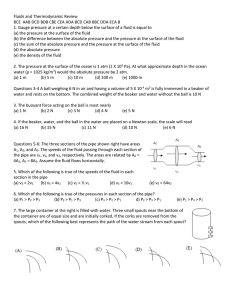
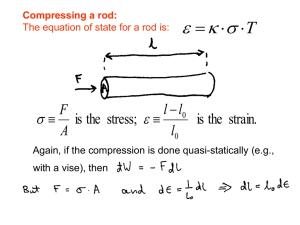
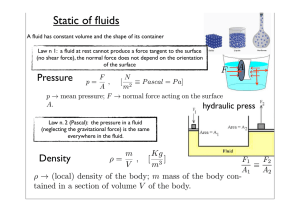
Fluids and Thermodynamic Review BCE AAB DCD BDB CBE CEA
... (a) it increases (b) it remains constant (c) it decreases (d) it may increase or decrease depending on the shape of the rock 29. Salt water is denser than fresh water. A ship floats in both fresh water and salt water, the amount of water displaced by the salt water is (a) more (b) less (c) the same ...
... (a) it increases (b) it remains constant (c) it decreases (d) it may increase or decrease depending on the shape of the rock 29. Salt water is denser than fresh water. A ship floats in both fresh water and salt water, the amount of water displaced by the salt water is (a) more (b) less (c) the same ...
HEAT- Chapter 9
... temperature decreases; the exception is water Solids tend to have the smallest coefficient of volume Coefficient of Volume Expansion- a number assigned to different material to show the thermal expansion characteristic of the material Gases have highest coefficient; solids the lowest ...
... temperature decreases; the exception is water Solids tend to have the smallest coefficient of volume Coefficient of Volume Expansion- a number assigned to different material to show the thermal expansion characteristic of the material Gases have highest coefficient; solids the lowest ...
Band Shift Crude cell extract
... Spin down ~30ml of culture of an OD600 ~0.4-0.5, wash with iced H2O, remove all liquid and freeze on dry ice (or continue to step 3) Thaw cells on ice for 10-15 minutes (no more) Add 2ml/gram of cells of binding buffer + DTT & protease inhibitors to tubes Vortex to resuspend pellet and add ~ ½ the v ...
... Spin down ~30ml of culture of an OD600 ~0.4-0.5, wash with iced H2O, remove all liquid and freeze on dry ice (or continue to step 3) Thaw cells on ice for 10-15 minutes (no more) Add 2ml/gram of cells of binding buffer + DTT & protease inhibitors to tubes Vortex to resuspend pellet and add ~ ½ the v ...
Chapter 20
... Liquid to solid: freezing, latent heat of solidification Solid to liquid: melting, latent heat of fusion Liquid to gaseous: boiling, latent heat of vaporization Gaseous to liquid: condensation, latent heat of condensation Solid to gaseous: sublimation, latent heat of sublimation Gaseous to solid: su ...
... Liquid to solid: freezing, latent heat of solidification Solid to liquid: melting, latent heat of fusion Liquid to gaseous: boiling, latent heat of vaporization Gaseous to liquid: condensation, latent heat of condensation Solid to gaseous: sublimation, latent heat of sublimation Gaseous to solid: su ...
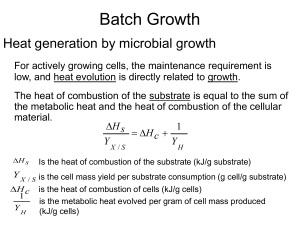
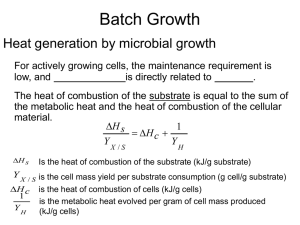
heat evolution
... Y X / S is the cell mass yield per substrate consumption (g cell/g substrate) H c is the heat of combustion of cells (kJ/g cells) ...
... Y X / S is the cell mass yield per substrate consumption (g cell/g substrate) H c is the heat of combustion of cells (kJ/g cells) ...
Countercurrent exchange

Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some component, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass.The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the diagram at the right, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that was used for heating. With cocurrent or parallel exchange the heated and cooled fluids can only approach one another. The result is that countercurrent exchange can achieve a greater amount of heat or mass transfer than parallel under otherwise similar conditions. See: flow arrangement.Countercurrent exchange when set up in a circuit or loop can be used for building up concentrations, heat, or other properties of flowing liquids. Specifically when set up in a loop with a buffering liquid between the incoming and outgoing fluid running in a circuit, and with active transport pumps on the outgoing fluid's tubes, the system is called a Countercurrent multiplier, enabling a multiplied effect of many small pumps to gradually build up a large concentration in the buffer liquid.Other countercurrent exchange circuits where the incoming and outgoing fluids touch each other are used for retaining a high concentration of a dissolved substance or for retaining heat, or for allowing the external buildup of the heat or concentration at one point in the system.Countercurrent exchange circuits or loops are found extensively in nature, specifically in biologic systems. In vertebrates, they are called a Rete mirabile, originally the name of an organ in fish gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. It is mimicked in industrial systems. Countercurrent exchange is a key concept in chemical engineering thermodynamics and manufacturing processes, for example in extracting sucrose from sugar beet roots.Countercurrent multiplication is a similar but different concept where liquid moves in a loop followed by a long length of movement in opposite directions with an intermediate zone. The tube leading to the loop passively building up a gradient of heat (or cooling) or solvent concentration while the returning tube has a constant small pumping action all along it, so that a gradual intensification of the heat or concentration is created towards the loop. Countercurrent multiplication has been found in the kidneys as well as in many other biological organs.