Representations in the Human Prefrontal Cortex
... would follow the same representational model as the more posterior cortex from which it was derived, especially given the rapid increase in PFC size and complexity that occurred with the evolution of modern humans. A parsimonious hypothesis is that the PFC encodes unique representations of complex b ...
... would follow the same representational model as the more posterior cortex from which it was derived, especially given the rapid increase in PFC size and complexity that occurred with the evolution of modern humans. A parsimonious hypothesis is that the PFC encodes unique representations of complex b ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
Module 4 Notes
... A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge of each hemisphere’s special functions. In the laboratory, investigators ask a split-brain patient to loo ...
... A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge of each hemisphere’s special functions. In the laboratory, investigators ask a split-brain patient to loo ...
- Birkbeck, University of London
... modularity in peripheral versus central processes, distracts and detracts from his work. In particular, mental processes can employ a language of thought without that language being in any way similar to standard functional or procedural programming languages. In addition, communication between (per ...
... modularity in peripheral versus central processes, distracts and detracts from his work. In particular, mental processes can employ a language of thought without that language being in any way similar to standard functional or procedural programming languages. In addition, communication between (per ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • motor coordination – links cerebrum and cerebellum – Parkinson’s disease • degeneration of the substantia nigra ...
... • motor coordination – links cerebrum and cerebellum – Parkinson’s disease • degeneration of the substantia nigra ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... specific body area (somatotopic) • diff. parts of body are not equally represented – hands and face have larger areas dedicated to processing of information ...
... specific body area (somatotopic) • diff. parts of body are not equally represented – hands and face have larger areas dedicated to processing of information ...
Trainee Content for Day 1, Segment 4C
... (3) the parietal lobes, which link sensory and motor functions and provide a sense of the spatial location of the body Examples of functions: When you enjoy a good meal—the taste, aroma and texture of the food—the parietal lobes are at work. The forward parts of these lobes, just behind the motor ar ...
... (3) the parietal lobes, which link sensory and motor functions and provide a sense of the spatial location of the body Examples of functions: When you enjoy a good meal—the taste, aroma and texture of the food—the parietal lobes are at work. The forward parts of these lobes, just behind the motor ar ...
BIOL 2402 Lecture Outline Chapter 5
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
Exam 1 Review - Central Connecticut State University
... • 5. A dermatome is • A) an area of the skin innervated by a given spinal nerve. • B) an instrument used to record impulses in the spinal cord. • C) the point at which sensory nerves make contact with motor nerves. • D) an area of the skin that has no touch receptors. ...
... • 5. A dermatome is • A) an area of the skin innervated by a given spinal nerve. • B) an instrument used to record impulses in the spinal cord. • C) the point at which sensory nerves make contact with motor nerves. • D) an area of the skin that has no touch receptors. ...
Nervous System 2
... c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you can think logically about which organ ...
... c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you can think logically about which organ ...
BRAIN ANATOMY Central Nervous System (CNS) is the brain and
... are so critical. The brain is the executive of you; and, it is as critical as the heart. It is so important to protect your brain; hence, the brain and spinal cord are protected by bone. They are encased in the skull and the vertebrate in the spine. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)are the nerves that ...
... are so critical. The brain is the executive of you; and, it is as critical as the heart. It is so important to protect your brain; hence, the brain and spinal cord are protected by bone. They are encased in the skull and the vertebrate in the spine. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)are the nerves that ...
Paper
... neurons) showed different patterns of responses. Fast spiking cell tended to show transient responses and increased their firing rates following CS presentation, whereas a complementary pattern was observed in the regular spiking cells. Our results enhance our understanding of neural mechanism under ...
... neurons) showed different patterns of responses. Fast spiking cell tended to show transient responses and increased their firing rates following CS presentation, whereas a complementary pattern was observed in the regular spiking cells. Our results enhance our understanding of neural mechanism under ...
Biographies2008 - Coalition of Care and Support Providers in
... an extensive knowledge of community care policy, public procurement and practice issues which has been gained from her work in service commissioning, delivery and development within both the statutory and voluntary sectors. TMF work with people with a wide range of needs –which gives her a breadth o ...
