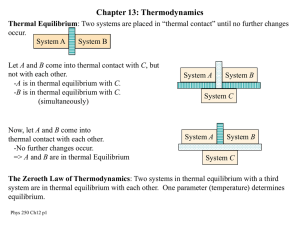
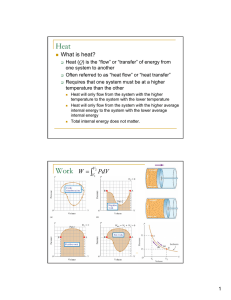
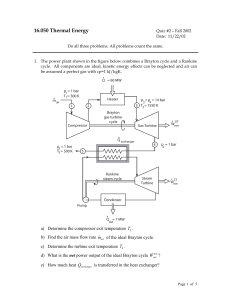
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
Practice sheet #8: thermodynamics.
... The methanol in an automobile engine must be in the gas phase before it can react. Calculate the heat (in KJ) that must be added to 1.00 Kg of liquid methanol to raise its temperature from 25°C to its normal boiling point, 65°C, knowing that the molar heat capacity of liquid methanol is 81.6J/°Cmol. ...
... The methanol in an automobile engine must be in the gas phase before it can react. Calculate the heat (in KJ) that must be added to 1.00 Kg of liquid methanol to raise its temperature from 25°C to its normal boiling point, 65°C, knowing that the molar heat capacity of liquid methanol is 81.6J/°Cmol. ...
p250c13
... Example: A refrigerator has a cp of 6.0. If the room temperature is 30 ºC, what is the lowest temperature that can be obtained inside the refrigerator? ...
... Example: A refrigerator has a cp of 6.0. If the room temperature is 30 ºC, what is the lowest temperature that can be obtained inside the refrigerator? ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Osmosis is the net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to one that has a lower water concentration. • Rate of diffusion of water is called the rate of osmosis. ...
... • Osmosis is the net diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to one that has a lower water concentration. • Rate of diffusion of water is called the rate of osmosis. ...
Notes 10 - CEProfs
... For a piston-cylinder system, two paths are shown from point 1 to 2. Compute the work in kJ done in going by path A from 1 to a to 2 (call the work WA) and by path B from 1 to b to 2 (call the work WB). ...
... For a piston-cylinder system, two paths are shown from point 1 to 2. Compute the work in kJ done in going by path A from 1 to a to 2 (call the work WA) and by path B from 1 to b to 2 (call the work WB). ...
Radiation
... beach umbrella also helps to cool you down. The umbrella absorbs the Sun's radiant energy and conducts heat through the metal rod into the sand, just as a lightning rod deflects a bolt of lightning from a house. So, is it temperature that makes you so hot? Not exactly. Temperature is only the measur ...
... beach umbrella also helps to cool you down. The umbrella absorbs the Sun's radiant energy and conducts heat through the metal rod into the sand, just as a lightning rod deflects a bolt of lightning from a house. So, is it temperature that makes you so hot? Not exactly. Temperature is only the measur ...
Heat Work
... may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the ...
... may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the ...
The Heat Equation - Rose
... (use ρ = c0 + c1 u)) to see that the temperature u obeys the same equation. We’ll usually work in terms of the temperature u, since it’s a more familiar quantity. There’s another situation in which the heat equation frequently appears: when ρ(x, t) denotes the concentration of some substance dissolv ...
... (use ρ = c0 + c1 u)) to see that the temperature u obeys the same equation. We’ll usually work in terms of the temperature u, since it’s a more familiar quantity. There’s another situation in which the heat equation frequently appears: when ρ(x, t) denotes the concentration of some substance dissolv ...
15.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics
... the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
... the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
Cost-effectiveness: An Engineers`s Real Job
... • The pitot-static probe measures slow moving fluids well. • Thus, the pitot-static probe would make a great blood pressure ...
... • The pitot-static probe measures slow moving fluids well. • Thus, the pitot-static probe would make a great blood pressure ...
Lecture 6 – Thermochemistry
... A student wishes to determine the heat capacity of a coffee-cup calorimeter. After she mixes 100.0 g of water at 58.5°C with 100.0 g of water, already in the calorimeter, at 22.8°C, the final temperature of the water is 39.7°C. Calculate the heat capacity of the ...
... A student wishes to determine the heat capacity of a coffee-cup calorimeter. After she mixes 100.0 g of water at 58.5°C with 100.0 g of water, already in the calorimeter, at 22.8°C, the final temperature of the water is 39.7°C. Calculate the heat capacity of the ...
heat engine
... The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of the work done to the input heat: ...
... The efficiency of a heat engine is defined as the ratio of the work done to the input heat: ...
Lesson Plans - University High School
... Kinetic Molecular Theory- Molecules are in constant, continuous motion. The temperature of the sample reflects the average KE of the molecules in the sample. ...
... Kinetic Molecular Theory- Molecules are in constant, continuous motion. The temperature of the sample reflects the average KE of the molecules in the sample. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis - Washington State University
... Diffusing particles undergo random walks • Because of collisions with other particles, a diffusing particle changes direction on a picosecond time scale. Therefore, individual particles move about randomly and tend to return to the same spots. • However, if there is a concentration gradient, the av ...
... Diffusing particles undergo random walks • Because of collisions with other particles, a diffusing particle changes direction on a picosecond time scale. Therefore, individual particles move about randomly and tend to return to the same spots. • However, if there is a concentration gradient, the av ...
Countercurrent exchange

Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some component, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass.The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the diagram at the right, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that was used for heating. With cocurrent or parallel exchange the heated and cooled fluids can only approach one another. The result is that countercurrent exchange can achieve a greater amount of heat or mass transfer than parallel under otherwise similar conditions. See: flow arrangement.Countercurrent exchange when set up in a circuit or loop can be used for building up concentrations, heat, or other properties of flowing liquids. Specifically when set up in a loop with a buffering liquid between the incoming and outgoing fluid running in a circuit, and with active transport pumps on the outgoing fluid's tubes, the system is called a Countercurrent multiplier, enabling a multiplied effect of many small pumps to gradually build up a large concentration in the buffer liquid.Other countercurrent exchange circuits where the incoming and outgoing fluids touch each other are used for retaining a high concentration of a dissolved substance or for retaining heat, or for allowing the external buildup of the heat or concentration at one point in the system.Countercurrent exchange circuits or loops are found extensively in nature, specifically in biologic systems. In vertebrates, they are called a Rete mirabile, originally the name of an organ in fish gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. It is mimicked in industrial systems. Countercurrent exchange is a key concept in chemical engineering thermodynamics and manufacturing processes, for example in extracting sucrose from sugar beet roots.Countercurrent multiplication is a similar but different concept where liquid moves in a loop followed by a long length of movement in opposite directions with an intermediate zone. The tube leading to the loop passively building up a gradient of heat (or cooling) or solvent concentration while the returning tube has a constant small pumping action all along it, so that a gradual intensification of the heat or concentration is created towards the loop. Countercurrent multiplication has been found in the kidneys as well as in many other biological organs.