Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
... When the liquids being distilled have similar boiling points, normal distillation can’t separate them completely but simply gives a purer mixture. In this case a fractionating column is used. This provides a large surface area for condensation meaning much purer ‘fractions’ are produced. The most im ...
Chapter 23 Metals and Metallurgy
... Phosphorus Sulfur Carbon Metals and Metallurgy © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... Phosphorus Sulfur Carbon Metals and Metallurgy © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
CHEMISTRY REVISION GUIDE for CIE IGCSE Coordinated Science
... Paper chromatography is a technique that can be used to separate mixtures of dyes or pigments and is used to test the purity of a mixture or to see what it contains. Firstly a very strong solution of the mixture is prepared which is used to build up a small intense spot on a piece of absorbent paper ...
... Paper chromatography is a technique that can be used to separate mixtures of dyes or pigments and is used to test the purity of a mixture or to see what it contains. Firstly a very strong solution of the mixture is prepared which is used to build up a small intense spot on a piece of absorbent paper ...
8.3 Metals - UNSW Chemistry
... aluminium (initially for use in the military) and after two years effort had produced a little more than 2 kg of metal. The investment was written off and the aluminium that was produced was used to produce the first set of aluminium cutlery. Visiting dignitaries used the silver service, visiting he ...
... aluminium (initially for use in the military) and after two years effort had produced a little more than 2 kg of metal. The investment was written off and the aluminium that was produced was used to produce the first set of aluminium cutlery. Visiting dignitaries used the silver service, visiting he ...
Silicon Deposition
... • Most metallization systems employ Al or Al alloys for the primary interconnection layers • Al almost conducts as well as Cu and Ag and will readily deposit in thin films that adhere to all the materials used in the fabrication of integrated circuits ...
... • Most metallization systems employ Al or Al alloys for the primary interconnection layers • Al almost conducts as well as Cu and Ag and will readily deposit in thin films that adhere to all the materials used in the fabrication of integrated circuits ...
Module-2-s-and-d-elements - Львівський національний медичний
... view until the latter half of the 18th century. In 1781 the British chemist Henry Cavendish synthesized water by detonating a mixture of hydrogen and the air. However, the results of his experiments were not clearly interpreted until two years later, when the French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisie ...
... view until the latter half of the 18th century. In 1781 the British chemist Henry Cavendish synthesized water by detonating a mixture of hydrogen and the air. However, the results of his experiments were not clearly interpreted until two years later, when the French chemist Antoine Laurent Lavoisie ...
MAGNETIC GARNETS, YxGd3-xFe5O12 TUNABLE MAGNETIC
... made using the precursor Na2S1-xSex formed by coprecipitation of Na2S/Na2Se mixtures from liquid ammonia • High quality cation solid solutions such as Mo1-xWxS2 can be made by melting together the metal halides MoCl5 and WCl6, followed by reaction with Na2S ...
... made using the precursor Na2S1-xSex formed by coprecipitation of Na2S/Na2Se mixtures from liquid ammonia • High quality cation solid solutions such as Mo1-xWxS2 can be made by melting together the metal halides MoCl5 and WCl6, followed by reaction with Na2S ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids
... • Atoms may assemble into crystalline or amorphous structures. • Common metallic crystal structures are FCC, BCC, and HCP. Coordination number and atomic packing factor are the same for both FCC and HCP crystal structures. • We can predict the density of a material, provided we know the atomic weigh ...
... • Atoms may assemble into crystalline or amorphous structures. • Common metallic crystal structures are FCC, BCC, and HCP. Coordination number and atomic packing factor are the same for both FCC and HCP crystal structures. • We can predict the density of a material, provided we know the atomic weigh ...
A comparative study between friction stir welding
... material with the tool edges, inducing plastic deformation. The probe is slightly shorter than the thickness of the work piece [2]. The FSW joint is created by friction heating with simultaneous severe plastic deformation of the weld zone material. The stirring of the tool minimizes the risk of havi ...
