Anatomy and Physiology
... Brain uses 25 percent of the glucose in your system and about 75 percent of your Oxygen So blood is pretty important When blood supply is cut off to the brain you get a stroke ...
... Brain uses 25 percent of the glucose in your system and about 75 percent of your Oxygen So blood is pretty important When blood supply is cut off to the brain you get a stroke ...
Study Questions-Ch2
... The __________ is involved with responses related to fear relatively quickly, allowing people to respond to danger sometimes before even being consciously aware that it exists: ...
... The __________ is involved with responses related to fear relatively quickly, allowing people to respond to danger sometimes before even being consciously aware that it exists: ...
Attention
... • Emotional learning and memory • Neural circuit associated with fear learning and memory SP however, had declarative memory for the experimental task and reported that she understood the association between the blue square and the electrical shock, and anticipated being shocked when shown the blue ...
... • Emotional learning and memory • Neural circuit associated with fear learning and memory SP however, had declarative memory for the experimental task and reported that she understood the association between the blue square and the electrical shock, and anticipated being shocked when shown the blue ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... • Understanding of the brain’s structure and composition • Explains how bio chemical reactions determine our thoughts, feelings and actions ...
... • Understanding of the brain’s structure and composition • Explains how bio chemical reactions determine our thoughts, feelings and actions ...
Brain Anatomy
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
Any Words in the Brain’s Language? Tatiana V. Chernigovskaya ()
... contribution of the homologous contralateral cortex, as suggested by brain lesion studies (Caplan et al., 1996; Grodzinsky, 1995;). The activation level of Broca’s area correlated with syntactic complexity in some PET studies for both visual (Just et al., 1996) and auditory (Caplan et al., 1999) sen ...
... contribution of the homologous contralateral cortex, as suggested by brain lesion studies (Caplan et al., 1996; Grodzinsky, 1995;). The activation level of Broca’s area correlated with syntactic complexity in some PET studies for both visual (Just et al., 1996) and auditory (Caplan et al., 1999) sen ...
Basic Forms of Learning Classical Conditioning Evidence of Learning
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
Lesson 1
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
Lesson 1
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
Neuroaesthetics Researchers unravel the biology of beauty and art
... them. For example, faces deemed to be beautiful by the viewer activate the fusiform gyrus and adjacent areas more than do faces deemed less beautiful. The issue of how much and what kind of valuation takes place in sensory cortices is an area of active neuroscientific inquiry, with implications for ...
... them. For example, faces deemed to be beautiful by the viewer activate the fusiform gyrus and adjacent areas more than do faces deemed less beautiful. The issue of how much and what kind of valuation takes place in sensory cortices is an area of active neuroscientific inquiry, with implications for ...
Outline12 CNS - Napa Valley College
... Lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital Functional brain areas: frontal lobe - primary motor area, speech (Broca’s) area; prefrontal cortex - higher-level thinking, planning, judgment, personality parietal lobe - primary somatosensory area; sensory association areas occipital lobe - visual cor ...
... Lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital Functional brain areas: frontal lobe - primary motor area, speech (Broca’s) area; prefrontal cortex - higher-level thinking, planning, judgment, personality parietal lobe - primary somatosensory area; sensory association areas occipital lobe - visual cor ...
The left hemisphere
... Brain power evolves because there is a need for it. Some environments require all of it for us to survive and reproduce. Evolutionary changes are constrained by physical and temporal factors. Going up the evolutionary chain, we see more bumps or convolutions (folds) on the brains of the “higher” ev ...
... Brain power evolves because there is a need for it. Some environments require all of it for us to survive and reproduce. Evolutionary changes are constrained by physical and temporal factors. Going up the evolutionary chain, we see more bumps or convolutions (folds) on the brains of the “higher” ev ...
The Brain.
... The main motor area controls the main skeletal muscles of the body and the main sensory area receives input from the various skin receptors all over the body. The areas are duplicated onto the two cerebral hemispheres, which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the ...
