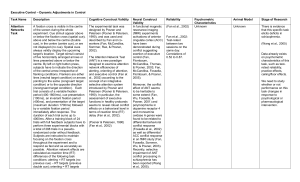
Parieto-prefrontal pathway
... environments more efficiently. •Speculation: It makes sense that the hippocampus and the parieto-medial temporal pathway are connected via many both direct and indirect projections – this large number of connections between these areas allow the two to integrate their information to form the best co ...
... environments more efficiently. •Speculation: It makes sense that the hippocampus and the parieto-medial temporal pathway are connected via many both direct and indirect projections – this large number of connections between these areas allow the two to integrate their information to form the best co ...
The Brain
... composed of right and left cerebral hemispheres. It performs higher functions like interpreting touch, vision and hearing, as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and fine control of movement. ...
... composed of right and left cerebral hemispheres. It performs higher functions like interpreting touch, vision and hearing, as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and fine control of movement. ...
From Vision to Movement
... response to dominate in later areas, especially primary motor cortex. Parietal areas are intermediate. A variant of the anti-reach task is to train people to make reaches while looking through prisms that reverse everything you see left-to-right. You will even see your hand reversed, but of course t ...
... response to dominate in later areas, especially primary motor cortex. Parietal areas are intermediate. A variant of the anti-reach task is to train people to make reaches while looking through prisms that reverse everything you see left-to-right. You will even see your hand reversed, but of course t ...
Key to midterm - UCSD Cognitive Science
... trance theory of hypnosis, people enter an altered trance-like state in which they are highly susceptible to suggestion. Other theories, specifically the sociological and task-motivation theories argue that one’s willingness to play a role and eagerness to please are what characterizes hypnosis as n ...
... trance theory of hypnosis, people enter an altered trance-like state in which they are highly susceptible to suggestion. Other theories, specifically the sociological and task-motivation theories argue that one’s willingness to play a role and eagerness to please are what characterizes hypnosis as n ...
Syllabus P140C (68530) Cognitive Science
... – Where does mental activity take place in the brain? – How is processing actually done with neural activity? ...
... – Where does mental activity take place in the brain? – How is processing actually done with neural activity? ...
GROUP “A” L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 1 1 -
... 1. Describe the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain’s levels and structures, and summarize the functions of its structures. 4. Describe the biochemical aspects of brain and how genetics increase our und ...
... 1. Describe the nature and basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain what neurons are and how they process information. 3. Identify the brain’s levels and structures, and summarize the functions of its structures. 4. Describe the biochemical aspects of brain and how genetics increase our und ...
The Brain - Academic Computer Center
... Converts impulses from the ear and relate them to pitch, rhythm, and loudness ...
... Converts impulses from the ear and relate them to pitch, rhythm, and loudness ...
The Brain: Your Crowning Glory
... these major brain structures. The Hindbrain The lowest part of the brain, the hindbrain, is also the oldest part in evolutionary terms. The hindbrain includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. These structures control such basic life-support functions as breathing and heart rate. The medulla and po ...
... these major brain structures. The Hindbrain The lowest part of the brain, the hindbrain, is also the oldest part in evolutionary terms. The hindbrain includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. These structures control such basic life-support functions as breathing and heart rate. The medulla and po ...
Myers AP - Unit 03B
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
Unit 03B
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
UNIT XI
... • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover a ...
... • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover a ...
L03 Brain Script Addendum
... We know that the amygdala is important for emotions, especially fear. This has been examined in an experiment wherein cats had their amygdala electrically stimulated which resulted in them arching their backs in an angry-defensive response that suggests anger and aggression also involve the amygdala ...
... We know that the amygdala is important for emotions, especially fear. This has been examined in an experiment wherein cats had their amygdala electrically stimulated which resulted in them arching their backs in an angry-defensive response that suggests anger and aggression also involve the amygdala ...
Perception – Gain Control
... di Pellegrino, G., Ciaramelli, E., & Ladavas, E. (2007). The regulation of cognitive control following rostral anterior cingulate cortex lesion in humans. J Cogn Neurosci, 19(2), 275-286. Eagle, D. M., & Robbins, T. W. (2003). Inhibitory control in rats performing a stop-signal reaction-time task: e ...
... di Pellegrino, G., Ciaramelli, E., & Ladavas, E. (2007). The regulation of cognitive control following rostral anterior cingulate cortex lesion in humans. J Cogn Neurosci, 19(2), 275-286. Eagle, D. M., & Robbins, T. W. (2003). Inhibitory control in rats performing a stop-signal reaction-time task: e ...
Unit 03B- The Brain - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences Instructor: Professor Sebastian Seung
... MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.641J, Spring 2005 - Introduction to Neural Networks Instructor: Professor Sebastian Seung ...
... MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.641J, Spring 2005 - Introduction to Neural Networks Instructor: Professor Sebastian Seung ...
Os textos são da exclusiva responsabilidade dos autores
... 1 - Laboratory of Neurobiology of Human Behavior, Centro Hospitalar do Porto; 2- Division of Behavioral Neurology and Cognitive Neuroscience, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine Grant nº 201/08 Background: Acquisition of novel perceptual or perceptual-motor skills appears to depend on mult ...
... 1 - Laboratory of Neurobiology of Human Behavior, Centro Hospitalar do Porto; 2- Division of Behavioral Neurology and Cognitive Neuroscience, University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine Grant nº 201/08 Background: Acquisition of novel perceptual or perceptual-motor skills appears to depend on mult ...
unit 3b brain
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
... involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. ...
Lesson1 Powerpoint
... Orientation selectivity Orientation selectivity in primary visual cortex. ...
... Orientation selectivity Orientation selectivity in primary visual cortex. ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Medulla Oblongata o Relays sensory information to thalamus and to other portions of the brain stem o Autonomic centers for regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of ot ...
... Medulla Oblongata o Relays sensory information to thalamus and to other portions of the brain stem o Autonomic centers for regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of ot ...
Exam 4
... -Describe sensations and the classification of sensory receptors (Describe the different ways to classify sensory receptors). -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensor ...
... -Describe sensations and the classification of sensory receptors (Describe the different ways to classify sensory receptors). -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensor ...
Ch 12. Executive Functions and Frontal Lobes Introduction
... What memory functions are associated with prefrontal cortex? How do these mnemonic functions differ from other types of memory? Compared to the visual cortex, it has been difficult to identify subregions of the prefrontal cortex. What are some of the current hypotheses concerning functional speciali ...
... What memory functions are associated with prefrontal cortex? How do these mnemonic functions differ from other types of memory? Compared to the visual cortex, it has been difficult to identify subregions of the prefrontal cortex. What are some of the current hypotheses concerning functional speciali ...
The Brain - Polk School District
... • Outer cortex (gray matter) and inner region (white matter). • Coordination, balance, and posture; coordinates sensory input from inner ear and the muscles to provide accurate control of position and movement. • Damage would show loss of muscle tone and ...
... • Outer cortex (gray matter) and inner region (white matter). • Coordination, balance, and posture; coordinates sensory input from inner ear and the muscles to provide accurate control of position and movement. • Damage would show loss of muscle tone and ...
FinalStudyGuide
... & what their production is called, how long they live, what cells destroy them, etc. What is the % of red blood cells in a sample called? What is erythropoietin & when is it released? Study features/characteristics of WBC, what are they properly called, their primary functions, conditions that ...
... & what their production is called, how long they live, what cells destroy them, etc. What is the % of red blood cells in a sample called? What is erythropoietin & when is it released? Study features/characteristics of WBC, what are they properly called, their primary functions, conditions that ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.