Water is able to absorb a high amount of heat before
... The resistance to sudden temperature changes makes water an excellent habitat, allowing organisms to survive without experiencing wide temperature fluctuation. Furthermore, because many organisms are mainly composed of water, the property of high heat capacity allows highly regulated internal body t ...
... The resistance to sudden temperature changes makes water an excellent habitat, allowing organisms to survive without experiencing wide temperature fluctuation. Furthermore, because many organisms are mainly composed of water, the property of high heat capacity allows highly regulated internal body t ...
Le Châtelier`s Principle
... • Make more reactants because more collisions with the products will occur • A stress was applied and the system compensated for this change What will removing CO2 do? • Shift to make more products ...
... • Make more reactants because more collisions with the products will occur • A stress was applied and the system compensated for this change What will removing CO2 do? • Shift to make more products ...
Cell Transport I
... Certain substances can diffuse straight across the phospholipid bilayer Phospholipid bilayer ...
... Certain substances can diffuse straight across the phospholipid bilayer Phospholipid bilayer ...
calculating specific heat capacity - Mikus
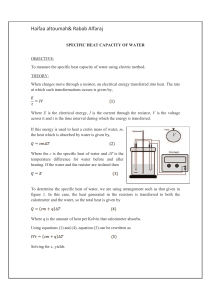
... When in contact with each other, objects at different temperatures transfer thermal energy until they reach the same temperature. This is called thermal equilibrium. Conservation of energy requires that the thermal energy lost by the hotter object as it cools be equal to the thermal energy gained by ...
... When in contact with each other, objects at different temperatures transfer thermal energy until they reach the same temperature. This is called thermal equilibrium. Conservation of energy requires that the thermal energy lost by the hotter object as it cools be equal to the thermal energy gained by ...
CHE 301 Problem set #3
... a. Calculate the time required for complete consumption of formaldehyde. b. If the initial temperature of formalin solution is at 60oC, estimate the heat to be added or removed if the reaction mixture is to be maintained at 60oC. c. If the initial temperature of formalin solution is at 0oC, determin ...
... a. Calculate the time required for complete consumption of formaldehyde. b. If the initial temperature of formalin solution is at 60oC, estimate the heat to be added or removed if the reaction mixture is to be maintained at 60oC. c. If the initial temperature of formalin solution is at 0oC, determin ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... Water is the medium – a substance through which something is transmitted or carried for every chemical reaction that sustains life. Freezing and Melting Melting point – a point at which a substance changes from a solid to a ...
... Water is the medium – a substance through which something is transmitted or carried for every chemical reaction that sustains life. Freezing and Melting Melting point – a point at which a substance changes from a solid to a ...
HormonesCascade
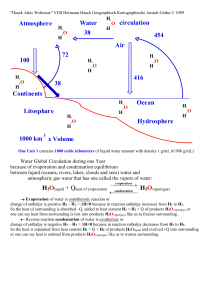
... One Unit 1 contains 1000 cubic kilometers of liquid water amount with density 1 g/mL (0.996 g/mL) ...
... One Unit 1 contains 1000 cubic kilometers of liquid water amount with density 1 g/mL (0.996 g/mL) ...
Countercurrent exchange

Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some component, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass.The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the diagram at the right, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that was used for heating. With cocurrent or parallel exchange the heated and cooled fluids can only approach one another. The result is that countercurrent exchange can achieve a greater amount of heat or mass transfer than parallel under otherwise similar conditions. See: flow arrangement.Countercurrent exchange when set up in a circuit or loop can be used for building up concentrations, heat, or other properties of flowing liquids. Specifically when set up in a loop with a buffering liquid between the incoming and outgoing fluid running in a circuit, and with active transport pumps on the outgoing fluid's tubes, the system is called a Countercurrent multiplier, enabling a multiplied effect of many small pumps to gradually build up a large concentration in the buffer liquid.Other countercurrent exchange circuits where the incoming and outgoing fluids touch each other are used for retaining a high concentration of a dissolved substance or for retaining heat, or for allowing the external buildup of the heat or concentration at one point in the system.Countercurrent exchange circuits or loops are found extensively in nature, specifically in biologic systems. In vertebrates, they are called a Rete mirabile, originally the name of an organ in fish gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. It is mimicked in industrial systems. Countercurrent exchange is a key concept in chemical engineering thermodynamics and manufacturing processes, for example in extracting sucrose from sugar beet roots.Countercurrent multiplication is a similar but different concept where liquid moves in a loop followed by a long length of movement in opposite directions with an intermediate zone. The tube leading to the loop passively building up a gradient of heat (or cooling) or solvent concentration while the returning tube has a constant small pumping action all along it, so that a gradual intensification of the heat or concentration is created towards the loop. Countercurrent multiplication has been found in the kidneys as well as in many other biological organs.