... The main motor area controls the main skeletal muscles of the body and the main sensory area receives input from the various skin receptors all over the body. The areas are duplicated onto the two cerebral hemispheres, which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the ...
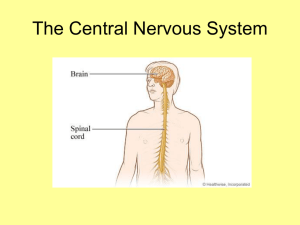
Central Nervous System - tvhs2011
... •The brain has two hemispheres; the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere. It consist of three major parts: - Brain Stem: the brain stem controls the involuntary movements of the body. - Cerebellum: the cerebellum controls the coordination of the body. - Cerebral: the cerebral controls thought, i ...
... •The brain has two hemispheres; the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere. It consist of three major parts: - Brain Stem: the brain stem controls the involuntary movements of the body. - Cerebellum: the cerebellum controls the coordination of the body. - Cerebral: the cerebral controls thought, i ...
Following the discussion about mirror neurons and imagery we want
... phenomenal of imitative decodification was hypothesised many years before mirrors neurons hypothesis was formulated. In our research we examined the level of mentalis muscle tension in 36 students and during the presentation of three slides reproducing facial expressions. Analysis showed an increase ...
... phenomenal of imitative decodification was hypothesised many years before mirrors neurons hypothesis was formulated. In our research we examined the level of mentalis muscle tension in 36 students and during the presentation of three slides reproducing facial expressions. Analysis showed an increase ...
Lecture 12
... Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ability to change con ...
... Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ability to change con ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... -interprets all senses except smell -synapses for voluntary movement Hypothalamus -controls the autonomic nervous system -coordinates the nervous and endocrine systems ...
... -interprets all senses except smell -synapses for voluntary movement Hypothalamus -controls the autonomic nervous system -coordinates the nervous and endocrine systems ...
may - Suffolk County Community College
... 18. People can simultaneously process many aspects of sensory information such as color, shape, and size. This best illustrates the functioning of multiple: A) ACh agonists. B) reflexes. C) neural networks. D) ACh antagonists. 19. The body's chemical communication system that is much slower than the ...
... 18. People can simultaneously process many aspects of sensory information such as color, shape, and size. This best illustrates the functioning of multiple: A) ACh agonists. B) reflexes. C) neural networks. D) ACh antagonists. 19. The body's chemical communication system that is much slower than the ...
Introduction to Psychology
... The Brain Limbic System a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus (ch. 8), amygdala, and ...
... The Brain Limbic System a doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus (ch. 8), amygdala, and ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... 2. brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization) a. the specialization of function in each hemisphere 3. split brain patients a. the corpus collosum has been cut to treat severe epilepsy b. can’t orally report information presented to only the right hemisphere of the brain iii. Association area ...
... 2. brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization) a. the specialization of function in each hemisphere 3. split brain patients a. the corpus collosum has been cut to treat severe epilepsy b. can’t orally report information presented to only the right hemisphere of the brain iii. Association area ...
action potential
... planning, and emotional control •Temporal lobe—primary receiving area for auditory information •Occipital lobe—primary receiving area for visual information •Parietal lobe—processes somatic information ...
... planning, and emotional control •Temporal lobe—primary receiving area for auditory information •Occipital lobe—primary receiving area for visual information •Parietal lobe—processes somatic information ...
Neuroanatomy- anatomy of nerve cell (neuron)
... Reticular Formation – responsible for body arousal (Mnemonic: tic toc an alarm clock wakes you up) ...
... Reticular Formation – responsible for body arousal (Mnemonic: tic toc an alarm clock wakes you up) ...
Biology of the Mind
... areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. In general, human emotions, thoughts, and behaviors result from the intricate coordination of many brain areas. Language, for example, depends on a chain of events in several brain regions. ...
... areas. They are involved in higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. In general, human emotions, thoughts, and behaviors result from the intricate coordination of many brain areas. Language, for example, depends on a chain of events in several brain regions. ...