C1a Revision notes - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... be used for windows. While glass is transparent and so lets light into a building, buildings with lots of glass can be too hot in the summer. ...
... be used for windows. While glass is transparent and so lets light into a building, buildings with lots of glass can be too hot in the summer. ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
... 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
Solute
... Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, ionized phase of matter as found on the sun. ...
... Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, ionized phase of matter as found on the sun. ...
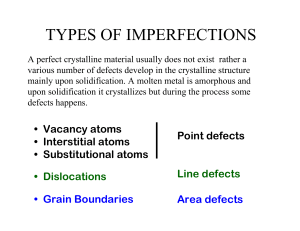
TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS
... when the difference in atomic radii between the two atom types is less than about : 15% .Otherwise the solute atoms will create substantial lattice distortions and a new phase will form. ∆r% =[ (r solute – r solvent) / r solvent ] x 100 ≤ ±15% 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility t ...
... when the difference in atomic radii between the two atom types is less than about : 15% .Otherwise the solute atoms will create substantial lattice distortions and a new phase will form. ∆r% =[ (r solute – r solvent) / r solvent ] x 100 ≤ ±15% 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility t ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemical and PHYSICAL properties *b. elements can NOT be BROKEN down into other substances by any CHEMICAL means c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] ...
... 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemical and PHYSICAL properties *b. elements can NOT be BROKEN down into other substances by any CHEMICAL means c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood
... and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & _________ = calcium [___] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [___]; for nervous system = copper [___]; for blood = iron [___] *e. There are currently ____ known _____________ and ___ are found in nature, while the others are ______________________ (man-made), b ...
... and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & _________ = calcium [___] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [___]; for nervous system = copper [___]; for blood = iron [___] *e. There are currently ____ known _____________ and ___ are found in nature, while the others are ______________________ (man-made), b ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...
... d. Water (H2O) is always 1 g hydrogen for every 8 g of O present, while H2O2 is always 1 g hydrogen for every 16 g of O present. These are distinctly different compounds, each with its own unique relative number and types of atoms present. e. A chemical equation involves a reorganization of the atom ...
Non-metals:
... CANNOT be pounded or shaped into a wire Poor conductors of heat Poor conductor of electricity Metals: Most elements are metals (left side of periodic table) Conducts electricity well Conducts heat well Shiny in appearance CAN BE SHAPED (pounded, bent or drawn into wire) Solids at room temp (except m ...
... CANNOT be pounded or shaped into a wire Poor conductors of heat Poor conductor of electricity Metals: Most elements are metals (left side of periodic table) Conducts electricity well Conducts heat well Shiny in appearance CAN BE SHAPED (pounded, bent or drawn into wire) Solids at room temp (except m ...
HERE
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
Periodic Table Test – Study Guide What state of matter are almost all
... How did Dobereiner classify elements? similar properties How did he place these elements together? in triads (groups of 3) with increasing atomic mass Why did Mendeleev leave blank spaces on the periodic table? for undiscovered elements What does the modern periodic law say? chemical and physical pr ...
... How did Dobereiner classify elements? similar properties How did he place these elements together? in triads (groups of 3) with increasing atomic mass Why did Mendeleev leave blank spaces on the periodic table? for undiscovered elements What does the modern periodic law say? chemical and physical pr ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... C. Mixtures 1. MIXTURE consists of TWO or more substances that are MIXED / BLENDED together, but do NOT react ____________ to form a NEW substance, instead keeping their original PROPERTIES 2. Mixtures are not ______ substances (not an element or compound) 3. Components of a MIXTURE are NOT all I ...
... C. Mixtures 1. MIXTURE consists of TWO or more substances that are MIXED / BLENDED together, but do NOT react ____________ to form a NEW substance, instead keeping their original PROPERTIES 2. Mixtures are not ______ substances (not an element or compound) 3. Components of a MIXTURE are NOT all I ...
ASTM and the Metals Industry
... in Railroad, Marine and other Heavy Duty Service at Temperatures Up to 650°F (345°C). ...
... in Railroad, Marine and other Heavy Duty Service at Temperatures Up to 650°F (345°C). ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [__] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [__]; for nervous system = copper [__]; for blood = iron [__] *e. There are currently 118 known ______________ and ___ are found in nature, while the others are ________________________ (man-made), but we ...
... and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & BONES = calcium [__] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [__]; for nervous system = copper [__]; for blood = iron [__] *e. There are currently 118 known ______________ and ___ are found in nature, while the others are ________________________ (man-made), but we ...
Iron - University of Minnesota Duluth
... remove oxygen from iron oxide cmps. • We say that iron is reduced by CO. Iron accepts electrons to go from an oxidation state +3 in Fe2O3 to an oxidation state of 0 in Fe (via +8/3 and +2). • Note that oxygen starts out bonded to Fe but ends up bonded to C because the C-O bond is stronger than the F ...