... material with the tool edges, inducing plastic deformation. The probe is slightly shorter than the thickness of the work piece [2]. The FSW joint is created by friction heating with simultaneous severe plastic deformation of the weld zone material. The stirring of the tool minimizes the risk of havi ...
Phase Transformations
... The martensitic transformation occurs without composition change The transformation occurs by shear without need for diffusion The atomic movements required are only a fraction of the interatomic spacing The shear changes the shape of the transforming region → results in considerable amount ...
... The martensitic transformation occurs without composition change The transformation occurs by shear without need for diffusion The atomic movements required are only a fraction of the interatomic spacing The shear changes the shape of the transforming region → results in considerable amount ...
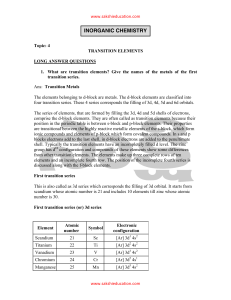
inorganic chemistry - Sakshieducation.com
... The elements belonging to d-block are metals. The d-block elements are classified into four transition series. These 4 series corresponds the filling of 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d orbitals. The series of elements, that are formed by filling the 3d, 4d and 5d shells of electrons, comprise the d-block elements ...
... The elements belonging to d-block are metals. The d-block elements are classified into four transition series. These 4 series corresponds the filling of 3d, 4d, 5d and 6d orbitals. The series of elements, that are formed by filling the 3d, 4d and 5d shells of electrons, comprise the d-block elements ...
Communicating Research to the General Public
... When asked to describe inorganic chemistry, one of the easiest responses is to describe it as the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and ...
... When asked to describe inorganic chemistry, one of the easiest responses is to describe it as the opposite of organic chemistry, as the name implies, and then describe organic chemistry. However, this does an injustice to the field of inorganic chemistry, which we interact with on a daily basis and ...
Year 9 Science revison _15-16_ end of year CHEM
... iv) The compound RbSO4 dissolves in water, but the element Rb doesn’t. Why ? The compound is made up of ions bonded together. When it dissolves in water, these ions separate from each other. They are charged (+ and -) and able to attract to and bond with water. This is why the ionic compound CAN dis ...
... iv) The compound RbSO4 dissolves in water, but the element Rb doesn’t. Why ? The compound is made up of ions bonded together. When it dissolves in water, these ions separate from each other. They are charged (+ and -) and able to attract to and bond with water. This is why the ionic compound CAN dis ...
SoM-1.3 - WordPress.com
... meter is 80kN and working stress is 75Mpa.Also determine the total elongation of rod. Take ...
... meter is 80kN and working stress is 75Mpa.Also determine the total elongation of rod. Take ...
Mixtures
... dissolving. In solutions, the solute is the substance that is dissolved, and the solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve, in the solvent. A substance that is insoluble, or unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous and ther ...
... dissolving. In solutions, the solute is the substance that is dissolved, and the solvent is the substance in which the solute is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve, in the solvent. A substance that is insoluble, or unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous and ther ...
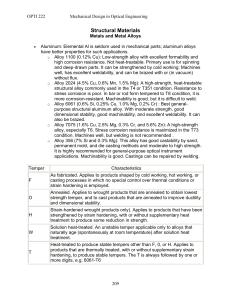
Structural Materials
... various degrees of cold working. Alloys containing appreciable amounts of magnesium when supplied in strain-hardened tempers are usually given a final elevated temperature treatment called stabilizing to ensure stability of properties. Heat-Treatable Alloys The initial strength of alloys in this gro ...
... various degrees of cold working. Alloys containing appreciable amounts of magnesium when supplied in strain-hardened tempers are usually given a final elevated temperature treatment called stabilizing to ensure stability of properties. Heat-Treatable Alloys The initial strength of alloys in this gro ...
Elements – (Metals)
... Bronsted Lowry acid and base also fits Lewis definition but there is also a more general definition Acid Base ...
... Bronsted Lowry acid and base also fits Lewis definition but there is also a more general definition Acid Base ...
