Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... cortex does not simply send out nonspecific “control signals.” Explicit representation of information that is internally sustained, rather than externally driven, enables the prefrontal cortex to subserve time integration, planning, decision-making, and other executive processes. The discovery of me ...
... cortex does not simply send out nonspecific “control signals.” Explicit representation of information that is internally sustained, rather than externally driven, enables the prefrontal cortex to subserve time integration, planning, decision-making, and other executive processes. The discovery of me ...
Name
... 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What ...
... 3. What is the structure of a neuron and what kinds of neurons are found in the body? 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What ...
LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
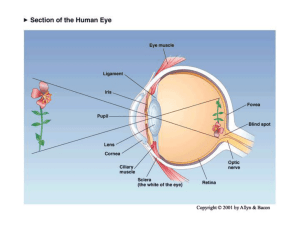
... involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The part of each optic nerve between the optic chiasm and the lateral geniculate nucleus. Amygdala An almond-shaped brain structure in the limbic system at the base of the inside of each temporal lobe , contiguous with ...
... involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The part of each optic nerve between the optic chiasm and the lateral geniculate nucleus. Amygdala An almond-shaped brain structure in the limbic system at the base of the inside of each temporal lobe , contiguous with ...
Annual Review of Neuroscience
... Most neurophysiological studies of cognition use relatively basic tasks (“pay attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher level than any other lab. We have taught monkeys to juggle multiple things in memory, anticipate and imagine forthcoming event ...
... Most neurophysiological studies of cognition use relatively basic tasks (“pay attention here.” “hold one thing in mind”) The Miller Lab has taken monkey training to a higher level than any other lab. We have taught monkeys to juggle multiple things in memory, anticipate and imagine forthcoming event ...
Discovering spatial working memory fields in prefrontal cortex
... cortex does not simply send out nonspecific “control signals.” Explicit representation of information that is internally sustained, rather than externally driven, enables the prefrontal cortex to subserve time integration, planning, decision-making, and other executive processes. The discovery of me ...
... cortex does not simply send out nonspecific “control signals.” Explicit representation of information that is internally sustained, rather than externally driven, enables the prefrontal cortex to subserve time integration, planning, decision-making, and other executive processes. The discovery of me ...
MS-PowerPoint
... • The cortex provides flexibility in behavior • Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
... • The cortex provides flexibility in behavior • Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
Target in Field Search: Distractor in Field - Smith
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... o Substantia nigra = The midbrain structure that controls unconscious motor movements ...
... o Substantia nigra = The midbrain structure that controls unconscious motor movements ...
Posterior Parietal Cortex: Space…and Beyond
... presented stimuli were identical matches. If the nonmatch rule was in effect, monkeys instead had to release a lever if the two stimuli were not the same as one another. Matching and nonmatching are abstract rules because they can be applied to any stimulus and are not directly dependent on the phys ...
... presented stimuli were identical matches. If the nonmatch rule was in effect, monkeys instead had to release a lever if the two stimuli were not the same as one another. Matching and nonmatching are abstract rules because they can be applied to any stimulus and are not directly dependent on the phys ...
Self-Guided Study for Chapter 12 and Review
... 14. Know the structure of the cerebellum. Know the function of the cerebellum. 15. Describe how the cerebellum and the motor cortex communicate to plan muscle movements. 16. Know the functions of the peduncles in the brain stem. 17. Know the parts of the limbic system and its overall function. 18. K ...
... 14. Know the structure of the cerebellum. Know the function of the cerebellum. 15. Describe how the cerebellum and the motor cortex communicate to plan muscle movements. 16. Know the functions of the peduncles in the brain stem. 17. Know the parts of the limbic system and its overall function. 18. K ...
Unit 2 The Brain
... – There are three types of neurons you need to know for the test. • Sensory • Interneurons • Motor ...
... – There are three types of neurons you need to know for the test. • Sensory • Interneurons • Motor ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
The Brain and the Nervous System
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
... Convoluted (folded, wrinkled) structure enables more tissue to fit The cortex provides flexibility in behavior Divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 paired lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal ...
Defining the Self: The Orientation Association Area
... OAA so that we can experience a rich sense of the self. iii. The prefrontal cortex actually has many different complex functions. However, for the purposes of this book, we will focus primarily on its ability to help us to focus attention. iv. In terms of the attention association areas function, a ...
... OAA so that we can experience a rich sense of the self. iii. The prefrontal cortex actually has many different complex functions. However, for the purposes of this book, we will focus primarily on its ability to help us to focus attention. iv. In terms of the attention association areas function, a ...
Brain Advanced 2
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
The Human Brain - Peoria Public Schools
... The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. • Define cephalizationa. The development of the head region. • State the number of neurons in the human brain. a. 86 Billion • Describe the advantage of having a brain. a. Communication between the billions of neurons is more rapid tha ...
... The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. • Define cephalizationa. The development of the head region. • State the number of neurons in the human brain. a. 86 Billion • Describe the advantage of having a brain. a. Communication between the billions of neurons is more rapid tha ...
Eye Movement Control by the Cerebral Cortex Charles Pierrot
... and 24, prepare all the frontal ocular motor areas involved in intentional saccade control to act in the forthcoming motor behaviour. • PCC: reflexive saccade control (?) – fMRI study shows that the PCC is active during reflexive saccades. – Activation during PEM ...
... and 24, prepare all the frontal ocular motor areas involved in intentional saccade control to act in the forthcoming motor behaviour. • PCC: reflexive saccade control (?) – fMRI study shows that the PCC is active during reflexive saccades. – Activation during PEM ...
Chapter 2
... Identify the basic components of the neuron, describe the action potential, and explain the processes that take place within the neuron when it is activated. ...
... Identify the basic components of the neuron, describe the action potential, and explain the processes that take place within the neuron when it is activated. ...
Study Guide
... The following study guide is exactly that, a guide. Use it to direct your studies for the first exam. The text should be used to clarify any questions you have. You are still responsible for all class notes covered or not covered in my lectures. Good luck to you all. CHAPTER 13: Peripheral Nervous S ...
... The following study guide is exactly that, a guide. Use it to direct your studies for the first exam. The text should be used to clarify any questions you have. You are still responsible for all class notes covered or not covered in my lectures. Good luck to you all. CHAPTER 13: Peripheral Nervous S ...
PSYCH 2 StudyGuide
... experience sensations of falling. Stage 2 is a deeper stage of sleep and is characterized by sleep spindles. Stage 3 is transitional while Stage 4 emits large, slow delta waves (also apparent in stage 3). After the first cycle you return to REM- in between 2 and 1. Heart rate rises and breathing bec ...
... experience sensations of falling. Stage 2 is a deeper stage of sleep and is characterized by sleep spindles. Stage 3 is transitional while Stage 4 emits large, slow delta waves (also apparent in stage 3). After the first cycle you return to REM- in between 2 and 1. Heart rate rises and breathing bec ...
Inhibition
... – If there is disagreement between the task at hand and a recent memory, this will take longer because you need to resolve the conflict ...
... – If there is disagreement between the task at hand and a recent memory, this will take longer because you need to resolve the conflict ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.