... remove oxygen from iron oxide cmps. • We say that iron is reduced by CO. Iron accepts electrons to go from an oxidation state +3 in Fe2O3 to an oxidation state of 0 in Fe (via +8/3 and +2). • Note that oxygen starts out bonded to Fe but ends up bonded to C because the C-O bond is stronger than the F ...
Sec 7.3
... Halogens – combine readily with metals and form salts. A salt is a compound in which a metal is combined with one or more nonmetals. Noble Gases – are said to be inert. Group 18. This means they do not readily mix with other elements, Their outer electron shells are full and therefore stable. This m ...
... Halogens – combine readily with metals and form salts. A salt is a compound in which a metal is combined with one or more nonmetals. Noble Gases – are said to be inert. Group 18. This means they do not readily mix with other elements, Their outer electron shells are full and therefore stable. This m ...
CHEM1411,chapter 1-2-3 exercises 1. In 1828, the diameter of the
... 5. A piece of a metal alloy with a mass of 114 g was placed into a graduated cylinder that contained 25.0 mL of water, raising the water level to 42.5 mL. What is the density of the metal? A) 0.154 g/cm3 B) 0.592 g/cm3 C) 2.68 g/cm3 D) 6.51 g/cm3 E) 7.25 g/cm3 ...
... 5. A piece of a metal alloy with a mass of 114 g was placed into a graduated cylinder that contained 25.0 mL of water, raising the water level to 42.5 mL. What is the density of the metal? A) 0.154 g/cm3 B) 0.592 g/cm3 C) 2.68 g/cm3 D) 6.51 g/cm3 E) 7.25 g/cm3 ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... ____ 72. When compared to the main group metals, transition metals have melting and boiling points that are _____. a. always lower c. about the same b. usually higher d. usually lower ____ 73. Transition elements, such as chromium, are likely to have _____. a. an oxidation number of 1+ c. multiple ...
... ____ 72. When compared to the main group metals, transition metals have melting and boiling points that are _____. a. always lower c. about the same b. usually higher d. usually lower ____ 73. Transition elements, such as chromium, are likely to have _____. a. an oxidation number of 1+ c. multiple ...
Atoms, compounds and elements - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... one of the basic substances that are made of atoms of only one kind and that cannot be separated because it is a pure substance ...
... one of the basic substances that are made of atoms of only one kind and that cannot be separated because it is a pure substance ...
experiment 8 precipitation hardening in 2024
... Interstitialcy. Atom occupying an interstitial site not normally occupied by an atom in the perfect crystal structure or an extra atom inserted into the perfect crystal such that two atoms occupy positions close to a singly occupied atomic site in the perfect structure. Natural aging. When a cohere ...
... Interstitialcy. Atom occupying an interstitial site not normally occupied by an atom in the perfect crystal structure or an extra atom inserted into the perfect crystal such that two atoms occupy positions close to a singly occupied atomic site in the perfect structure. Natural aging. When a cohere ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... 2) Compounds: Substances made up of elements which are combined in very well defined proportions, compounds can be decomposed in their components by chemical means. 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) S ...
... 2) Compounds: Substances made up of elements which are combined in very well defined proportions, compounds can be decomposed in their components by chemical means. 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) S ...
Preparation of Sm–Ru bimetallic alloy films on Ru(0001) surface by
... process, as seen in figure 1, is pointing towards the formation of intermetallic compounds of certain fixed compositions. Similar observations have been reported on Al/Ru(0001) and Sm/Cu(111) systems (Wu et al 1995). The decrease and increase in intensities respectively of Sm 3d and Ru 3d are not li ...
... process, as seen in figure 1, is pointing towards the formation of intermetallic compounds of certain fixed compositions. Similar observations have been reported on Al/Ru(0001) and Sm/Cu(111) systems (Wu et al 1995). The decrease and increase in intensities respectively of Sm 3d and Ru 3d are not li ...
akdeniz university faculty of engineering 2013
... signals, control of traffic in network , fundamentals of transport modeling, traffic analysis at intersections, ITS. Introduction, Introduction to numerical analysis methods in engineering problems, Basic equations of linear elasticity theory, Energy methods, Finite elements based on the displacemen ...
... signals, control of traffic in network , fundamentals of transport modeling, traffic analysis at intersections, ITS. Introduction, Introduction to numerical analysis methods in engineering problems, Basic equations of linear elasticity theory, Energy methods, Finite elements based on the displacemen ...
Alloy

An alloy is a mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal and another element. Alloys are defined by metallic bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of metal elements (a single phase) or a mixture of metallic phases (two or more solutions). Intermetallic compounds are alloys with a defined stoichiometry and crystal structure. Zintl phases are also sometimes considered alloys depending on bond types (see also: Van Arkel-Ketelaar triangle for information on classifying bonding in binary compounds).Alloys are used in a wide variety of applications. In some cases, a combination of metals may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the combination of metals imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Examples of alloys are steel, solder, brass, pewter, duralumin, phosphor bronze and amalgams.The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the alloy. They can be further classified as homogeneous (consisting of a single phase), or heterogeneous (consisting of two or more phases) or intermetallic.