Plastic deformation of Fe–Al polycrystals strengthened with Zr
... the grain boundary skeleton was formed. Unfortunately, the orientation at the phase boundaries and especially within the eutectic cannot be evaluated by the OIM method because of its limited spatial resolution of 1 m [20]. Studies on B2 intermetallic alloys show that low Σ boundaries (e.g. Σ1 and Σ ...
... the grain boundary skeleton was formed. Unfortunately, the orientation at the phase boundaries and especially within the eutectic cannot be evaluated by the OIM method because of its limited spatial resolution of 1 m [20]. Studies on B2 intermetallic alloys show that low Σ boundaries (e.g. Σ1 and Σ ...
Answer Key
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
Answers - Benjamin
... precise customer specifications for the concentration of each element. Steel manufacture by a continuous process would be economical only if one type of steel were being produced. Otherwise, there would be a lot of wastage and accurate control of the composition would not be so easy. ...
... precise customer specifications for the concentration of each element. Steel manufacture by a continuous process would be economical only if one type of steel were being produced. Otherwise, there would be a lot of wastage and accurate control of the composition would not be so easy. ...
O 95: Metal Substrates: Adsorption of Atoms and Inorganic Molecules
... In this study we combine quantitative LEED–IV, STM and DFT calculations to reinvestigate the adsorption behavior of oxygen on the Rh(100) surface in the coverage regime up to 0.67 ML. In this range three distinct phases exist: A (2 × 2)–O [1], a (2 × 2)–2O [2] and a (3×1)–2O structure [3]. The propo ...
... In this study we combine quantitative LEED–IV, STM and DFT calculations to reinvestigate the adsorption behavior of oxygen on the Rh(100) surface in the coverage regime up to 0.67 ML. In this range three distinct phases exist: A (2 × 2)–O [1], a (2 × 2)–2O [2] and a (3×1)–2O structure [3]. The propo ...
The Big book of C1 chemistry
... using scrap iron. During electrolysis positive ions move towards the negative electrode. Aluminium and titanium cannot be extracted from their oxides by reduction with carbon. Current methods of extraction are expensive because: there are many stages in the processes large amounts of energy are ...
... using scrap iron. During electrolysis positive ions move towards the negative electrode. Aluminium and titanium cannot be extracted from their oxides by reduction with carbon. Current methods of extraction are expensive because: there are many stages in the processes large amounts of energy are ...
3 chemical foundations: elements, atoms and ions
... The element sulphur, S, is found as a ring structure consisting if 8 S-atoms. Its correct designation, S8, is not often used; usually as shorthand the symbol S is (incorrectly) used. The atom symbol shorthand is commonly used for all of the metal atoms. There are only two elements that are liquid in ...
... The element sulphur, S, is found as a ring structure consisting if 8 S-atoms. Its correct designation, S8, is not often used; usually as shorthand the symbol S is (incorrectly) used. The atom symbol shorthand is commonly used for all of the metal atoms. There are only two elements that are liquid in ...
Use of Copper-Base Shape Memory Alloys in Seismic Energy
... determine the evolution of transformation temperature with time. They also developed a one-dimensional model to predict the damping performance of the materials for long-term actions. This paper examines the suitability of copper-based SMAs for use in energy dissipation devices for civil engineering ...
... determine the evolution of transformation temperature with time. They also developed a one-dimensional model to predict the damping performance of the materials for long-term actions. This paper examines the suitability of copper-based SMAs for use in energy dissipation devices for civil engineering ...
Alloy

An alloy is a mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal and another element. Alloys are defined by metallic bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of metal elements (a single phase) or a mixture of metallic phases (two or more solutions). Intermetallic compounds are alloys with a defined stoichiometry and crystal structure. Zintl phases are also sometimes considered alloys depending on bond types (see also: Van Arkel-Ketelaar triangle for information on classifying bonding in binary compounds).Alloys are used in a wide variety of applications. In some cases, a combination of metals may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the combination of metals imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Examples of alloys are steel, solder, brass, pewter, duralumin, phosphor bronze and amalgams.The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the alloy. They can be further classified as homogeneous (consisting of a single phase), or heterogeneous (consisting of two or more phases) or intermetallic.