Neuron
... lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). • Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
... lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). • Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
test prep
... 10. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior. C) The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than the t ...
... 10. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior. C) The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than the t ...
A Neuroscientific Approach to Emotion System for Intelligent Agents.
... with primary reinforcement. For example, fear might be produced by a sound (i.e., the conditioned stimulus) that has been previously associated with a painful stimulus (i.e., the primary reinforcer). This type of learning is referred to as “stimulusreinforcement association learning,” [9] and involv ...
... with primary reinforcement. For example, fear might be produced by a sound (i.e., the conditioned stimulus) that has been previously associated with a painful stimulus (i.e., the primary reinforcer). This type of learning is referred to as “stimulusreinforcement association learning,” [9] and involv ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Feeding, fleeing, fighting, and sex Reticular formation Network of neurons Alert and arouse higher brain Limbic system Ring of structures important to learning and emotional behavior ...
... Feeding, fleeing, fighting, and sex Reticular formation Network of neurons Alert and arouse higher brain Limbic system Ring of structures important to learning and emotional behavior ...
L21-Cerebral Hemisph..
... anterior to primary motor cortex. It is more extensive than primary motor cortex (about 6 times) Functions: It works with the help of basal ganglia, thalamus, primary motor cortex, posterior parietal cortex. It plays role in planning and anticipation of a specific motor act. ...
... anterior to primary motor cortex. It is more extensive than primary motor cortex (about 6 times) Functions: It works with the help of basal ganglia, thalamus, primary motor cortex, posterior parietal cortex. It plays role in planning and anticipation of a specific motor act. ...
Learning - Dot Point 2.
... a doughnut-shaped neural system between the hindbrain and the cerebral hemispheres. • Key structures under consideration: – Hippocampus – Amygdala ...
... a doughnut-shaped neural system between the hindbrain and the cerebral hemispheres. • Key structures under consideration: – Hippocampus – Amygdala ...
Inside the Human Brain
... largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. ...
... largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... • The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to specific behaviors • Most behavior involves neural activity in many brain parts • Here we are generalizing! The brain is not as simple as we will make it sound! ...
... • The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to specific behaviors • Most behavior involves neural activity in many brain parts • Here we are generalizing! The brain is not as simple as we will make it sound! ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... Auditory-evoked brainstem potentials are generated in the brainstem, far from the recording site and can be used to detect hearing impairment. ...
... Auditory-evoked brainstem potentials are generated in the brainstem, far from the recording site and can be used to detect hearing impairment. ...
Brain Jeopardy
... The portion of the peripheral nervous system that sends communications between the central nervous system and the internal organs and glands – we do not consciously control it. ...
... The portion of the peripheral nervous system that sends communications between the central nervous system and the internal organs and glands – we do not consciously control it. ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... aggression, submission, memory, body temperature, sexual behavior, emotions, and motivation for behavior. It is responsible for physical reactions to emotions. Limbic system also interprets olfactory sensations. Hippocampus converts short-term memories to long term.Thalamus also has sensory relaying ...
... aggression, submission, memory, body temperature, sexual behavior, emotions, and motivation for behavior. It is responsible for physical reactions to emotions. Limbic system also interprets olfactory sensations. Hippocampus converts short-term memories to long term.Thalamus also has sensory relaying ...
Part2
... A)Basic emotions B)Secondary emotions C)Bipolar disorder These are called this because they are universal across all cultures, differing only in how they may be expressed. ...
... A)Basic emotions B)Secondary emotions C)Bipolar disorder These are called this because they are universal across all cultures, differing only in how they may be expressed. ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
Pituitary malfunctions
... 2. The front of the brain is on the left side of the diagram; the back of the brain is on the right. 3. The cerebrum is the sum of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The cerebellum is labeled on the diagram above. The cerebrum is responsible for higher forms of thinking, including ...
... 2. The front of the brain is on the left side of the diagram; the back of the brain is on the right. 3. The cerebrum is the sum of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The cerebellum is labeled on the diagram above. The cerebrum is responsible for higher forms of thinking, including ...
NEUROSCIENCE REVIEW
... Cesar was involved in a motorcycle accident and ever since he has had problems understanding what his parents, friends & teachers are saying. What area of his brain was most likely affected by the accident? ...
... Cesar was involved in a motorcycle accident and ever since he has had problems understanding what his parents, friends & teachers are saying. What area of his brain was most likely affected by the accident? ...
Evernote Questions
... 43. Cortical areas that are not primarily concerned with sensory, motor, or language functions are: A) called projection areas. B) called association areas. C) located mostly in the parietal lobe. D) located mostly in the temporal lobe. ...
... 43. Cortical areas that are not primarily concerned with sensory, motor, or language functions are: A) called projection areas. B) called association areas. C) located mostly in the parietal lobe. D) located mostly in the temporal lobe. ...
... function optimization, artificial neural network training and fuzzy system control. PSO is also already a new and fast-developing research topic [5]. The BI system is inspired by the biological disposition of animals and mimics biomechanisms. From the beginning of the 1990s, the NN technology attrac ...
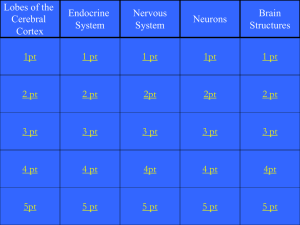
The Brain Game: Adopted from Rod Plotnik: Table created by Mary
... infection) while in college. He received good medical attention but still the infection took its toll on certain parts of his brain, so that now Paul cannot store new long-term memories. What part of the brain did the encephalitis damage? Leon’s car was broadsided by a semi causing Leon’s head to sm ...
... infection) while in college. He received good medical attention but still the infection took its toll on certain parts of his brain, so that now Paul cannot store new long-term memories. What part of the brain did the encephalitis damage? Leon’s car was broadsided by a semi causing Leon’s head to sm ...
Functional neuroimaging of anxiety
... acquisition and expression of Pavlovian fear conditioning • The amygdalae, especially the basolateral nuclei, are involved in mediating the effects of emotional arousal on the strength of the memory for the event ...
... acquisition and expression of Pavlovian fear conditioning • The amygdalae, especially the basolateral nuclei, are involved in mediating the effects of emotional arousal on the strength of the memory for the event ...