module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
... Module Preview The cerebral cortex, representing the highest level of brain development, is responsible for our most complex functions. Each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex has four geographical areas: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Although small, welldefined regions within ...
... Module Preview The cerebral cortex, representing the highest level of brain development, is responsible for our most complex functions. Each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex has four geographical areas: the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes. Although small, welldefined regions within ...
Neurology for Psychiatrists - the Peninsula MRCPsych Course
... Right temporal lobe lesions - interpret nonverbal auditory stimuli (e.g. music) ...
... Right temporal lobe lesions - interpret nonverbal auditory stimuli (e.g. music) ...
INTRODUCTION: LANGUAGE DISORDERS IN ADULTS
... In this paper, Wernicke described a new type of aphasia--an impairment of comprehension, a sensory as opposed to a motor malfunction. Whereas Broca's patient could understand but could not speak, Wernicke's patient could speak but could not fully comprehend. Wernicke's new type of aphasia also had ...
... In this paper, Wernicke described a new type of aphasia--an impairment of comprehension, a sensory as opposed to a motor malfunction. Whereas Broca's patient could understand but could not speak, Wernicke's patient could speak but could not fully comprehend. Wernicke's new type of aphasia also had ...
The Brain - College of Alameda
... to how much space the brain gives to processing information about that body part. For example, because so many neurons process information from the hands and lips, the homunculus’s hands and lips are remarkably oversized; while the area devoted to the hips do not take up much room (see picture on ...
... to how much space the brain gives to processing information about that body part. For example, because so many neurons process information from the hands and lips, the homunculus’s hands and lips are remarkably oversized; while the area devoted to the hips do not take up much room (see picture on ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... Regions of the brain that communicate i.e. “associate associate”” with primary regions of the brain. ...
... Regions of the brain that communicate i.e. “associate associate”” with primary regions of the brain. ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Two parts for sensations: conscious recognition of the crude, less critical sensations of pain, temperature, and touch Neurons relay all kinds of sensory impulses, except possibly olfactory, to the cerebrum emotions by associating sensory impulses with feeling of pleasantness and unpleasantness ...
... Two parts for sensations: conscious recognition of the crude, less critical sensations of pain, temperature, and touch Neurons relay all kinds of sensory impulses, except possibly olfactory, to the cerebrum emotions by associating sensory impulses with feeling of pleasantness and unpleasantness ...
How the Brain Pays Attention
... need for neuroscience research—not just in terms of the public health effects of brain disorders, but also because of its potential impact beyond treating people with diseases, including, for example, how we teach our children and how we deal with the effects of aging. Research at the McGovern Insti ...
... need for neuroscience research—not just in terms of the public health effects of brain disorders, but also because of its potential impact beyond treating people with diseases, including, for example, how we teach our children and how we deal with the effects of aging. Research at the McGovern Insti ...
CNS_notes
... bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of both pathways 1st order neuron cell body in DRG 1st order neuron’s axon enters spinal cord via dorsal root 2nd order neuron’s axon crosses midline, terminates in thalamus (synapse onto target neur ...
... bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of both pathways 1st order neuron cell body in DRG 1st order neuron’s axon enters spinal cord via dorsal root 2nd order neuron’s axon crosses midline, terminates in thalamus (synapse onto target neur ...
The Cognitive Process and Formal Models of Human Attentions
... filter model (Broadbent, 1958), the attenuator model (Treisman, 1960), the transparent transformation model (Lachman et al., 1979), and the pertinence model (Norman & Shallice, 1986). Definition 1: Attention is a perceptive process of the brain that focuses the mind or the perceptive engine on exter ...
... filter model (Broadbent, 1958), the attenuator model (Treisman, 1960), the transparent transformation model (Lachman et al., 1979), and the pertinence model (Norman & Shallice, 1986). Definition 1: Attention is a perceptive process of the brain that focuses the mind or the perceptive engine on exter ...
brain
... (long distance connections between frontal and parietal/occipital regions) and increase in local connectivity (particularly in visual areas) ...
... (long distance connections between frontal and parietal/occipital regions) and increase in local connectivity (particularly in visual areas) ...
brain
... (long distance connections between frontal and parietal/occipital regions) and increase in local connectivity (particularly in visual areas) ...
... (long distance connections between frontal and parietal/occipital regions) and increase in local connectivity (particularly in visual areas) ...
Part 1: From Ion Channels to behavior, HT2009 Course
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
Pain
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
1 - CSU, Chico
... Short-term memory is derived from a temporarily activated subset of information in longterm memory. This activated subset may decay as a function of time unless it is refreshed, although evidence for decay is tentative at best. A subset of the activated information is the focus of attention, which a ...
... Short-term memory is derived from a temporarily activated subset of information in longterm memory. This activated subset may decay as a function of time unless it is refreshed, although evidence for decay is tentative at best. A subset of the activated information is the focus of attention, which a ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... Memory loss • Bilateral removal of hippocampus produces profound deficits in memory function. – loss of capacity to form new long term memories (process of consolidation impaired) – retention of memories prior to surgery – short term memory intact – loss of ability to transfer most types of learnin ...
... Memory loss • Bilateral removal of hippocampus produces profound deficits in memory function. – loss of capacity to form new long term memories (process of consolidation impaired) – retention of memories prior to surgery – short term memory intact – loss of ability to transfer most types of learnin ...
Brain_stemCh45
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
PPT - UCI Cognitive Science Experiments
... – Where does mental activity take place in the brain? – How is processing actually done with neural activity? ...
... – Where does mental activity take place in the brain? – How is processing actually done with neural activity? ...
Brain Regions
... • Info arrives at the caudate nucleus and the putamen from sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by th ...
... • Info arrives at the caudate nucleus and the putamen from sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by th ...
Your Amazing Brain:
... Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Brain does not fully mature until age 25-30 years ...
... Your brain makes up about 2% of body weight yet takes 20% of the body’s blood supply Brain does not fully mature until age 25-30 years ...
Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
... • Somatosensory association area – Integrates different sensory information from PSC and produces an understanding of what is being felt ...
... • Somatosensory association area – Integrates different sensory information from PSC and produces an understanding of what is being felt ...
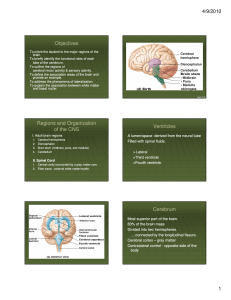
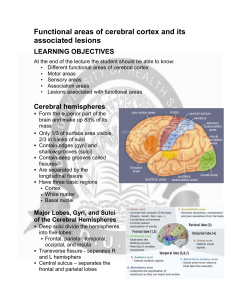
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Piriform Lobe - Limbic System ...
... Piriform Lobe - Limbic System ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
... • N.B. NE is a neurochemical correlate of attention! • Also, acetylcholine suggested to be vital for plasticity ...
... • N.B. NE is a neurochemical correlate of attention! • Also, acetylcholine suggested to be vital for plasticity ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.