... an extensive knowledge of community care policy, public procurement and practice issues which has been gained from her work in service commissioning, delivery and development within both the statutory and voluntary sectors. TMF work with people with a wide range of needs –which gives her a breadth o ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
... The complex cognitive task require the integrative activity of many component operations. Patient with specific brain lesion may lost the ability of one particular operation. Study dysfunctional behavior can help identify the component operations that underlie normal cognitive performance. Kee ...
Slides
... Derive multiple representations from same stimulus (physical, phonetic identity, conceptual category) Each require finite amount of time (serial stages) ...
... Derive multiple representations from same stimulus (physical, phonetic identity, conceptual category) Each require finite amount of time (serial stages) ...
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
... contrast enhances pituitary because of no blood brain barrier, the adenoma has less blood supply and is therefore less enhanced. The Pit. is an endocrine organ so it is highly vascular to release various endocrine hormones into the circulation quickly. ...
... contrast enhances pituitary because of no blood brain barrier, the adenoma has less blood supply and is therefore less enhanced. The Pit. is an endocrine organ so it is highly vascular to release various endocrine hormones into the circulation quickly. ...
Major Parts of the Brain:
... 31. _____ Links the two hemispheres and interconnects areas within the hemispheres as well. 32. _____ Performs abstract functions using the help of all of the association areas 33. _____ Predicts consequences of actions and causes anxiety, frustration, tension; estimates time and sequence of events ...
... 31. _____ Links the two hemispheres and interconnects areas within the hemispheres as well. 32. _____ Performs abstract functions using the help of all of the association areas 33. _____ Predicts consequences of actions and causes anxiety, frustration, tension; estimates time and sequence of events ...
The nervous system
... many ways to separate the parts of the brain. Brain parts can be separated on the basis of what they look like to the naked eye, under a microscope, or by what certain brain parts do. The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system and all of the nerves found in our body make up the per ...
... many ways to separate the parts of the brain. Brain parts can be separated on the basis of what they look like to the naked eye, under a microscope, or by what certain brain parts do. The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system and all of the nerves found in our body make up the per ...
Document
... 1. Back portion – primarily motor functions 2. Front portion (prefrontal cortex) – higher level process (e.g., planning) ...
... 1. Back portion – primarily motor functions 2. Front portion (prefrontal cortex) – higher level process (e.g., planning) ...
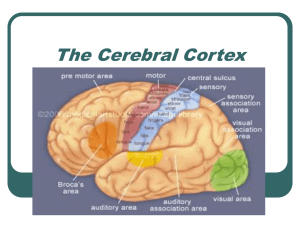
The Cerebral Cortex
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
... ¾ of the cerebral cortex is uncommitted to sensory or muscular activity Neurons in these association areas integrate information & therefore cannot be neatly mapped Found in all four lobes & increase in more intelligent animals. ...
Chapter 7 part two
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
... One theory that brings together all of the reviewed attention effects (top-down biases, gain modulation, enhancement and suppression) is Desimone and Duncan’s ‘biased competition’model of attention. The theory rests on three assumptions. First, given the limits on our ability to process several stim ...
Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... 4. Cerebrum – the lobes o Cerebrum – largest portion of the brain o Divided into 4 lobes/hemispheres: o Frontal lobe: primary motor area and conscious thought o Temporal lobe: primary auditory, smell, and speech area o Parietal lobe: primary somatosensory and taste area o Occipital lobe – primary vi ...
... 4. Cerebrum – the lobes o Cerebrum – largest portion of the brain o Divided into 4 lobes/hemispheres: o Frontal lobe: primary motor area and conscious thought o Temporal lobe: primary auditory, smell, and speech area o Parietal lobe: primary somatosensory and taste area o Occipital lobe – primary vi ...
Programming Techniques 804G5
... neural models conceptual spaces qualitative representations naive physics ...
... neural models conceptual spaces qualitative representations naive physics ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.