and its ...
Unit chemical bonds
... 2. In Parenthesis ( ) write a Roman Numeral to indicate the ox # of the Transition metal in this compound 3. Write name of nonmetal and Change end to “-ide” ...
... 2. In Parenthesis ( ) write a Roman Numeral to indicate the ox # of the Transition metal in this compound 3. Write name of nonmetal and Change end to “-ide” ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and solution
... the ore is dissolved and the sulfur is converted to the sulfate ion. Barium nitrate is added which causes the sulfate to precipitate out as BaSO4. The original sample has a mass of 3.187 g. The dried BaSO4 has a mass of 2.005 g. What is the percent of sulfur in the original ore? ...
... the ore is dissolved and the sulfur is converted to the sulfate ion. Barium nitrate is added which causes the sulfate to precipitate out as BaSO4. The original sample has a mass of 3.187 g. The dried BaSO4 has a mass of 2.005 g. What is the percent of sulfur in the original ore? ...
Honors Chemistry Final Essay Questions 2007
... label the states of the reactants and products on both the balanced equation and the net ionic equation, and list the spectator ions and driving force for each of the reactions. a. silver nitrate solution + magnesium bromide solution b. barium chloride solution + potassium sulfate solution c. sulfur ...
... label the states of the reactants and products on both the balanced equation and the net ionic equation, and list the spectator ions and driving force for each of the reactions. a. silver nitrate solution + magnesium bromide solution b. barium chloride solution + potassium sulfate solution c. sulfur ...
Ionic compound

In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a structure by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are called cations and the negatively charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ions such as the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic species such as the carbonate ion (CO32−) in calcium carbonate. Individual ions within an ionic compound usually have multiple nearest neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network, usually in a crystalline structure.Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, and are hard and brittle. As solids they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.Ionic compounds without the acidic hydrogen ion (H+), or the basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−), are also known as salts and can be formed by acid-base reactions. Ionic compounds containing hydrogen ions are classified as acids and compounds containing hydroxide or oxide ions are classified as bases.